Introduction to Condition in MySQL
Condition in MySQL is an open-source RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) that uses a standard language SQL – Structured Query Language for manipulating, storing, and retrieving database records. In simple words, we can say that MYSQL is a Database server that is a fast, secure, and easy-to-use application for many small and big businesses and different purposes – Web Database, Data Warehousing, E-Commerce, Logging applications, and more. It’s also important to ensure that your database is accessible through the correct mysql port, especially when configuring remote connections or troubleshooting connectivity issues.
A database encompasses one or multiple tables with rows and columns. A name represents each table, and SQL statements perform any action on a database. Here, we will discuss Conditional statements in MYSQL, which are based on some conditional expressions. An expression can be any arrangement of MySQL literals like variables, operators, and functions that, on execution, returns a logical value if the condition is satisfied.
Conditional Operators in MySQL
Let’s first view some of the important SQL statements with the syntax:
1. SELECT– extracts/selects records from a database. ‘*’ denotes ‘all’.
SELECT column1, column2,...... FROM table_name;
SELECT * FROM table_name;2. UPDATE– updates existing fields in a database
UPDATE tablename SET col1 = value1, col2 = value2, ... WHERE condition;3. DELETE– deletes records from a database
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;4. DROP DATABASE – Deletes database
DROP DATABASE database_name;5. INSERT INTO– adds new records into the database
INSERT INTO name_of_table (col1,col2, ...) VALUES (val1, val2, ...);6. CREATE DATABASE– generates a new database
CREATE DATABASE databasename;7. CREATE TABLE– generates a new table
CREATE TABLE tablename ( col1 datatype, col2 datatype, col3 datatype, .... );8. ALTER TABLE– make changes to a table
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype;9. DROP TABLE– removes a table
DROP TABLE table_name;10. CREATE INDEX– produces an index (search key)
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column1, column2, ...);11. DROP INDEX– removes an index
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name;Types of SQL Operators
The different types of SQL Operators are given below:
1. SQL Arithmetic Operators
| Operators | Descriptions |
| + | Add |
| – | Subtract |
| * | Multiply |
| / | Divide |
| % | Modulo |
2. SQL Bitwise Operators
| Operator | Description |
| & | Bitwise AND |
| | | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Bitwise exclusive OR |
3. SQL Comparison Operators
| Operator | Description |
| = | Equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| <> | Not equal to |
4. SQL Logical Operators
| Operator | Description |
| ALL | TRUE if all of the subquery values satisfy the condition. |
| AND | TRUE if all the conditional expressions separated by AND are TRUE. |
| ANY | TRUE if any of the subquery values satisfy the condition. |
| BETWEEN | TRUE if the operand is inside the series of comparisons. |
| EXISTS | TRUE if the subquery results in one or more fields. |
| IN | TRUE if the operand matches one of a list of expressions. |
| LIKE | TRUE if the operand equals a pattern. |
| NOT | Shows a record if the condition(s) is FALSE. |
| OR | TRUE if any of the conditions separated by OR is valid. |
| SOME | TRUE if any of the subquery values satisfy the condition. |
5. Conditional Operators
You can learn and practice SQL queries from educba.com in a straightforward understanding way.
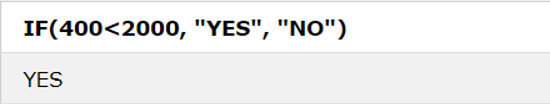
1. IF() Function
If the condition is TRUE result is “YES,” and if the condition is FALSE, then “NO”.
Syntax:
IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)SQL Statement:
SELECT IF(400<2000, "YES", "NO");Output:
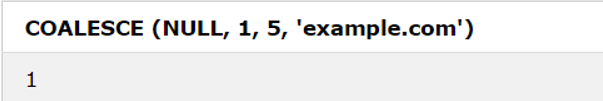
2. COALESCE () Function
Results in the first non-null value in a list.
Syntax:
COALESCE (val1, val2, ...., val_n)SQL Statement:
SELECT COALESCE (NULL, 1, 5, 'example.com');Output:
3. CASE Function
Checks all the conditions, and if the first condition is met, returns a value and will not read further. If no conditions are fulfilled, then the value will be returned in the ELSE clause. But again, it will return NULL if no ELSE portion and no conditional expressions are true.
Syntax:
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
WHEN conditionN THEN resultN
ELSE result
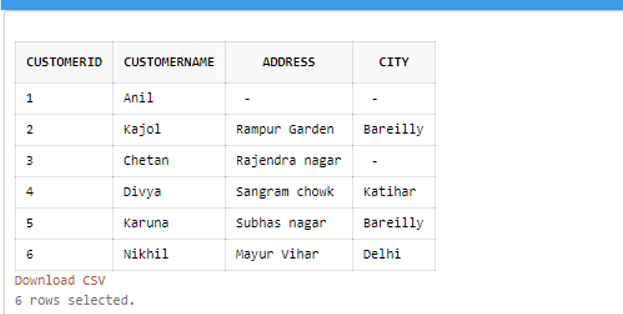
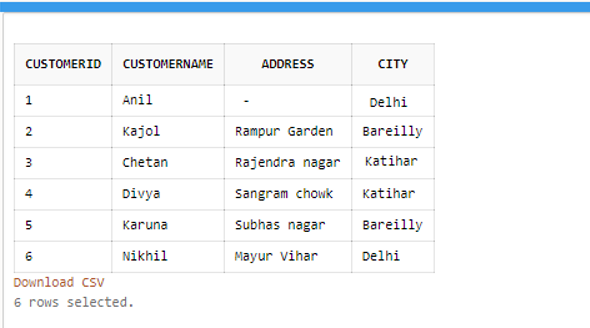
END;Suppose a table Customer:
SQL Statement:
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerName, Address FROM Customers
ORDER BY (CASE
WHEN Address IS NULL THEN City
ELSE Address
END);Output:
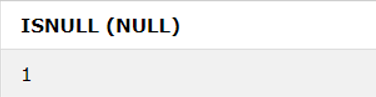
4. ISNULL () Function
Results 1 if the expression is NULL; otherwise, returns 0.
Syntax:
SELECT ISNULL (expr)SQL Statement:
SELECT ISNULL (NULL);Output:
SQL Statement:
SELECT ISNULL ("Hello!");Output:
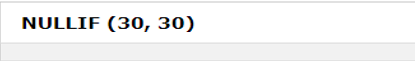
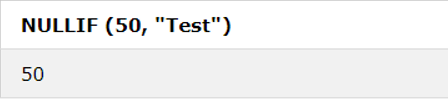
5. NULLIF () Function
If two expressions are equal on the comparison, then it returns NULL. Otherwise, if not, then the first expression is the result.
Syntax:
SELECT NULLIF (expr1, expr2)SQL Statement:
SELECT NULLIF (30, 30);Output:
SQL Statement:
SELECT NULLIF (50, "Test");Output:
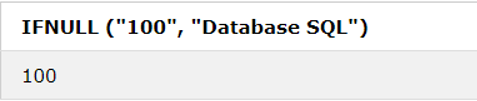
6. IFNULL () Function
A particular value is returned if the expression is NULL; if NOT NULL, it returns the expression. Syntax:
SELECT IFNULL (expr, alt_value)SQL Statement:
SELECT IFNULL (NULL, "Learning SQL");Output:
SQL Statement:
SELECT IFNULL ("100", "Database SQL");Output:
7. GREATEST
It results in the biggest value from a list of two or multiple terms. If any conditional expression in the list is NULL, it returns NULL.
Syntax:
SELECT GREATEST (expr1, expr2 [...])SQL Statement:
SELECT GREATEST(10, 35, 88, 55);Output:
8. IN
Check whether a value is inside a set of given or listed values. We can use it with CHECK, WHERE, and creation of views.
Syntax:
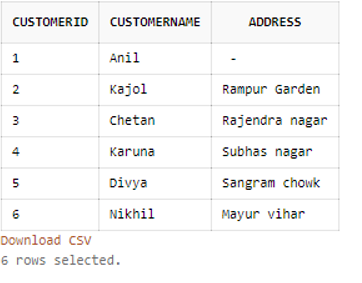
WHERE column IN (y1, y2, y3 [...])SQL Statement:
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE city IN ('Bareilly', 'Katihar',’Delhi’);Output:
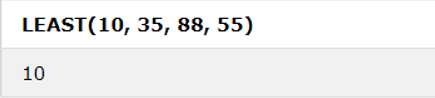
9. LEAST
It provides the least value from the list of two or multiple expressions; the result will be NULL if there is a NULL value expression in the list.
Syntax:
SELECT LEAST (expr1, expr2 [, ...])SQL Statement:
SELECT LEAST (10, 35, 88, 55); Output:Conclusion – Condition in MySQL
If we want to create a website that displays data from a database, we need to know the following:
- An RDBMS database platform such as MS Access, SQL Server, MySQL.
- PHP, ASP, Python, Java, Node.js, JavaScript-like server-side scripting languages.
- Query language SQL to access the records from the database we want to show on the webpage.
- Knowledge of HTML and CSS to elegance the page.
Generally, IFandCASE is the standard conditional statement used in MYSQL. These conditional operators have reduced using multiple OR conditions for SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE SQL statements. So, conditional operators in MYSQL are probably helpful for filtering the data and providing exact results based on certain conditions so that it saves our time and effort in fetching information from the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Condition in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.