Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to Data Modeling in MongoDB
Data modeling in MongoDB is different from structured query language databases, in SQL databases we have defined the structure of database and tables but in MongoDB, there is no need to define any structure of database or tables.MongoDB data models are basically divided into two types i.e. normalized data model and embedded data model. Based on the structure and requirement we can use the data models, at the time of database creation. The main motive is to fulfill the requirement and needs of the application and characteristic performance of the database.
Syntax of Data Modeling in MongoDB
Below is the syntax of data modeling in MongoDB.
- Embedded Data Model
{
_id: ,Field_of_document1: "",Field_of_document2: "",Field_of_document3: "", Field_of_document4: ""
},
Document1: {
Field1: "",-- Sub document 1 using embedded Model in MongoDB.
Field2: ""
Array_field1: ""
},
Document2: {
Field1: "",
Field2: "",-- Sub document 2 using embedded Model in MongoDB.
Array_field1: ""
}
- Normalized Data Model
Document1: {
_id (field used to reference the document): "",
Field2: ""-- Document 1 using in normalized Model in MongoDB.
Array_field1: "" }
Document2: {
User_id (Field 1): "", -- Reference of document 1
Field2: "", -- Document 2 using in normalized Model in MongoDB. Array_field1: ""}
Document3: {
User_id(Field 1): "", -- Reference of document 1
Field2: "", -- Document 3 using in normalized Model in MongoDB. Array_field1: ""}
Parameters of Data Modeling in MongoDB:
Below is the parameter description syntax in MongoDB:
- Document 1 to Document N: We have used one or multiple documents. On the basis of type of data modeling, we have select the document in MongoDB. MongoDB data model is divided into two types.
- Field 1 t Field N: We have used multiple fields in one document while designing a data model. We have used different fields of a different documents.
- Array Field: We can select a field as an array while designing a data model in MongoDB.We have used different data types of the array while designing a data model in MongoDB.
How Does Data Modeling Work in MongoDB?
Below is the working of data modeling in MongoDB:
1. MongoDB document contains different types of fields and objects in the collection that we have used in MongoDB schema.
2. We need to consider the below points while designing a data model are as follows.
- Define and design schema on the basis of application and user requirements.
- Combine one or multiple documents or objects into a single document. If we don’t require this object in a single document then we need to separate this as per requirement.
- Make the duplicate data of the application while implementing the data model.
- Apply joins of write operations, don’t apply it on reading operations.
- For better performance of the database, optimize our database schema.
- We need to do better aggregation on the schema to improve database performance.
3. The data model in MongoDB is basically divided into two types:
1. Embedded Data Model
- Embedded model has joined one or more related documents into a single document.
- The embedded data model is very important and useful to join one or more related documents into one single document.
- This data model allows the application to retrieve multiple related data from a single document or database operation.
2. Normalized Data Model
- The normalized data model is also known as the reference data model. This data model is used to store the relationship including data links from one documents to multiple documents.
- The normalized data model is very important and useful to one or more documents with each other.
- Normalized or reference data model is consist one to one or one-to-many relationships between the documents.
4. Based on the structure and requirement we can use the data models at the time of database creation.
Examples to Implement Data Modeling
Below is an example of data model in MongoDB.
Example #1 – Embedded Data Model
Without Using the Embedded Data Model:
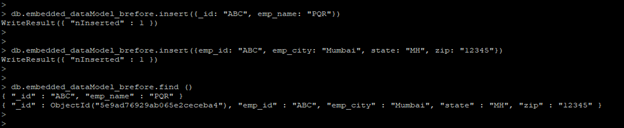
- In the below example we have inserted two different documents without using any data model.
- After inserting this document we have created an embedded data model of two different documents into one collection model.
The below example shows without using the embedded data model.
Code:
db.embedded_dataModel_brefore.insert({_id: "ABC", emp_name: "PQR"})
db.embedded_dataModel_brefore.insert({emp_id: "ABC", emp_city: "Mumbai", state: "MH", zip: "12345"})
db.embedded_dataModel_brefore.find ()
Output:
Using Embedded Data Model
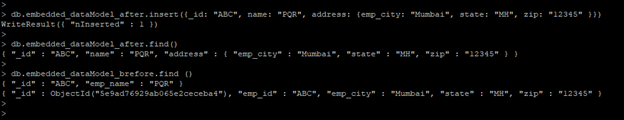
In the below example, we have using the embedded data model.
- We have to create a single document of the above two created documents. The below example shows that creating a single document of two documents using an embedded data model are as follows.
Code:
db.embedded_dataModel_after.insert({_id: "ABC", name: "PQR", address: {emp_city: "Mumbai", state: "MH", zip: "12345" }})
db.embedded_dataModel_after.find()
Output:
Example #2 – Normalized Data Model
Without Using the Normalized Data Model
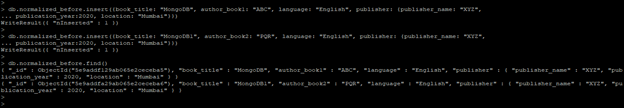
- In the below example, we have not used a normalized model to create documents. The below example shows that without using the normalized data model are as follows.
- We have inserted two documents into the collection without taking reference of another document.
Code:
db.normalized_before.insert({book_title: "MongoDB", author_book1: "ABC", language: "English", publisher: {publisher_name: "XYZ", publication_year:2020, location: "Mumbai"}})
db.normalized_before.insert({book_title: "MongoDB1", author_book2: "PQR", language: "English", publisher: {publisher_name: "XYZ", publication_year:2020, location: "Mumbai"}})
db.normalized_before.find()
Output:
Using Normalized Data Model
In the below example, we have using a normalized data model.
- In the below example, we have to create three documents and giving reference to the above two documents at the time of creation.
- In the above two documents, publisher data is repeated two times so we have a giving reference of those documents.
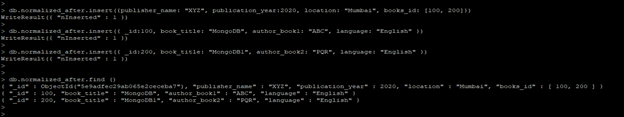
Code:
db.normalized_after.insert({publisher_name: "XYZ", publication_year:2020, location: "Mumbai", books_id: [100, 200]}
db.normalized_after.insert({_id:100, book_title: "MongoDB", author_book1: "ABC", language: "English" })
db.normalized_after.insert({_id:200, book_title: "MongoDB1", author_book2: "PQR", language: "English" })
db.normalized_after.find ()
Output:
Conclusion
Embedded and normalized data models are two types of data models available. In embedded data model we join related documents into single documents while in the normalized data model we implement the reference link of one or more documents. The data model is very important and useful,
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Data Modeling in MongoDB. Here we discuss how Does Data Modeling Work in MongoDB and its different types along with its examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –