Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Days Sales Outstanding
The term “days sales outstanding” refers to the average days a company takes to collect the receivables after selling them on credit. In other words, the metric assesses the ability of the company’s collection department and the company’s negotiating power among its customers. It is also known as the “average collection period”, “day’s sales in receivable,” and “accounts receivable period”.
Formula
To derive the formula for days sales outstanding, you divide the average accounts receivable for the period by the net credit sales of the same period. Then, you multiply the result by 365 to express it in terms of days. The formula is as below:
The average receivable is the mean of the receivable at the start of the year (opening receivable) and at the end of the year (closing receivable). Net credit sales simply mean sales that are executed, not credit. However, if details about net credit sales are unavailable, it is advisable to use the entire sales as a proxy for net credit sales.
Examples of Days Sales Outstanding (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to better understand the Days Sales Outstanding formula calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
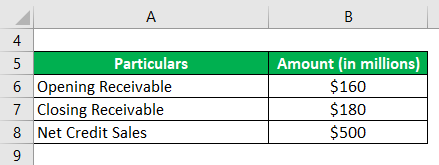
Let us take the example of a company named MNB Ltd, which manufactures furniture in the state of North Carolina. The promoter wants to know about the company’s current credit policy. Calculate the day’s sales outstanding to help the promoter. Use the following information:
Solution:
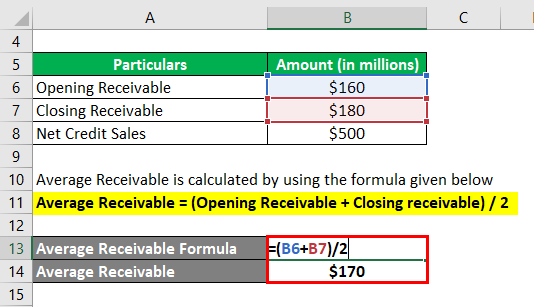
The formula to calculate average receivables are as below
Average Receivable = (Opening Receivable + Closing receivable) / 2
- Average Receivable = ($160 million + $180 million) / 2
- Average Receivable = $170 million
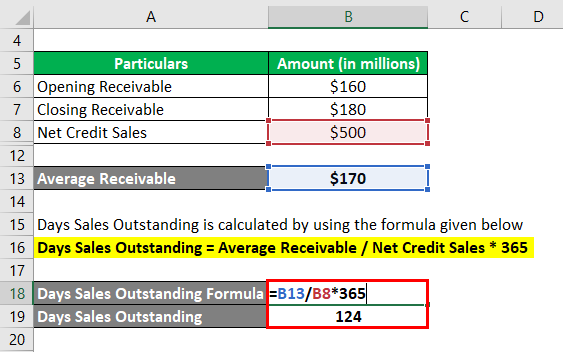
The formula to calculate days sales outstanding is as below
Days Sales Outstanding = Average Receivable / Net Credit Sales * 365
- DSO = $170 million / $500 million * 365
- DSO = 124 days
Therefore, MNB Ltd.’s day’s sales outstanding for the year stood at 124 days.
Example – #2
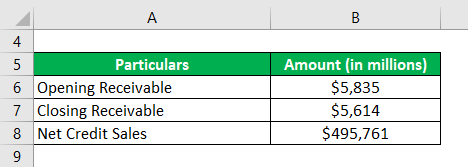
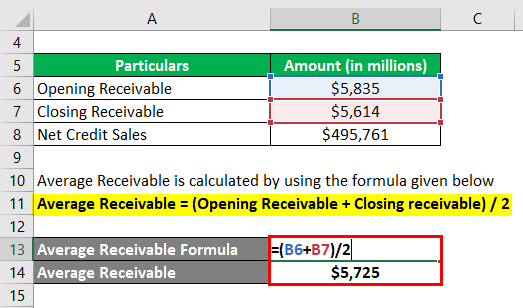
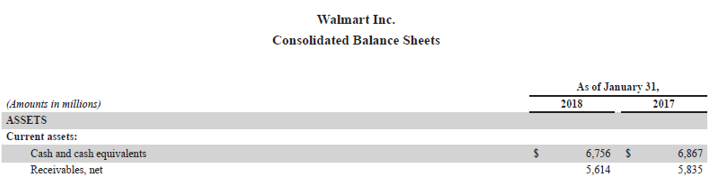
Let us take the example of Walmart Inc.’s latest annual report (2018) to demonstrate the calculation of the day’s sales outstanding. As per the annual report, the company registered net sales of $495,761 million, while the opening receivable (net) for the period stood at $5,835 million and the closing receivable (net) stood at $5,614 million. Calculate the day’s sales outstanding of Walmart Inc. for the year 2018 by using the given information.
Solution:
Average Receivable = (Opening Receivable + Closing receivable) / 2
- Average Receivable = ($5,835 million + $5,614 million) / 2
- Average Receivable = $5,724.5 million
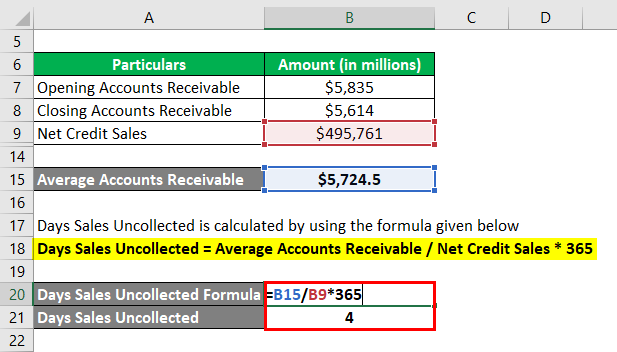
Days Sales Outstanding = Average Receivable / Net Credit Sales * 365
- DSO = $5,724.5 million / $495,761 million * 365
- DSO = 4 days
Therefore, Walmart Inc. collected its receivables in 4 days during 2018.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Limitations of DSO
Some of the limitations of DSO are:
- Using the metric for comparing companies with significantly different proportions of credit sales is not very useful. It is difficult to infer anything significant by comparing a company with a low proportion of credit sales to a company with a high share of credit sales.
- It is also not the textbook indicator of a company’s accounts receivable efficiency because the metric is impacted by fluctuating sales volumes, such that any increase in sales will result in lower day sales outstanding.
- The calculation is based on receivables at the year’s start and end. As such, the metric may fail to depict the true picture for businesses characterized by peak season in the middle of the year as the calculation uses values as on the balance sheet date.
- Another flaw is that if there is no clarity about the proportion of credit sales, the entire sales are considered net credit sales. Such proxy frequently results in an understated value that is not correct.
Important Points to Note about Days Sales Outstanding
Some important points about the DSO are:
- The metric indicates how quickly the customers pay their dues or how the company’s collection department works.
- It can be a good benchmark for assessing a company’s cash flow. However, it is advisable to monitor the trends in days sales outstanding over a period of time.
- A lower value for DSO is seen as a positive as it indicates that the company can collect the receivables quickly. On the other hand, a higher value may be a sign of weak credit policies, which can be seen as a matter of concern. The reason for higher value is that customers are taking more time to pay, or the salespeople are offering longer payment terms to increase sales.
Conclusion
So, days sales outstanding is another liquidity metric used to determine how quickly a company can collect the receivables. Financial analysts need to understand the concept of DSO as it is a crucial part of the working capital assessment.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Days Sales Outstanding. Here we discuss how it can be calculated using a formula and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –