Updated July 31, 2023
Difference Between Shares Duty vs Tariff
The government imposes duties on specific commodities, financial transactions, goods, etc., imported into the domestic country and on goods manufactured within the country. Duty is nothing but the amount of money paid on imported or exported products. A tariff is a kind of tax levied on the import of goods and services from other countries by a government for protective purposes and revenue purposes. The government imposes tariffs to restrict trade from a particular country or reduce the import of specific goods and services. Tariff increases the prices of foreign goods and services and, thus, makes them more expensive for the final beneficiary, that is, customers. Tariff acts as a barrier to free trade between countries. The tariff also can be levied on both export and import.
Duty
The government considers duties an indirect tax because they are indirect and similar to a consumption tax, making them obligated to pay money. Imported duty and Exported duty vary from country to county, and countries around the world levy duties on importing and exporting goods to raise revenue and protect domestic industries from foreign competition. The duty Rate varies from product to product.
There are different types of duties, as mentioned below:
- Import Duty: The domestic country popularly imposes a duty on goods imported from other countries, known as Import duty. Import duty is also referred to as customs duty.
- Export Duty: If goods are exported outside the country, then the government will charge some taxes. Such taxes are called an export duty. This duty is also called an excised duty. So export duty is the charges imposed on goods produced within the country.
Tariff
Tariff increases the prices of imported goods, and because of this, the domestic producer need not reduce their prices from increased competition. Because of this, the domestic consumer has to pay a higher price for imported goods. Tariffs are useful to a nation as they help increase revenue for the government and also help in increasing the GDP of the country.
There are several types of Tariffs that government can impose, and below two types of tariffs are important and regularly applied.
- Specific Tariff: Fixed Tariff on one unit of goods imported and vary according to the type of goods imported.
- Ad Valorem Tariff: Certain percentage of a tariff is calculated on the total value of the imported item.
Let’s Say XYZ person is the importer of shoes, and he imports shoes to India total worth of Rupees 2,00,000.00, and the corresponding India tariff would be taxed percentage, which in this case, suppose 5%, so the duty of XYZ person, which he needs to pay to the government of India is Rupees 10,000.00
- Recently US President sharpened a trade war with China by imposing new tariffs of 200bn dollars on Chinese goods exported to the US market from China.
Head To Head Comparison Between Shares Duty vs Tariff (Infographics)
Below is the top 5 difference between Duty vs Tariff:
Key Differences Between Duty vs Tariff
Both Duties vs Tariffs are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences.
- Duty vs Tariff are both types of tax and are sometimes used interchangeably.
- In that case, if we mention the government and economy, the correct term to use is “impose a tariff,” whereas if we discuss rates and mention the amount, the term used is “levy a duty.”
- Duty is the amount paid by the importer or exporter of goods and services according to a tariff.
- Duty is a fee payable to the government on the import and export of goods as per the tariff rates decided or imposed by a government.
- Two major types of duties are customs duty and exercise duty, whereas two major types of tariffs are specific tariff and ad valorem tariff.
- Both add revenue to the government, and the government levies both.
- In general, governments impose tariffs on goods, while customers bear the burden of duties.
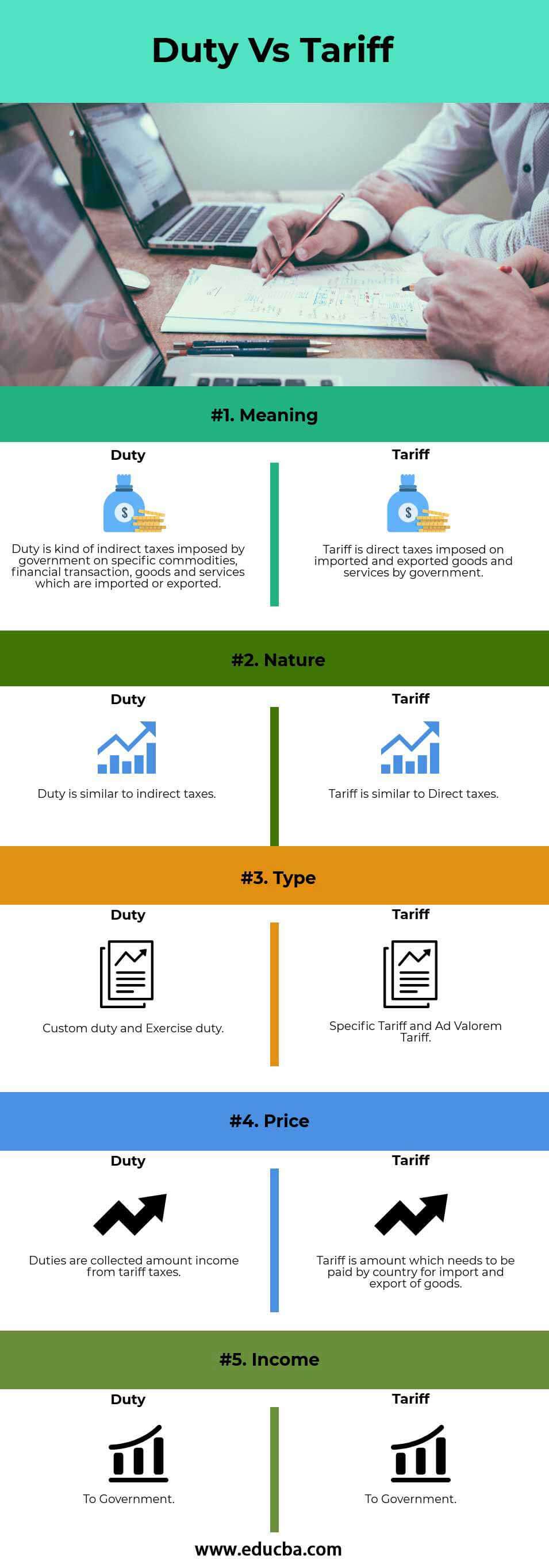
Duty vs Tariff Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Duty vs Tariff
| The Basis Of Comparison | Duty | Tariff |
| Meaning | The government imposes an indirect tax duty on specific commodities, financial transactions, goods, and services imported or exported. | The government imposes direct taxes on imported and exported goods and services, known as tariffs. |
| Nature | Duty is similar to indirect taxes. | A tariff is similar to Direct taxes. |
| Type | Customs duty and Exercise duty. | Specific Tariff and Ad Valorem Tariff. |
| Price | Tariff taxes collect duties as an amount of income. | A tariff is an amount that needs to be paid by the country for the import and export of goods. |
| Income | To Government. | To Government. |
Conclusion
The Department of Revenue, under the Ministry of Finance’s control, administers duties and tariffs in India. The government imposes duties and tariffs to increase tax revenue and control foreign products entering the domestic market. Duties and tariffs are forms of taxes and can be used interchangeably. They act as tools to control international trade and encourage domestic production. Tariffs are imposed on goods and services during transportation between customs areas, while duties represent the collected amounts from tariff taxes. Governments levy both on goods and financial transactions. Imposing duties and tariffs reduces consumer surplus while increasing producer surplus due to higher product prices.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Duty vs Tariff. Here we also discuss the Duty vs Tariff key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.