Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Days Inventory Outstanding
The term “days inventory outstanding” refers to the financial metric that measures the average time (expressed in terms of days) that a company takes to convert its stock inventory into sales during a specific period of time.
In other words, it is the average number of days that a company holds its inventory before selling it in the market. It is also known as “days in inventory”, “inventory days of supply,” and “the inventory period”.
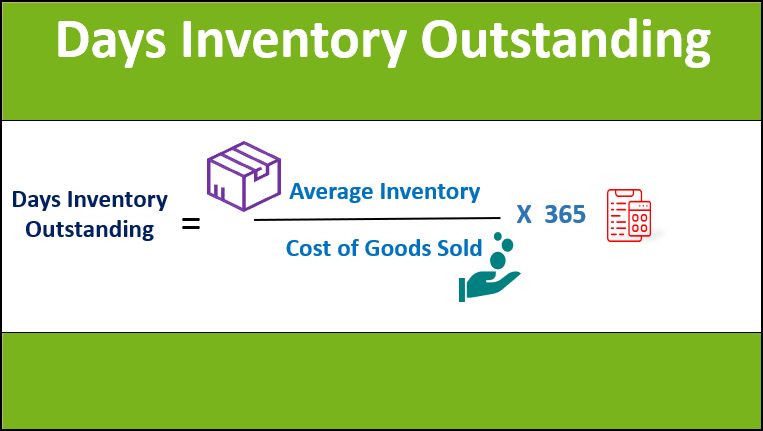
Formula
The formula for days inventory outstanding can be derived by dividing the average stock inventory holding during the period by the cost of goods sold during the period and then it is multiplied by 365 to express the value in terms of days. The formula is as below:
To calculate the average inventory, you take the mean of the inventory held at the start of the year (opening inventory) and at the end of the year (closing inventory). The cost of goods sold, also known as cost of sales, includes costs that can be directly apportioned to the production process, such as raw material cost and direct labor cost.
Examples of Days Inventory Outstanding (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the DIO in a better manner.
Example #1
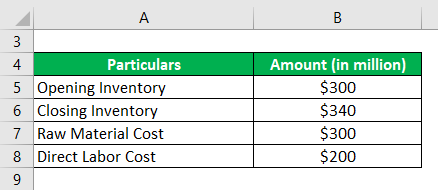
Let us take the example of a small manufacturing company to elucidate the calculation of days inventory outstanding. According to the latest annual report of the company, the following information is available:
Solution:
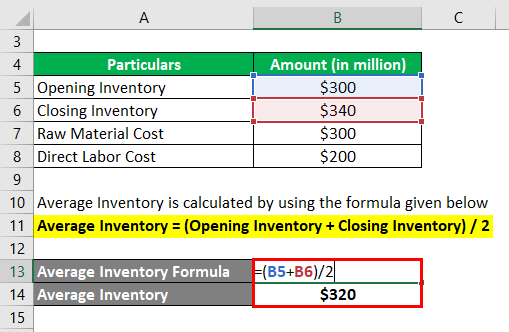
The formula used to calculate the average inventory is as follows:
Average Inventory = (Opening Inventory + Closing Inventory) / 2
- Average Inventory = ($300 million + $340 million) / 2
- Average Inventory = $320 million
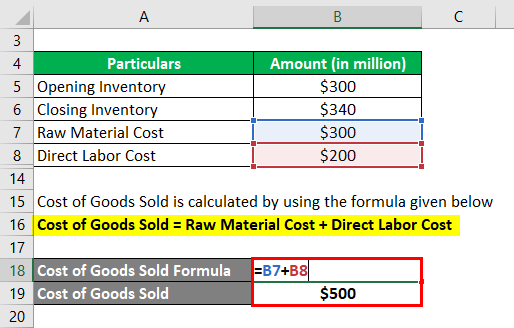
Cost of Goods Sold is calculated by using the formula given below
Cost of Goods Sold = Raw Material Cost + Direct Labor Cost
- Cost of Goods Sold = $300 million + $200 million
- Cost of Goods Sold = $500 million
The formula used to calculate the DIO is as follows:
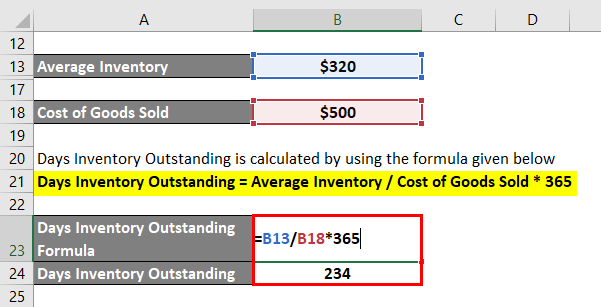
Days Inventory Outstanding = Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold * 365
- DIO = $320 million / $500 million * 365
- DIO = 234 days
Therefore, the day’s inventory outstanding of the company stood at 234 days.
Example #2
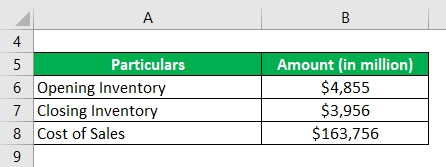
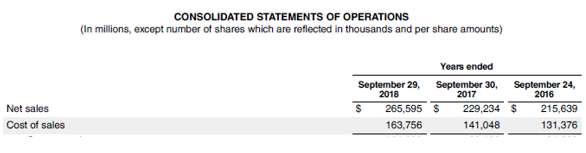
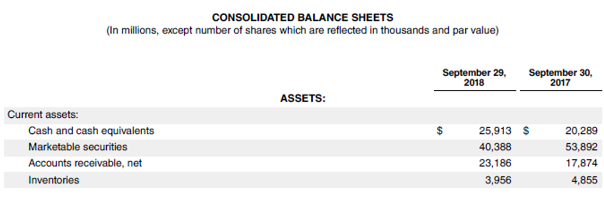
Now, we will take the example of Apple Inc.’s latest annual report (FY18). In the annual report, the company reported the cost of sales of $163,756 million, opening an inventory of $4,855 million and closing inventory of $3,956 million. Using the given information, calculate the days’ inventory outstanding for Apple Inc.
Solution:
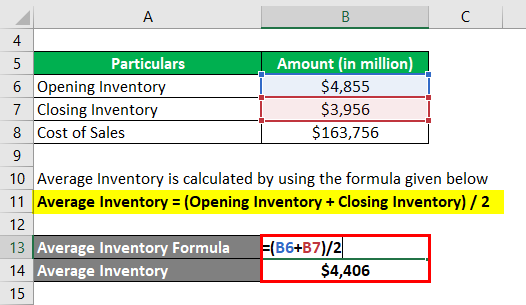
The formula used to calculate the average inventory is as follows:
Average Inventory = (Opening Inventory + Closing Inventory) / 2
- Average Inventory = ($4,855 million + $3,956 million) / 2
- Average Inventory = $4,406 million
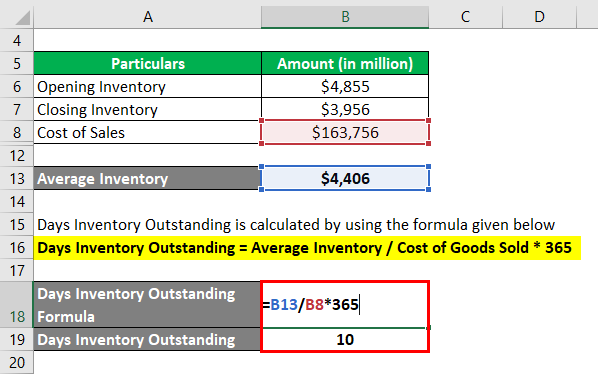
The formula used to calculate the DIO is as follows:
Days Inventory Outstanding = Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold * 365
- DIO = $4,406million / $163,756 million * 365
- DIO = 10 days
Therefore, the day’s inventory outstanding of Apple Inc. for the year 2018 stood at 10 days.
Source: d18rn0p25nwr6d.cloudfront.net
Limitations of Days Inventory Outstanding
Some of the limitations of DIO are:
- One of the major limitations is that the average inventory is calculated on the basis of the opening and closing inventory. As such, it is easy to manipulate both the numbers because they are balance sheet date figures. This flaw comes into play primarily in the case of seasonal businesses.
- The ratio in isolation does not provide any meaningful insights and as such it is advisable to compare the value vis-à-vis peers or industry.
Important Points about Days Inventory Outstanding
Some important points about DIO are:
- Inventory management is a vital factor of the working capital assessment and, as such most businesses. The day’s inventory outstanding is one of the best indicators to measure the efficiency level of a company in converting its inventory into sales.
- A low value for DIO indicates that the company is able to sell its inventory fairly quickly. As such, a low value is a sign of an efficient business in terms of inventory management and sales performance.
- Relatively high DIO can be a signal of distressed inventory management because it means that the stock inventory is held for too long before being sold, which increases the risk of obsolescence. The reason behind this can be either the purchase of too much inventory or poor sales performance.
- The measure can be used for comparing a company’s inventory management among its peers in the same operating industries.
Conclusion
So, days inventory outstanding is a liquidity measure that is essential to assess the ability of a company to transfer the stock inventory to generate sales. Although the ratio has its share of limitations, like most other financial metrics, several other aspects still make it a vital factor in the working capital assessment.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Days Inventory Outstanding formula. Here we discuss how the day’s outstanding inventory can be calculated using the formula with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –