Updated July 1, 2023
What are Financial Assets?
Financial assets are non-tangible, liquid assets that gain their value from the ownership of a firm (in the form of shares) or legal, contractual agreements (bonds). Owners can easily convert these assets to cash and use them to purchase tangible assets like real estate.
Thus, it makes it easier for companies to buy/sell as needed to fund their business. Some standard financial asset types are bonds, stocks, cash and cash equivalents, funds, deposits, etc.
Types of Financial Assets
1. Cash and the Cash Equivalents
(Source: Annual Report of McDonald’s for FY21)
Cash and cash equivalents are highly liquid financial asset types that are quickly convertible into cash without significant risk of loss in value. Examples include cash balances, bank balances, cheques received from parties but not yet cleared by the bank, commercial paper, and so on.
Cash and cash equivalents are important indicators of a company’s liquidity and ability to meet short-term obligations such as paying bills, salaries, and other expenses. Investors and analysts often pay close attention to a company’s cash and cash equivalents when evaluating its financial health and ability to generate future profits.
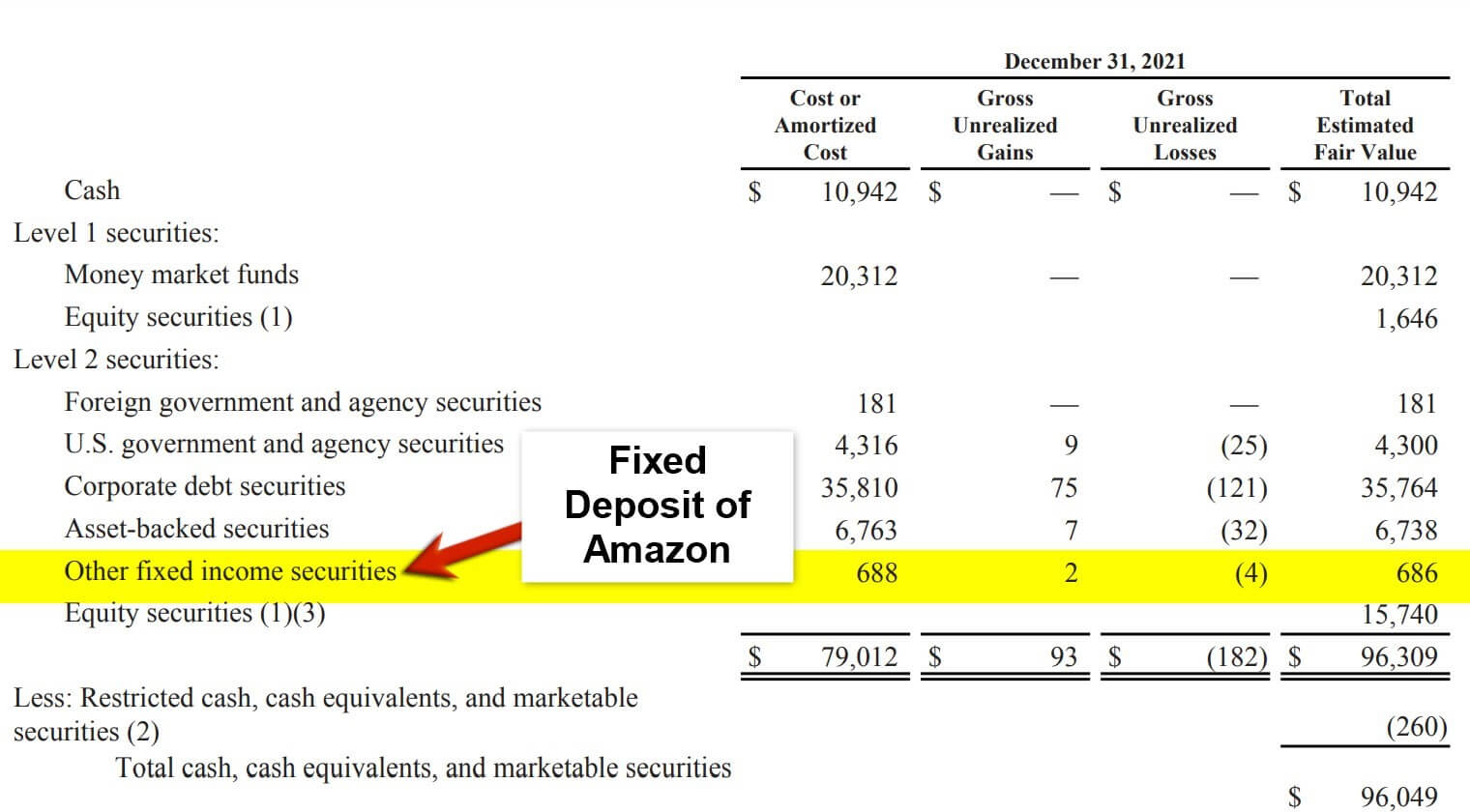
2. Fixed Deposits
(Source: Annual Report of Amazon for FY22)
Fixed deposits refer to the amount that the business deposits with some other entity in the expectation of earning returns on such money deposited in the form of interest. We can consider FDs a low-risk investment option as the interest rate offered remains the same, and there is no risk of losing money as long as the customer does not withdraw the deposit before the maturity date. However, they also typically offer lower returns than higher-risk investment options such as stocks or mutual funds.
In the above screenshot of Amazon Inc, we can spot that company the value of fixed income securities for cost or amortized cost is $688, gross unrealized gains is $2, gross unrealized losses is -$4, and total estimated fair value is $686.
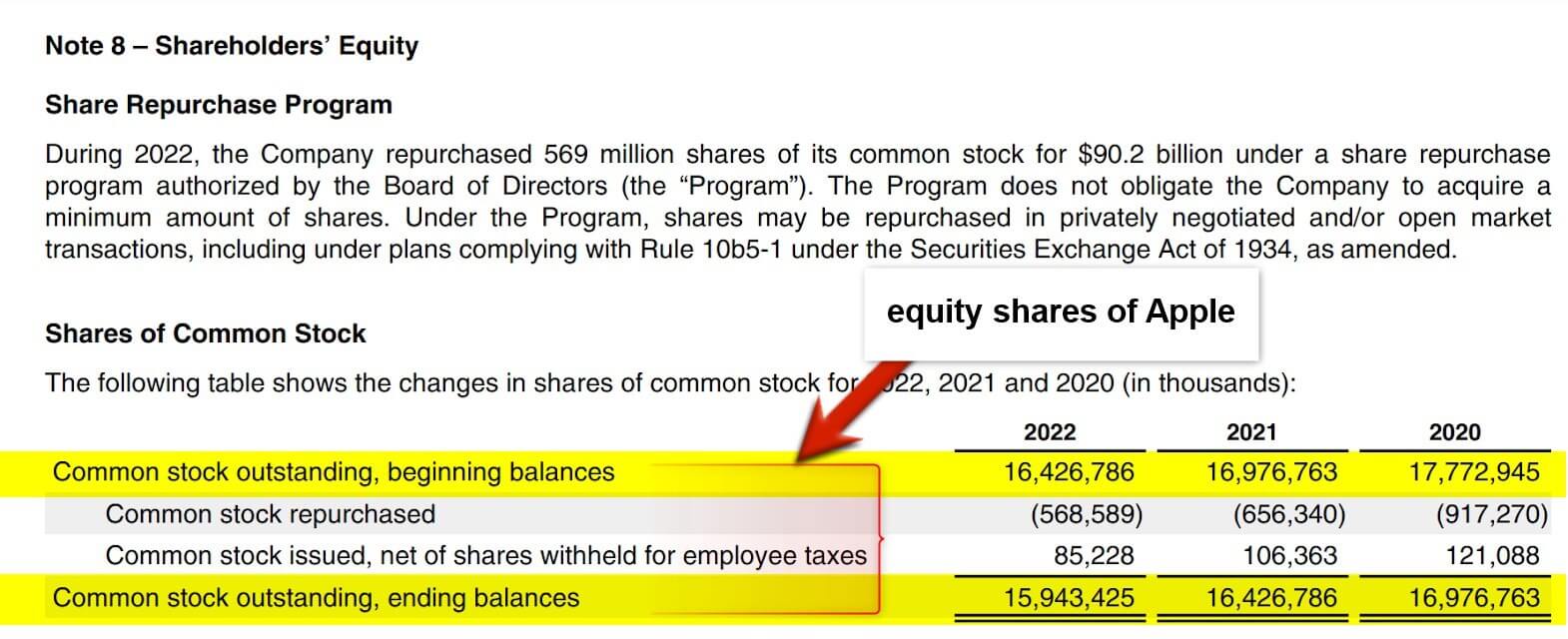
3. Equity Shares
(Source: Annual Report of Apple Inc. for FY22)
Equity shares, also known as common or ordinary shares, represent ownership in a company. When a person purchases equity shares in a company, they become a shareholder. They are entitled to a portion of the company’s profits, as well as voting rights in the company’s decision-making processes.
Equity shares differ from other financial asset types, such as bonds or preference shares, representing a fixed claim on a company’s earnings and assets. Moreover, we determine the value of equity shares by analyzing a company’s performance and demand for shares in the stock market. If a company performs well and earns profits, the value of its equity shares may increase, providing a return on investment for the shareholders. On the other hand, if the company performs poorly, the value of its equity shares may decrease, resulting in a loss for the shareholders.
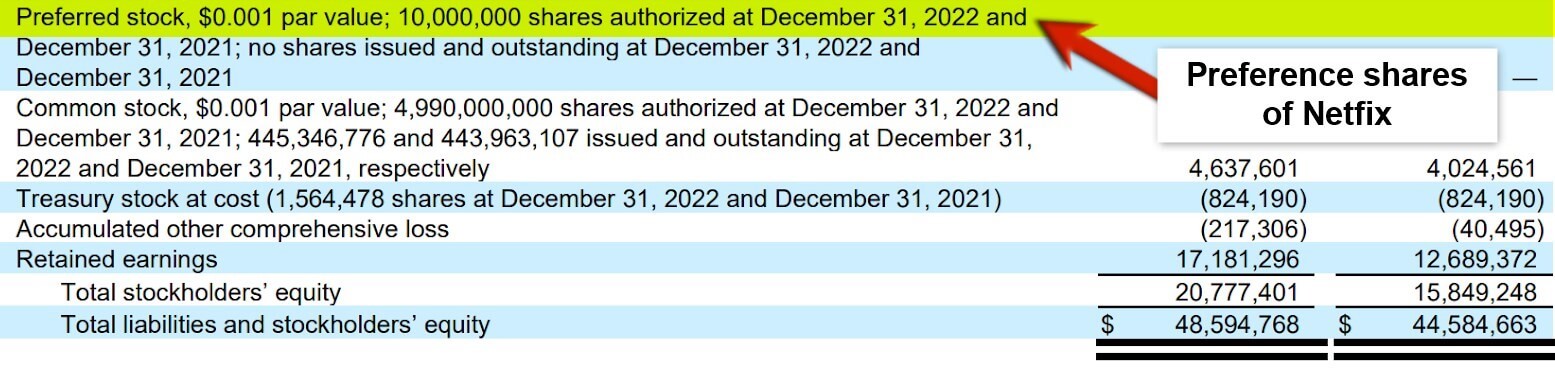
4. Preference Shares
(Source: Annual Report of Netflix Inc for FY22)
Preference shares are a type of security issued by a company that entitles the shareholder to certain rights and privileges not available to common shareholders. These rights typically include a fixed dividend payment, priority in receiving dividends over common shareholders, and priority in the event of liquidation.
Unlike common shares, which represent ownership in the company and provide the shareholder with voting rights, preference shares do not typically confer voting rights. However, some preference shares may have limited voting rights in certain circumstances. We can further classify the preference shares into different types, such as cumulative and non-cumulative preference shares, convertible preference shares, participating preference shares, and redeemable preference shares.
5. Debentures
(Source: Annual Report of Walmart for FY21)
Debentures are the financial asset types that give the debenture holders the right to receive the interest at a predetermined rate and on the specified due dates on the amount invested.
Debentures are usually long-term securities with maturities ranging from a few years to several decades. They offer a fixed rate of return to investors and are usually unsecured, meaning they are not backed by any specific asset of the issuer. Instead, debentures are backed only by the creditworthiness and reputation of the issuer. Debentures can be either convertible or non-convertible. Convertible debentures allow investors to convert their debt into equity at a predetermined price, while non-convertible debentures cannot be converted into equity.
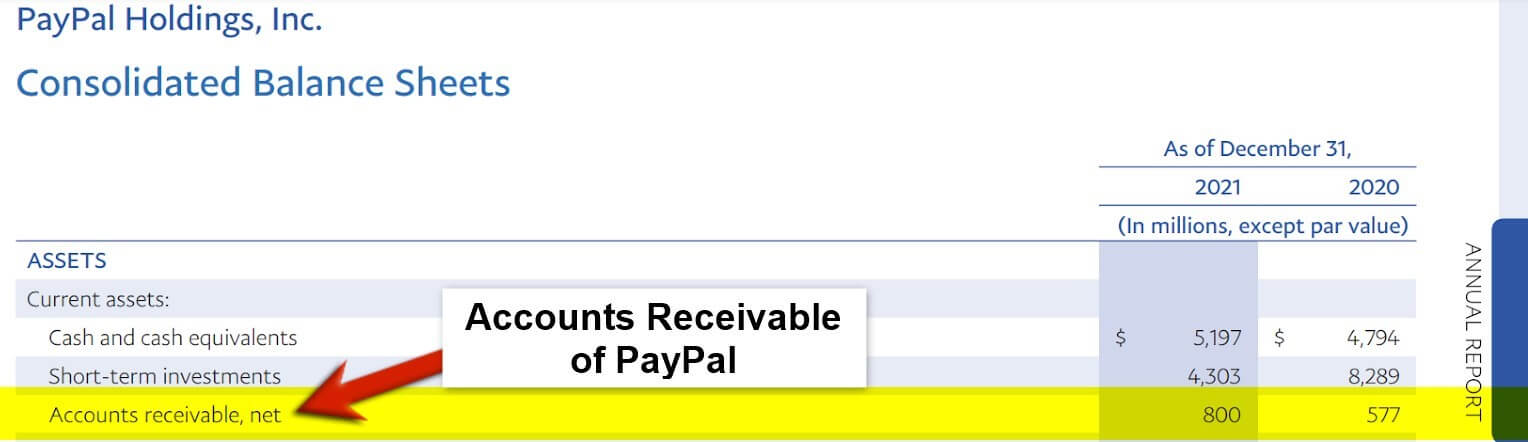
6. Accounts Receivable
(Source: Annual Report of PayPal Inc. for FY22)
When a company (selling party) makes sales on a credit basis, it has the right to receive the payment from the party who purchases its product (the debtor). So for the selling party, that debtor comes under the head of accounts receivable. In short, these are the assets that create a right to receive money in return for the credit sales made by the business within the credit period.
Also, they own the right to receive interest if the payment is delayed or not received within the allowable credit period. In such scenarios, the purchaser (Debtor) has to repay the purchase amount and the interest amount decided at the time of the sale of goods.
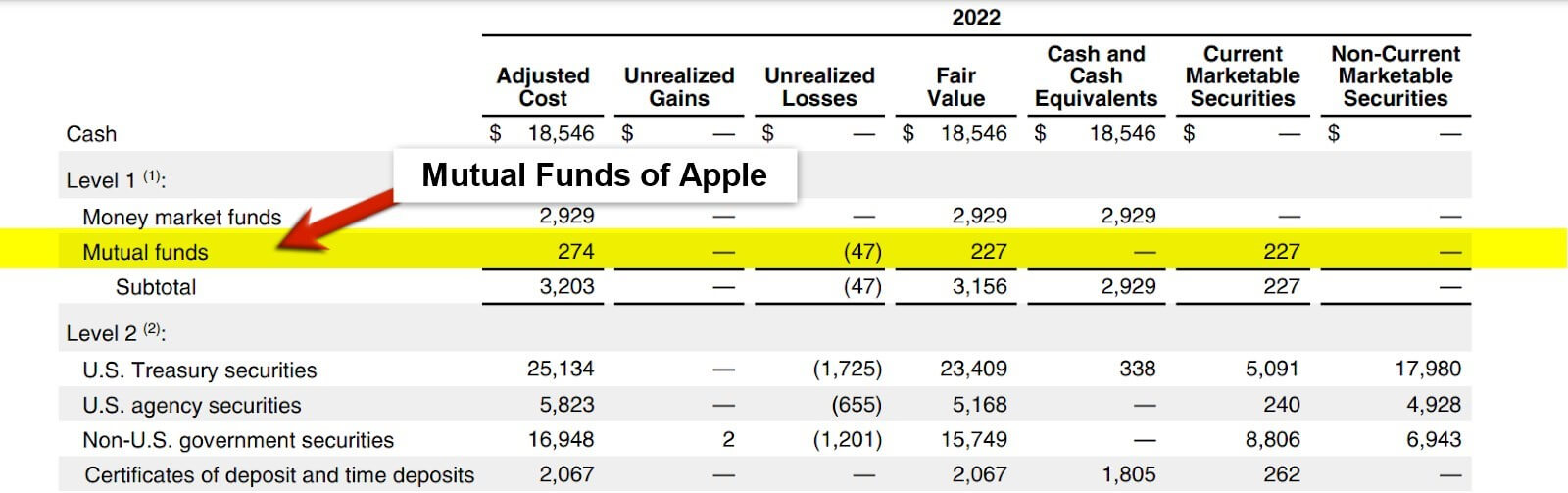
7. Mutual Funds
(Source: Annual Report of Apple Inc. for FY22)
A mutual fund is a pool of money collected from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. Investment professionals manage mutual funds and use the pooled money to invest in various assets to generate returns for investors.
When you invest in a mutual fund, you buy a share of the fund, representing a portion of the overall assets. The value of your investment will rise or fall with the value of the underlying assets. As the value of the investments in the fund increases or decreases, so does the value of the investor’s shares.
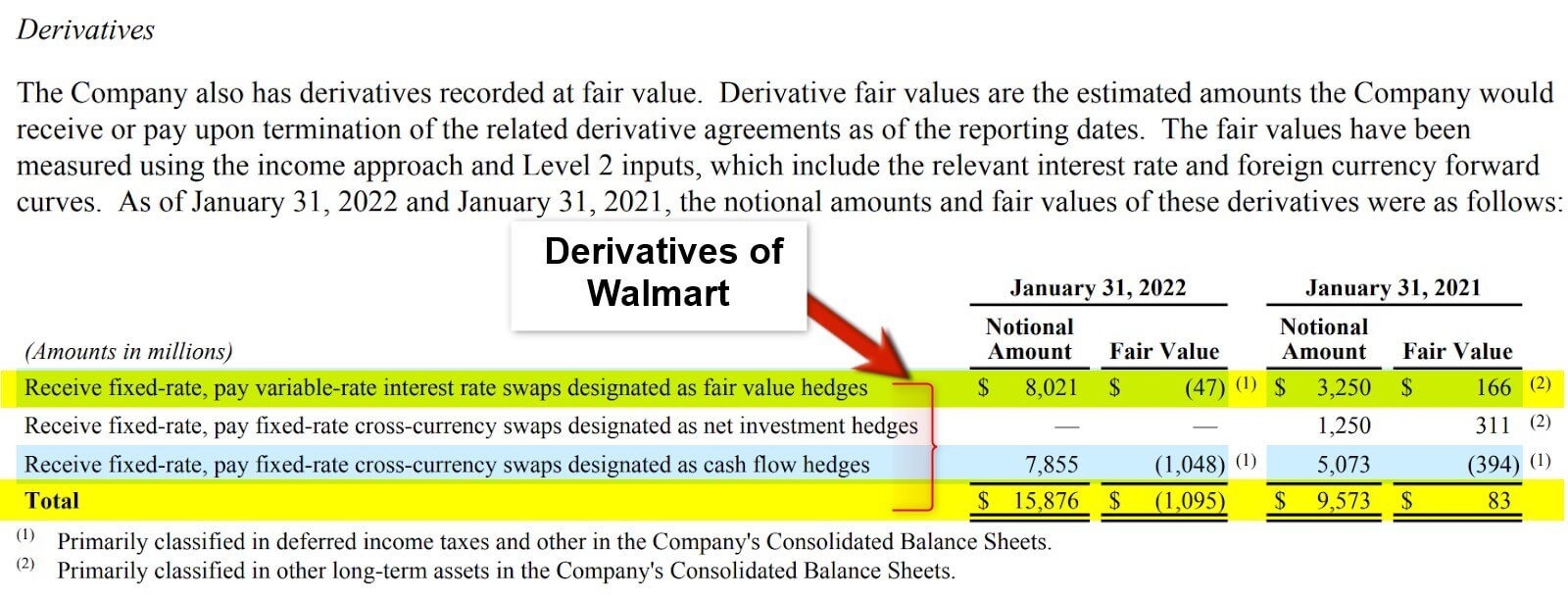
8. Derivatives
(Annual Report of Walmart Inc. for FY22)
In finance, derivatives are financial asset types that derive value from an underlying asset, such as a stock, bond, commodity, or currency. The value of a derivative depends on the underlying asset’s price movement.
Derivatives are useful in finance for risk management, speculation, and arbitrage. For example, a farmer may use futures contracts to lock in the price of a crop before the harvesting season to protect against price fluctuations. A hedge fund may use options contracts to speculate on the price movement of a stock or commodity. A bank may use swaps to hedge its interest rate risk.
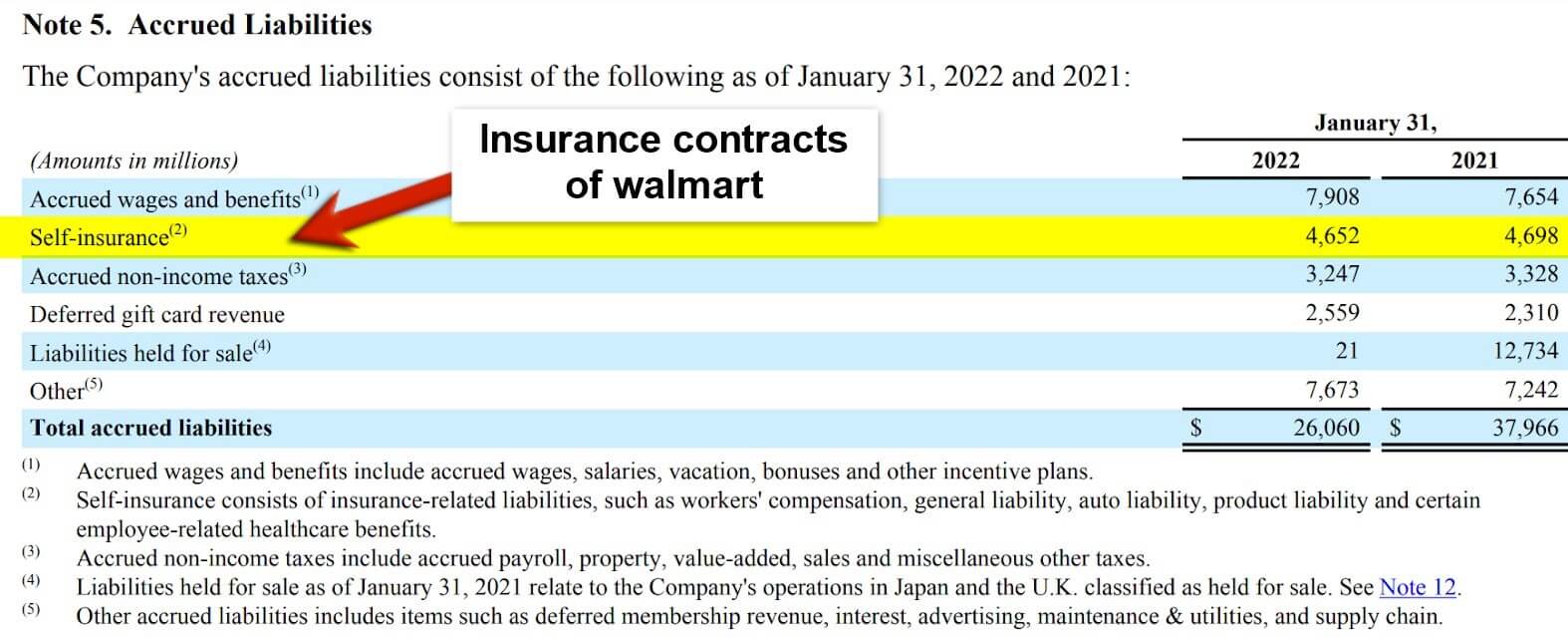
9. Insurance Contracts
(Source: Annual Report of Walmart Inc. for FY22)
Insurance contracts are another type of financial assets types where one party (known as a policyholder) pays a premium to the insurance companies to get the right to compensation when an uncertain future event in the business results in the loss of the business.
Let’s say a policyholder has taken a policy that gives the right to the policyholder to get compensation in case of fire. One day there was a fire incident in the business. The insurance company will compensate the business for the loss due to such a fire.
Characteristics of Financial Assets
- Liquidity: All financial asset types can be easily bought or sold in the market, making them highly liquid.
- Divisibility: Financial assets can be divided into smaller units, allowing investors to purchase or sell small quantities.
- Transferability: They can be transferred from one investor to another without affecting the underlying asset.
- Value: These assets have a measurable value, depending on the asset’s market price.
- Risk and Return: Financial assets carry varying risk and expected returns, with higher returns often accompanied by higher risk.
- Time to Maturity: Financial assets can have different maturities, ranging from short-term to long-term.
- Currency Denomination: Financial assets can be denominated in different currencies, subjecting them to exchange rate risk.
- Legal Agreements: These are legal agreements, such as contracts or prospectuses, which outline the terms of ownership and transferability.
In short, financial asset types provide investors with a range of investment opportunities to suit their risk preferences and investment objectives.
Benefits and Risks of Investing in Financial Assets
Benefits:
- Diversification: Financial asset types can provide a way to diversify an investor’s portfolio, which can help reduce overall risk.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Financial assets can offer higher returns than traditional savings accounts, which can help investors achieve their financial goals faster.
- Liquidity: Many financial assets are highly liquid, which means they can be easily bought and sold in the market, providing investors with flexibility.
- Professional Management: Some financial asset types, such as mutual funds, are managed by professional investment managers with expertise in analyzing markets and making investment decisions.
Risks:
- Market Risk: The value of financial asset types can change according to market conditions, which can be unpredictable and volatile.
- Credit Risk: Financial assets can also carry credit risk, which means there is a risk that the issuer may default on their obligations, leading to potential losses for investors.
- Inflation Risk: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of returns on financial assets over time.
- Liquidity Risk: Although financial assets can be highly liquid, in certain market conditions, such as a financial crisis, liquidity can dry up, making it difficult to sell the assets.
- Foreign Exchange Risk: If investors invest in foreign financial assets, they might face foreign exchange risk, which arises from fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
How to Invest in Financial Assets?
Investing in financial asset types requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some steps to consider when investing in financial assets:
Step 1: Determine your Investment Goals: Consider your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon for investing. Determine the amount of money you can afford to invest.
Step 2: Research Different Financial Assets: Learn about different financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and others. Consider the risks and potential returns associated with each asset class.
Step 3: Choose a Broker: You must choose a broker to buy and sell financial assets. Compare the fees and services different brokers offer to find the best fit for your needs.
Step 4: Open an Investment Account: Once you have selected a broker, open an investment account. You must provide personal information and complete the necessary paperwork to open an account.
Step 5: Create a Diversified Portfolio: Diversification is critical to managing risk when investing in financial assets. Consider investing in a mix of asset classes to help balance risk and potential returns.
Step 6: Monitor your Investments: Keep an eye on your investments and track their performance over time. Adjust your portfolio as needed based on changes in your investment goals or market conditions.
Step 7: Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with market news and trends that may affect your investments. Consider seeking advice from a financial professional to help you make informed investment decisions.
Common Misconceptions Related to Financial Assets
1. Investing in the stock market is too risky: Many people are cautious of investing in the stock market, deeming it too risky. Although there is some risk involved, it is also true that stocks have historically provided some of the best returns of any asset class over the long term. For example, over the past decade, Microsoft’s stock (NASDAQ: MSFT) has seen a significant increase of 969.5% in its share price, which results in significant returns for investors.
2. Bonds are always a safe investment: While bonds can be less risky than stocks, they are not always safe. The value of bonds can fluctuate due to several factors, including changes in interest rates, inflation, and credit quality. In some cases, bonds can even default, i.e., the issuer cannot make interest payments or repay the principal.
3. Investing is only for the wealthy: Another common misconception is that investing is only for the wealthy. Although some investment opportunities may require a minimum amount, there are many ways for people of all income levels to invest, e.g., employer-sponsored retirement plans, individual retirement accounts (IRAs), and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
4. You need to be an expert to invest: While it is true that investing requires some knowledge and skill, you do not need to be an expert to begin with. Many resources exist to help you learn investing, including books, websites, and online courses. Many investment platforms offer low-cost or free investment advice to help you get started.
5. Investing is a get-rich-quick scheme: It is important to recognize that investing is not a get-rich-quick scheme. Building wealth through investing requires patience, discipline, and a long-term perspective. Although there exist opportunities to earn high returns in the short term, the most successful investors stick to a well-diversified long-term investment strategy.
Global Financial Assets Types Markets
Globally, all the markets operate under a single stock exchange. The top stock exchanges are; New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), Nasdaq (XNAS), Shanghai Stock Exchange (XSHG), Euronext (XAMS), etc.
|
Markets |
Market Size | Top Players |
Trend |
| Mutual Funds Market | $54.93 trillion | BlackRock, Inc | The mutual funds market is predicted to grow at 9.76% CAGR between 2022 and 2027. Also, the market size will increase by USD 71.62 trillion. |
| The Vanguard Group | |||
| Fidelity Investments | |||
| Equity/Share Market | $93.7 trillion | Amazon. | The NSE Nifty jumped 99.75 points to 17,207.25 in March. |
| Alphabet. | |||
| Apple. | |||
| Debt Market | $119 trillion | Commercial Banks | After 2021, the global market suddenly declined by 20%. |
| Financial Institutions | |||
| Derivative Market | $18.3 trillion | Goldman Sachs | There’s been an increase of 47% increase in a period of six months from 2021 to 2022 |
| Bank of America Merrill Lynch | |||
| Morgan Stanley |
Final Thoughts
Thus, financial asset types are the most liquid assets of the company, which fulfills the cash need of the company. As a result, we cannot touch them physically, but they are important for the business to yield income in the form of dividends, interest, or any other asset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the classification of financial assets?
Answer: US GAAP divides financial asset types into three major categories for the classification and measurement of investments in securities. They are classified as trading (value derived from the net income), available for sale (value derived from other income sources), and held to maturity (repayment cost)
Q2. Differentiate between physical and financial asset types.
Answer: Physical assets are tangible assets with a physical form. Its example includes real estate, machinery, vehicles, equipment, inventory, and raw materials. Financial assets, on the other hand, are intangible assets that represent ownership in a company, debt obligations, or other financial instruments. Its example includes stocks, bonds, mutual funds, options, etc.
Q3. What are the most common financial assets types?
Answer: The most common financial asset is:
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Mutual funds
- Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Real-estate
- Derivatives
Recommended Articles
This is our guide to Financial Assets Types. Here are some further articles for expanding understanding: