Updated July 12, 2023
What is Enterprise Value?
Enterprise value is the sum total of the market value of the amount of equity, debt, and all other sources of financing of a company and therefore it is similar to the market capitalization, but it is a broader valuation methodology as the market capitalization only considers the market value of the equity component while the enterprise value includes all sources of financing.
Formula
The below formula is used for calculation.
Explanation
There are a few important points to note. Capital sources are evaluated at the market value instead of the book value, therefore the enterprise value number includes the performance of the company because the market value measures the same.
Enterprise value is a measure that is common in merger and acquisition analysis because, in such situations, the valuation of the entire company is required so that a takeover price can be determined. Based on the value number, a price is paid by the acquirer to the target company’s shareholders and creditors to own the assets of the company.
Examples of Enterprise Value (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
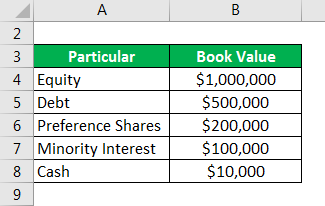
Suppose we are given the following information:
- We need to consider the market values of equity, debt, and minority interest
- Here we assume that the market value of the minority interest is the same as its book value, so we will use the book value as the proxy.
- Cash value does not change so we can use the given value
Solution:
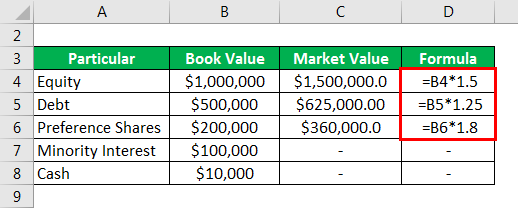
Market Value is calculated as
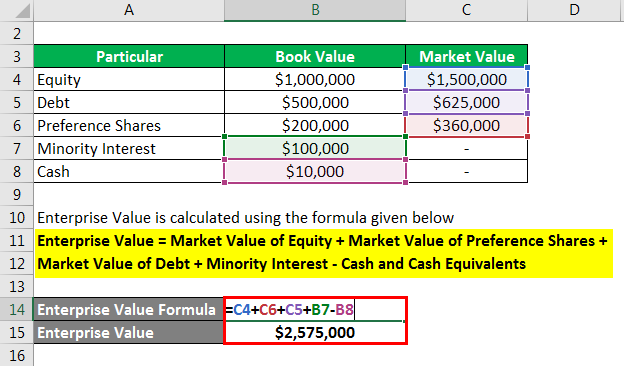
Enterprise Value is calculated using the formula given below
Enterprise Value = Market Value of Equity + Market Value of Preference Shares + Market Value of Debt + Minority Interest – Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Enterprise Value = 1500000+ 360000+625000+100000-10000
- Enterprise Value = $ 2575000
So the enterprise value is 2575000.
Now as part of an M&A transaction, this is what needs to be paid by the acquirer to the target so that it can acquire the target company. Any price paid higher than the enterprise value is for the goodwill of the company or for the synergies that the acquirer is expecting out of the acquisition.
Components of Enterprise Value
- Market Value of equity and preference shares is the market capitalization of these stocks
- At times market value might not be easily calculated, because sometimes it may happen that the debt issued by the company is not trading on the exchange, and therefore in such cases, market value is an approximation, or at times the book value is used as a proxy for the market value.
- Cash and cash equivalents are reduced from the valuation, the logic behind this is that if the enterprise value is being calculated as part of a takeover procedure, then it doesn’t make any sense that the acquirer pays more cash to buy the existing cash, instead, he will simply tell the target to take out the cash and cash equivalents and net the value of the enterprise.
- Minority interest is added because minority shareholders are also the owners of the target company and until and unless they are paid off for their share, they would not let go of it.
- So ultimately, It comes down to the settlement value that one company needs to pay to get rid of the claims of all the capital providers.
Difference Between Enterprise Value and Equity Value
- Meaning: Equity value is only the market capitalization of the equity capital and therefore a much narrower term to measure the value of the company. Enterprise value is a more comprehensive or broader measure of the value of the company as a whole.
- Purpose: Equity value should only be used to measure the value of the stock by a retail investor whereas it is most commonly used when the investors have control perspective or are planning a takeover transaction.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are the points that explain the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Comparison: This can be used for comparison of companies with different capital structures because it is not affected by the capital structure and therefore it is more useful when the price to earning method can’t be used.
- Control perspective: This is used in M&A transactions and therefore, the investors with control perspective prefer this measure to other measures.
- Multiple Approach: Equity value is used when we need to calculate the P?E multiple, while the enterprise value is used when we calculate the EV?EBITDA multiple. Therefore both the values have very different view of valuation and the correct multiple needs to be used where appropriate.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to Estimate: At times not all market values are available and therefore a lot of assumptions go into the calculation. Such components may include the minority interest or investment in associates because these are valued at original cost and therefore market value might be difficult to assume. Further debt related to pension liabilities might involve actuarial assumptions and all these estimation items may lead to putting off by quite a mark.
- Negative Enterprise Value: If the company has an unnecessarily high level of cash, this may become negative and be misleading as to whether the company is worth nothing. But that is actually not the case, just the cash available is very high, but the company still has a lot of worthwhile assets, which might not get captured properly.
Conclusion
Enterprise value is used mostly in the case of M&A transactions or when the investor has a control perspective because then the measures which include only the equity value don’t make much sense or present a complete picture. The measure is not free of flaws. It can be manipulated by the amount of available cash and therefore the analyst needs to be careful while calculating because otherwise, the measure can give misleading information.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Enterprise Value. Here we discuss how to calculate along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –