Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to the Doubly linked list in Data Structure
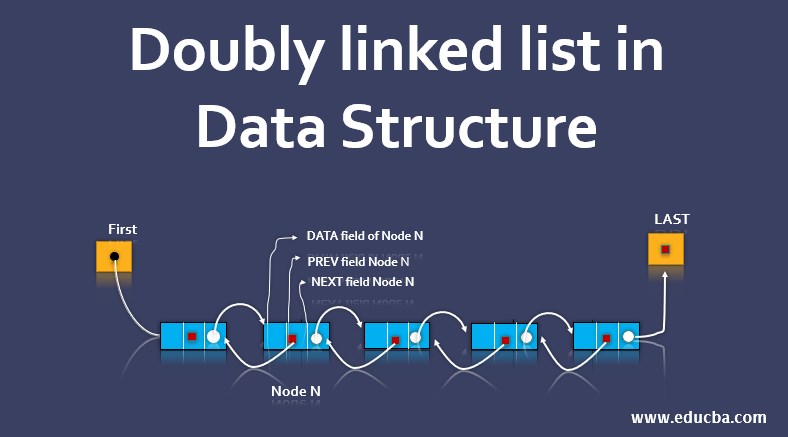
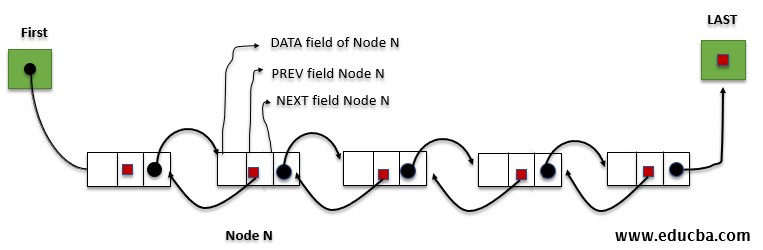
The doubly linked list is a linked list that can be traversed in both directions. This type of linked list has linked to the next and the previous node; thus, it is possible to come back to the previous node without traversing the whole list again. Thus we can say, a doubly linked list is a linear collection of data elements called nodes where each node is divided into 3 parts:-
- DATA Field– This field contains the value stored in that linked list.
- PREV Field– This field contains the location of the previous node of the list.
- NEXT Field – This field contains the location of the next node of the list.
How to perform a Doubly linked list in Data Structure?
While working with a one-way linked list, we have one DATA field that holds the DATA node’s value, and the NEXT field holds the location of the next node in the list. But we don’t have anything to access the proceedings node without traversing the list. In contrast, the Doubly linked list consists of one extra pointer to point to the node preceding the node at location LOC. When we need to delete an element at the Nth location, it can be done without traversing to that location.
Below is the structure for the node:-
Struct Node{
int data;
Node *NEXT;
Node *PREV;
}
Above LIST also needs FIRST and LAST pointer variables that point to the list’s first and last node respectively. Thus null pointer appears in the LAST node of the LIST because that marks the end of the list. Similarly, the PREV pointer of the list also contains a null pointer.
Memory Representation
A doubly linked list is maintained using linear arrays in the memory the same as a single linked list except now we require FIRST and LAST both pointer variables and one more pointer field in the node PREV. But the list for available space in the list is represented in the same manner.
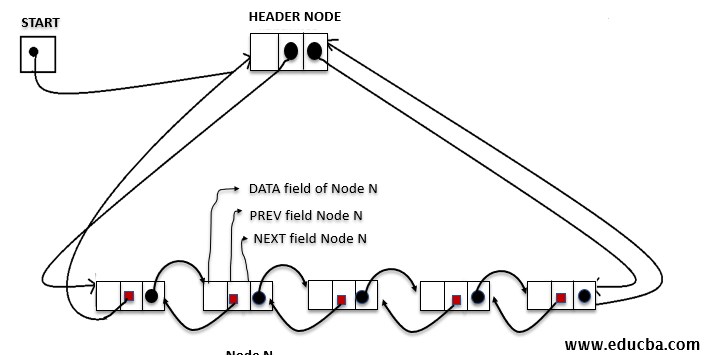
Doubly header linked list
This is a way to make doubly-linked as a circular list with a HEADER node which helps to traverse the list in a circular manner. Thus only one pointer variable START is required instead of FIRST and LAST, which will point to the HEADER.
The operation performed in a Doubly linked list in Data Structure.
Let us see some of the operations performed in the doubly linked list:
1. Traversal
This operation refers to visiting each node of the list one by one. We start from START or HEADER node, which contains the address of the first node of the list.
Consider the structure of the Node as below:-
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* NEXT; /*Pointer to the next node*/
struct Node* PREV; /*Pointer to the previous node*/
};
- NEXT – This is a pointer to the next node in the LIST
- PREV – This points to the previous node in the LIST.
TRAVERSE This algorithm is used to traverse the doubly linked list LIST and apply PROCESS to each node in the list.
1. Set PTR = NEXT[START]
2. Repeat steps 3 & 4 while PTR != START
3. Apply the PROCESS to DATA[PTR]
4. Set PREV[PTR] = PTR and PTR = NEXT[PTR]
5. Exit.
2. Searching
The doubly linked list also supports search operation to find an element ITEM in the LIST. Performing this operation for an ITEM on the LIST returns the location LOC of ITEM in the LIST. In case of ITEM is not present in the LIST it returns NULL.
SEARCH(DATA, PREV, NEXT, START, ITEM, LOC) This algorithm searches ITEM in doubly linked list LIST having START which holds the starting node’s location. This returns location LOC of ITEM.
1. Set PTR = NEXT[START].
2. Repeat while DATA[PTR] = ITEM & PTR!=START:
- Set PREV[PTR]=PTR and PTR= NEXT[PTR]
3. If DATA[PTR] = ITEM, then:
- Set LOC = PTR
- Else LOC = NULL
4. Exit.
3. Deletion
This operation refers to the deletion of an ITEM at a particular location LOC in a doubly-linked list. This operation leads to the updation of the PREVIOUS and NEXT pointers for the adjacent nodes. Below is the algorithm for the DELETION operation.
DELETION(DATA, NEXT, PREV, START, AVAIL, LOC) This algorithm is used to delete DATA node in LIST at location LOC.
- Set NEXT[PREV[LOC]] = NEXT[LOC] and PREV[NEXT[LOC]]=PRV[LOC]
- Set NEXT[LOC] = AVAIL and AVAIL = LOC
- Exit
Here in the case of organized data in the list and we need to delete a node at the nth location, we need to traverse n-1 elements if we have used a single linked list. With the doubly linked list’s help, this task can be done very easily and with less time.
4. Insertion
This operation refers to an ITEM insertion at a particular location LOC between items at location LOCA and LOCB. Thus while inserting PREV and NEXT pointers of LOCA and LOCB items need to be updated. Below is the algorithm for performing the insertion operation in the doubly linked list.
INSERTION(DATA, NEXT, PREV, START, AVAIL, LOCA., LOCB, ITEM) This algorithm is used to insert DATA node with ITEM as its value in LIST at a location between the nodes at LOCA and LOCB.
- [OVERFLOW?] If AVAIL = NULL, then Write: OVERFLOW & Exit.
- Set NEW = AVAIL, AVAIL= NEXT[AVAIL] and DATA[NEW] = ITEM.
- Set NEXT[LOCA] = NEW and NEXT[NEW] =LOCB, PREV[LOCB]= NEW and PREV[NEW] =LOCA.
- Exit.
In the above algorithm, we first check if a memory location is available in the AVAIL list for inserting a node.
Conclusion
The doubly linked list is not preferable over a single linked list often. Since there is one extra pointer being used for storing the previous node’s location, which comes with the cost of storage required and the time it takes for updating it. Thus the doubly linked list is only preferred in case we need to find the location of the previous node most often in our algorithm.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Doubly linked list in Data Structure. Here we discuss the introduction and perform a Doubly linked list in Data Structure with the various operations. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –