Updated June 14, 2023

Introduction to CSS font-variant
CSS font-variant property is defined as a variant of the font elements that converts lowercase letters into uppercase letters and used when we need small caps for a text in the document. Stylesheets can apply this property to various HTML tags, and designers have designed it to effectively maintain readability and weight when resizing the text size in a window.
Syntax
The general syntax of the font-variant property is as follows:
Selector {
Font-variant: value;
}This property takes four values among this normal, ad small-caps rule the property well. The values can be any of the following:
- Normal: This specifies a normal font variant and is considered to be a default value. It selects a font that is not small.
- small-caps: It selects a small-caps font by scaling by rendering small letters to uppercase letters.
- inherit: This keyword specifies the value which is inherited from the parent. This means it follows the root element.
- initial: This displays the default size value of the font.
How does font-variant property work in CSS?
As we know, CSS has font-property on HTML elements that helps change the look of the HTML elements. One of the font-property is font-variant. It gives stylistic font features in CSS 2 and CSS3. The font-variant property specifies whether to display text in small caps. It is different from regular capitals as small caps are separate properties of the regular font. The font-variant property interacts with the text-transform property. For instance, if the font is set to small caps and the text-transform property is set to lowercase, all the characters will be displayed in lowercase, even if the font supports small caps.
Let’s see how this property can be used with CSS and explain their working with real-time examples.
For instance, let us take
.css
#fontsmall {
font-variant: small-caps;
}.html
<p>This line is original text</p>
<p id="fontsmall">This text is creative CSS</p>The working process of the above code starts by taking the id=’fontsmall’ where it converts all letters except the first one into small caps. Additionally, the code displays the original caps slightly larger than the original capital letters. This property has good support in all browsers.
CSS3 property allows us to provide font features on a font of our wish and to check their working (using ligatures). Ligature looks at the text specified by two or more characters. For example, we are making Stylistic features on the capital letters.
font-variant-ligatures: common-ligatures;Making font-variant property to none resets all other specified none features like normal, small-caps. In CSS3, apart from the small-caps property, they have expanded properties like
- alternates
- caps
- east-Asian
- ligatures
- numeric
Examples to Implement CSS font-variant
Here we will explore some examples of how to use this property:
Example #1
Assigning Small Caps text to Capitals by setting CSS Property:
Code:
<!doctype html>
<title> Example on CSS font-Variant </title>
<style>
p
{font-size: 6vw;
}
.ab {
font-variant: small-caps;
}
</style>
<h1>Example on CSS font-Variant </h1>
<p class="ab"> Text with small caps </p>
<p> Original content </p>Output:

Explanation: Here, the paragraph class ‘ab’ is set to font-variant: small-caps; hence it changes the text into capital letters, and other paragraph text content remains normal with no change effects. And here is what it looks like when executing the above code snippets in the browser.
Example #2
Assigning an initial value to the text by setting CSS Property:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h2 {
color: purple;
}
h1 { color: yellow;
}
p.init {
font-variant: initial;
}
p.edu {
font-variant: initial;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1>Stylish Demo On page</h1>
<h2>font-variant:initial;</h2>
<p class="init">Online Web class. </p>
<p class="edu">
Hello, Welcome to our Portal on Easy Learning
</p>
</body>
</html>Output:

Explanation: No change is reflected in the output as we have set the font-variant to the initial; every text remains the small letters. Here is the output for the above code.
Example #3
Taking the border-style demo with the text content using small-caps:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.myclass {
border: 4px outset yellow;
background-color: lightorange;
text-align: center;
font-variant:small-caps;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Using div element</h1>
<div class="myclass">
<h2>This is the initial text</h2>
<p>Followed by next text</p>
</div>
<p>CSS Font Documentation Content. </p>
</body>
</html>Output:
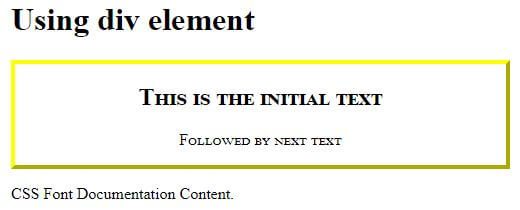
Explanation: In this case, the font-variant property is set to “small-caps”, while the class “content” is set to “uppercase”.
Example #4
Implementation of Font-variant – Ligatures:
Code:
<!doctype html>
<title>Example on CSS</title>
<link href="//fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lora" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
div {
font-family: calibri, serif;
font-size: 6vw;
}
.ligmode{
font-variant-ligatures: historical-ligatures;
color: green;
}
.ligon {
font-variant-ligatures: Discretionary ligatures;
color: blue;
}
</style>
<div>
<span class="ligmode">IIFA- fi</span>
<br> </br>
<span class="ligon">task-Final</span>
</div>Output:

Explanation: When we execute the above code, the text of the Span class’ ligmode ‘will display historical Ligatures, and with the span class ‘ligon’, the text will display discretionary ligatures.
Example #5
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.ff
{
font-variant: normal;
}
.ff1
{
font-variant: small-cap;
}
.ff2
{
font-variant: all-small-caps;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Most popular in CSS Style is.</p>
<p class="ff">Changing the normal font size and implementing small-caps effect.</p>
<p class="ff1">Hello world sample Example.</p>
<p class="ff2">DEVELOPERS MAKE USE OF THIS STYLING.</p>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #6
CSS font-variant showing a demo on CSS2 property values:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<h1> Welcome </h1>
<style>
p{font-family:Georgia,Verdana;
color:red;
background-color: lightblue;
font-size:1.7em;}
.norm{font-variant:normal;}
.smacaps{font-variant:small-caps;}
.inh{font-variant:inherit;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="norm">Font-Variant on the html page element</p>
<p class="smacaps">Font-Variant on the html page element</p>
<p class="inh">Font-Variant on the html page element</p>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #7
Using external CSS:
Code:
<div class="main">
<div class="content">
<p class="parent">
Here is a text with normal paragraph.
</p>
<p class="child">
Here is a text with normal paragraph <code>few transformation</code> and variant set to <code>uppercase</code>.
</p>
<p class="subchild">
HERE IS THE TEXT WITH UPPERCASED IN THE SOURCE CODE. <code>FANT</code> THE VALUE IS ASSIGNED TO <code>SMALL-CAPS</code>, BUT NO CHANGE IN THE PREVIOUS CASE.
</p>
</div>
</div>ff.css
body {
background-color: #8A2BE2;
color: #00FFFF;
font-size: 1.2em;
font-family: 'Helvetica Neue', Georgia, Arial, sans-serif;
}
.main {
margin: 30px auto;
max-width: 600px;
}
.content{
padding: 21px;
background-color: #000000;
}
.parent {
font-variant: small-caps;
}
.child {
font-variant: normal;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.subchild {
font-variant: small-caps;
}Output:

Conclusion
Therefore, this article explains how to use CSS property font-variant with their work and examples. Many programs are given here for a better guide on this property. To conclude, we have brought all the values and their work which is very helpful in creating a stylish website.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CSS font-variant” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.



