Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction to CentOS Add User to Group
The following article provides an outline for CentOS Add User to Group. In the Linux environment, we are having multiple applications and jobs running parallel. The CentOS operating system is supporting multiple user sessions also. Every user is having their own directory to manage their own files. But if they want to access a different file or directory, then it will be a problem. To overcome it, we can change the file or directory permission. But it is suitable for some user levels; if we have multiple users and we need to manage them individually, it will be a more complex task. To avoid it, we can add multiple users in a single group. Then, rather than managing the individual user, we only need to manage it as per the specific group level.
Syntax of CentOS Add User to Group
Given below is the syntax mentioned:
usermod [ OPTION ] [ GROUP NAME ] [ USER NAME ]
- usermod: We can use the “usermod” keyword in the syntax or command. It will accept arguments like different options, group name, user name, etc. Furthermore, the usermod will add the user (as username) to the specified group name as per the provided input. Thus, the usermod command will help to manage the user administration in the CentOS ecosystem.
- OPTION: As per the requirement, we can provide the different flags as the option that is compatible with the “usermod” command.
- GROUP NAME: We need to use the group name in the usermod command as per the requirement or need.
- USER NAME: As per the requirement or need, we need to use the user name in the usermod command.
How does CentOS Add User to Group Works?
The CentOS operating system supports multiple user platforms. In other words, we can say that it will support multiple user access and allow the run or deployment the multiple jobs or applications. But to manage the individual using it is not possible in the big infrastructures. To evade such conditions, we are using the grouping concepts. We can choose any subject like the project, department, location, etc. Accordingly to the subject value, we can group the necessary users into a specific group. Here, rather than managing the individual user, we can directly manage the group. If we do any changes in the group, it will automatically apply to those available in the necessary group.
Here, we are using the “usermod” command to add the user to the group. The usermod command will take the compatible options, group name, user name and update the user group.
Below is the list of options that are compatible with the usermod command.
Here, we are using the “usermod” command to add the user to the group. The usermod command will take the compatible options, group name, user name and update the user group.
Below is the list of options that are compatible with the usermod command.
1. -p, –password PASSWORD: If we use this option, then the password will be in an encrypted format. It will be returned the encrypted in terms of crypt(3). Note, we are not recommended to use this option because the password or the encrypted password (that we have entered on the shell window) will be visible by users listing the processes. Hence we are not using this option. While setup the password, please take that the password will suffice the system’s password policy as well.
2. -o, –non-unique: When will we use this option with the -u option then this option will help to allow the change of the user ID to a non-unique value
3. -R, –root CHROOT_DIR: This option will help to apply the modification in the CHROOT_DIR directory. It will use the configuration files from the CHROOT_DIR directory.
4. -P, –prefix PREFIX_DIR: This option will help to apply changes in the PREFIX_DIR directory. It will use the configuration files from the PREFIX_DIR directory. This option will not use the chroot directory. It will be intended for preparing a cross-compilation target. But here, there are some limitations also like the NIS, and the LDAP users or groups are not verified. Here, we are using the PAM authentication for the host files.
5. -s, –shell SHELL: It will help for the user’s new login shell. Initially, the setting will be field blank because it will cause the system to select the default login shell window.
6. -u, –uid UID: It will help to get the new numerical value of the user’s ID.
Examples of CentOS Add User to Group
Given below are the examples of CentOS Add User to Group:
Example #1
CentOS add user to group: Add the new user to group.
In the CentOS environment, we can add the new user to the existing group.
Code:
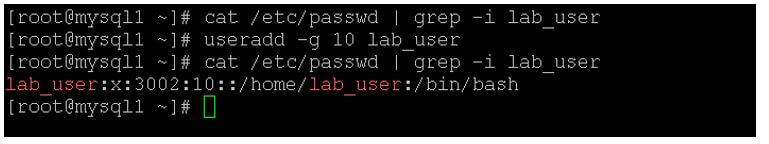
useradd -g 10 lab_user
Explanation:
- As per the above command, we are adding the new user, i.e. the “lab_user” in the group 10 id. We can fetch the group id from the “cat /etc/group | grep -i ‘Group Name”.
Output:
Example #2
CentOS add user to group: Change the primary group.
In the CentOS environment, we have the functionality to change the primary group of the user.
Code:
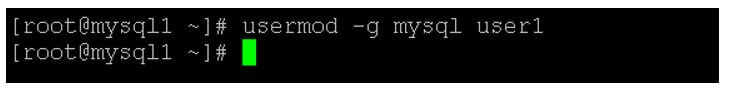
usermod -g mysql user1
Explanation:
- As per the above command, we are changing the user’s primary group from the user1 group to the new primary group, i.e. the MySQL group. In the usermod, we are using the “-g” option.
Output:
Example #3
CentOS add user to group: Change the secondary group.
With the help of the usermod command, we can also change the secondary group of the user.
Code:
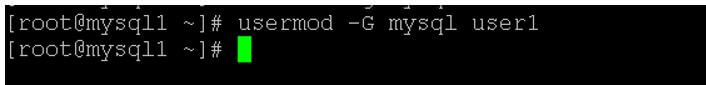
usermod -G mysql user1
Explanation:
- As per the above command, we are changing the user’s secondary group from the user1 group to the new secondary group, i.e. the MySQL group. In the usermod, we are using the “-G” option.
Output:
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of the “CentOS add user to group” with the proper explanation and command with different outputs. There are different ways to archive that, like when we will create the new user at the same time; we can add the new user into the group; otherwise, we can modify the user config also.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to CentOS Add User to Group. Here we discuss the introduction, how CentOS add user to group works? and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –