Updated October 17, 2023
What is the Credit Score Rating Scale?
Creditors use a credit score rating scale to assess an individual’s creditworthiness, i.e., a person’s likelihood of whether the company can pay the debt obligation fully on time. Different credit rating agencies provide credit ratings.
A rating is given to any issuer, i.e., an individual, corporate, state, or sovereign government seeking to borrow the money. The rating does not say whether an investor should really buy that bond, but it is just one of the most important parameters an investor should consider before investing in any bond. A rating suggests both the present situation and the impact of future events on credit risk.
What Does a Credit Score Rating Scale Not Indicate?
The rating does not suggest whether:-
- A credit score rating scale does not measure performance sectors like price fluctuations or market value.
- A-rated security is suitable for an investor or a group of investors and whether they should buy, sell, or hold the rated securities.
- A-rated security is appropriate as per an investor’s risk tolerance, or the price of a security is perfect for its rating.
- The market value of the security will change in the future, or no
Credit Rating Agency vs. Credit Bureau
A credit rating agency provides an opinion that relates to the debt repayment by the borrower, whereas a credit bureau provides information on past debt repayments by borrowers.
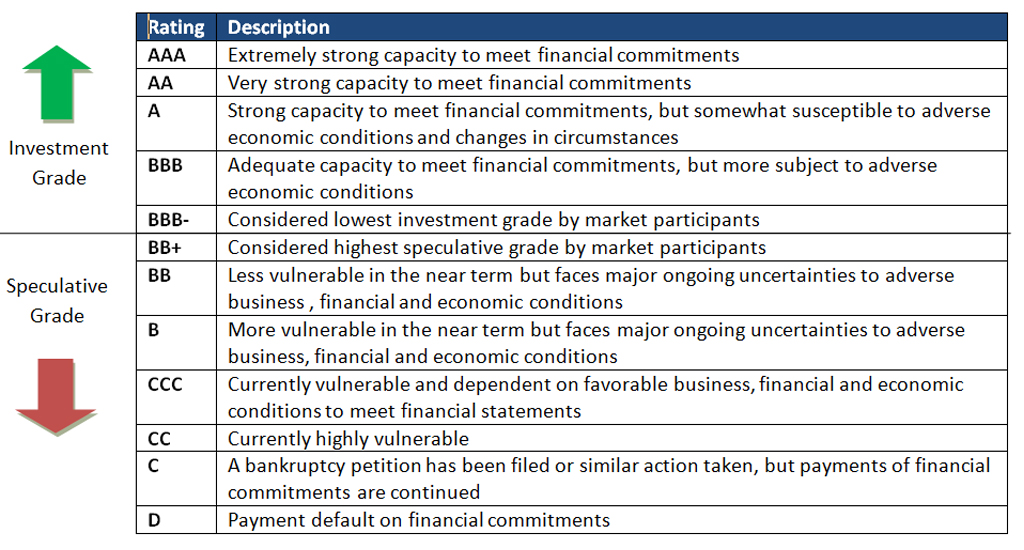
Credit Score Rating Scale
Every company has a different process for giving credit ratings and has a different credit score rating scale.
Source: Standard&Poor’s
Looking at this table, we can see that the higher the rating higher the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Bonds with different maturity periods are rated differently. Long-term ratings are assigned to bonds with more than 1 year of maturity. Short-term credit ratings are assigned to bonds having a maturity period of less than 1 year. Generally, long-term and short-term credit ratings are interlinked, so if an issuer’s long-term rating is downgraded, the short-term rating gets downgraded automatically.
Investment grade is referred to as securities rated as having higher credit quality. In contrast, Speculative grade, which is also referred to as non-investment grade, is referred to as debt securities where the issuer currently can repay. Still, uncertainties like adverse business or financial circumstances might have the ability to default.
Recovery Rating Scale
Some credit rating agencies also incorporate recovery ratings, which suggest the opinion about the amount that may get recovered in the event of default. This is one of the important factors in evaluating a company’s credit quality, mostly in the evaluation of non-investment-grade debt.
| Recovery Rating | Rating Description | Recovery Expectations(%) | Issuer rating relative to issuer credit rating |
| 1+ | High expectations, full recovery | 100 | +3 |
| 1 | Very high recovery | 90-100 | +2 |
| 2 | Substantial Recovery | 70-90 | +1 |
| 3 | Meaningful Recovery | 50-70 | 0 |
| 4 | Average Recovery | 30-50 | 0 |
| 5 | Modest Recovery | 10-30 | -1 |
| 6 | Negligible Recovery | 0-10 | -2 |
Source: Standard & Poor’s
In the year 2003, Standard & Poor’s started assigning recovery ratings. They use a rating scale instead of letters to express an opinion about the percentage of the principal and unpaid accrued interest, which investors can expect to receive in the case of default.
This Recovery opinion is based on different factors like:-
- The rights that investors and creditors may have to specific assets
- The potential liquidation value of the entity’s assets and
- The result of formal bankruptcy proceedings or informal out-of-court restructuring.
The recovery can be in any form
- Cash
- Debt
- Equity securities of a reorganized entity
- Combination of the three
Why Does Credit Rating Keep on Changing?
Credit ratings are not constant. They keep changing from time to time as the credit quality of an issue or issuer alters in ways that were not expected when a rating was assigned.
For example, consider a new technology that was not expected, which was not considered while assigning a rating to a company. This new technology might lead to a negative impact on the financials of the company. This may impact the downgrading of the current rating.
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles that will help you get more details about the Credit Score Rating scale, so just go through the link.