Updated July 12, 2023
What is Personal Income?
A person or household receives personal income, representing the total gross income obtained during a specific period. This income encompasses various sources such as compensation, salaries, wages, investment returns (such as dividends and interest income), variable pay, performance pay, employer contributions to retirement or pension plans, rental income, and business profits.
Alternatively, personal income can be described as the individual’s or household’s pre-tax income.
Formula
It is the Sum total of income received from all sources by individuals or households.
As discussed above, personal income can be calculated in either of two ways. The first method is adding up all income the individual or household receives for a period. The other method is adjusting the national income with the income received and earned but not received.
OR
Explanation
- At a micro level, individuals or households actively accumulate their gross income from various sources, representing the total sum of income received. To elaborate, household income shall mean the combined gross income from all sources of all the individuals in a particular house.
- At a macro level, personal income refers to the combined gross income of all households taken together in a country. In other words, to arrive at personal income at a national level, one needs to consider gross total income received by all households from all sources, such as compensation, interest, bonus, dividends, any social security benefits, etc.
- Personal income at the national level helps in understanding gross domestic consumption.
Examples
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
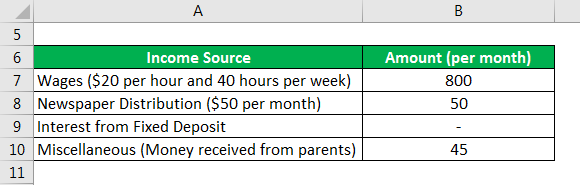
Let us take the example of Julie. Julie worked at a nearby restaurant and was paid wages at a rate of $20 per hour. She worked for 40 hours a week. Apart from this, Julie also distributes newspapers in the morning, for which she gets paid $50 a month. Julie has a fixed deposit of $10000 on which she earns interest at a rate of 8% per annum. Julie receives a nominal amount of $45 every month from her parents to help her in pursuing higher studies.
Solution:
- In order to calculate Julie’s income, we will have to first find out her annual income from each source of income.
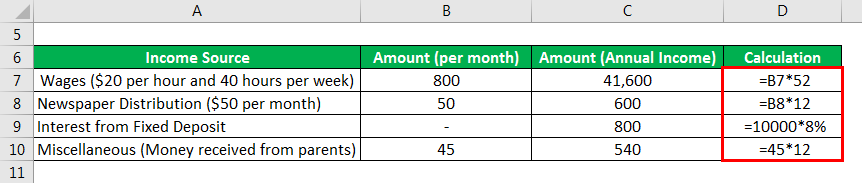
- Julie receives wages of $20 per hour and works 40 hours a week. Thus, she earns $800 (i.e. $20 * 40) per week. Therefore, she receives an annual wage of $41,600 (i.e. $800 * 52 weeks)
- Julie also receives income by distributing newspapers amounting to $50 per month. Thus, she earns $600 annually (i.e. $50 * 12 months)
- Julie receives interest on the fixed deposit she has made of $10,000 at an 8% annual interest rate. Hence, she is in receipt of interest amounting to $800 annually on the fixed deposit.
- Lastly, Julie receives $45 from her parents on a monthly basis with respect to her education.
The amount for Annual Income is calculated as:
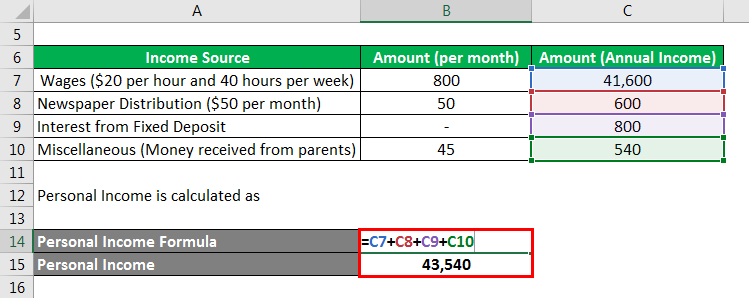
Combining the income from all sources, Julie’s personal income for the year is $43,540.
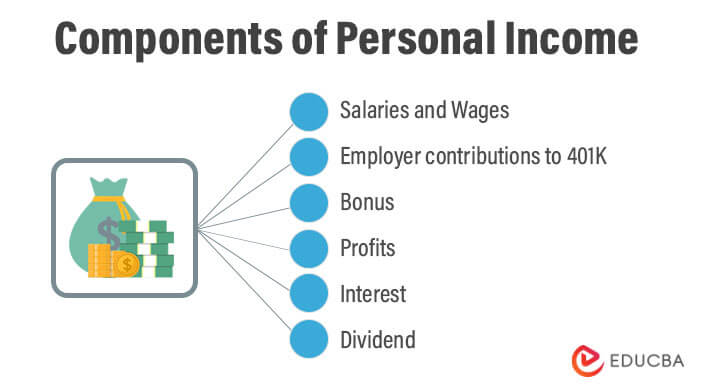
Components of Personal Income
It includes all the income the individual or household receives in a particular period. There can be varied sources through which the individual or household receives any income.
- Salaries and Wages: Compensation received from the employer towards services rendered
- Employer contributions to 401K: Contribution by the employer to employee’s retirement benefits
- Bonus: Variable pay received for services rendered in employment
- Profits: Profits received in business and distributed to owners
- Interest: Interest can be received on saving bank, fixed deposits, a loan given, investments, etc
- Dividend: Received on the investment made in the equity of a company
How to Calculate Personal Income?
In order to calculate the Personal income of an individual or a household, collate the first-hand details of all the income earned by the individual or household. The income received through all the sources, direct or indirect, totaled together provides us with the amount of personal income of the person or household. Direct sources of income encompass salaries, wages, performance-based compensation, business profits, and other comparable forms of revenue. Indirect sources of income mean income by way of interest, dividends, or any miscellaneous income, which is not related to the main / core business or profession.
Alternatively, one can calculate personal income by adjusting the national income using a specific factor. National income adjusted by the income received but not earned and income earned but not received shall also provide us with the amount of personal income.
Why is Personal Income Important?
- Personal income is basically the gross income of a person or a household. In other words, it depicts the purchasing power of the household.
- At the national level, it utilizes data to determine gross domestic consumption and calculate the consumer price index. It plays a crucial role in examining economic factors like the marginal propensity to consume, the marginal propensity to invest, consumption patterns, and trends in household income changes.
- Thus, it is a very important aspect from the point of the nation of view, wherein it provides a picture of the purchasing power of households in the country and the reflective changes in economic factors.
- Also, huge differences in the personal income of various households can throw light on economic disparities within the economy and can be a cause of concern in the long-term growth of the nation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Income
Advantages
From an individual eye-view, personal income can be useful in the following ways:
- Personal income, also referred to as gross income before tax, is important from a tax perspective, and brings ease to income tax calculations.
- Individuals have a better idea of their household’s annual gross income.
- This information is a valuable starting point for determining the household’s disposable income.
From a nation’s eye-view, personal income can have the following uses:
- Provides information on purchasing power in the economy.
- It actively measures purchasing power and consumption information, providing valuable insights into various economic factors.
- It helps in analyzing the trends and relations in changes in personal income viz a viz the spending habits of people.
Disadvantages
- It measures only the income received. It misses capturing the income which may have been earned but not received by the individual, for eg. the Undistributed Profits of a company in which a person has invested.
- Any income generated through the rolling of black money. Personal income does not account for income received unofficially.
- Laborers or Seasonal workers receive wages that do not have a fixed income. They receive wages only occasionally when there is work and would not be keeping a systematic record of income received.
- Any income received outside the country and taxed in the contracting state. Similarly, any income earned by a non-resident on the investment made in the country but taxed in his home country.
- Any income not disclosed in order to avoid paying taxes.
- In barter trade, participants engage in the exchange of goods or services without involving monetary transactions, leading to the potential omission of income recording.
Conclusion
Personal income is the total gross income received by an individual or household. It includes income received from each and every source for all the individuals in a household taken together. It reflects the purchasing power of the individual or household, as the case may be. From the individual’s point of view, it provides him with a picture of his household income and what is the annual gross earnings of such individual/household. From a macroeconomic point of view, a higher personal income depicts a higher purchasing power, which means there will be a higher amount of money rolling into the economy and thus indicating a better future growth prospect.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Personal Income. Here we discuss how to calculate Personal Income along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –