Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to CentOS Change Hostname
As we know, the Linux operating system supports multiple users to their eco-system. When are we deploying the CentOS operating system without configuring the hostname? Then the instance name will consider as local host. The scope of the communication is restricting to their instance only, i.e. if you want to communicate with the external world, then it will be more difficult. To avoid this condition, we need to change the hostname entry. There are multiple ways to do changes in the hostname.
Note: We need to follow the standard process while defining the hostname. Make sure that you should have a unique name / unique hostname in the network.
Syntax:
hostname [-a|--alias] [-d|--domain] [-f|--fqdn|--long] [-A|--all-fqdns] [-i|--ip-address] [-I|--all-ip-addresses] [-s|--short] [-y|--yp|--nis]
vi /etc/hosts
1) hostname: We can use the hostname keyword in the syntax or command. It will accept arguments like different options. We are using the different options in it like an alias, domain name, address, etc. The hostname command will help to get the relevant output in the CentOS environment.
2) vi/etc/hosts: This is an alternative option to edit the hostname. We need to edit the hostname in this file. We need to follow the specific pattern in it. First, we need to add the IP address of the machine. After that, the complete hostname is then the short hostname (without domain).
3) option: We can provide the different flags as the option that is compatible with the hostname command.
How does CentOS change hostname Command Works?
In the working environment, we are having multiple servers, applications, etc. It is very difficult to keep the system name or the IP address of every machine. To overcome this condition, we need to add or set up the hostname to the machine or instance. When any request may come in terms of the hostname, then the host’s file will check (path /etc/hosts). In this file, we have maintained the IP address, FQDN, short hostname. As per the hostname, it will map with the associated IP address.
Below are the list of rules that can be considered while defining the hostname in the system
- The hostnames should contain the letters, i.e. from a to z.
- It will also consider as digits also, i.e. from 0 to 9.
- In a special character, the hostnames will only consider the hyphen character ( – )
- In a special character, the hostnames will only consider the hyphen character ( . )
- The hostname will consider the combination of all three rules, but it should be start and end with a letter of the number.
- The hostname letters should be case insensitive.
- The length of the hostname is from 2 characters long to 63 characters.
- The hostname having the proper nomenclature. So that we can easily identify the host.
Below are the lists of options that are compatible with the hostname.
- -a, –alias: It will help to print the alias name of the host (if used). This option was deprecated, and in some operating systems, it is not be used anymore.
- -A, –all-fqdns: It will help to display all the FQDN’s associated with the machine.
- -d, –domain: It will print the name of the DNS domain.
- -F, –file filename: It will read the hostname from the specified file.
- -i, –ip-address: It will help to print the network address of the hostname. Suppose the hostname will be resolved, then only this option will works.
- -I, –all-ip-addresses: It will print all the network addresses of the host.
- -s, –short: It will print the short hostname. The hostname will print at the initial stage of the dot.
- -V, –version: It will help to print the version information on the standard output, and it will exit successfully.
- -y, –yp, –nis: It will print the NIS domain name. If it was set, then only it will display as per this option. Otherwise, it will not display.
- -h, –help: It will print the helpful information and exit automatically.
Examples
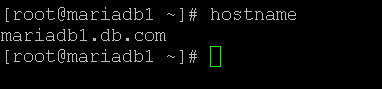
- CentOS hostname: Get the System Hostname
In the CentOS environment, it is a very simple way to find the hostname.
Command :
hostname
Explanation :
As per the below command, we are able to get the system hostname, i.e. the “mariadb1.db.com”. It will print the complete hostname with a domain name also like “db.com”.
Output :
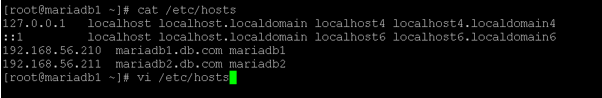
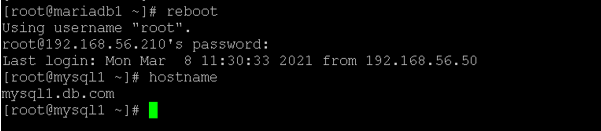
- CentOS hostname: Change the hostname
In the CentOS environment, we are able to change the hostname of the machine.
Command:
vi /etc/hosts
Explanation :
As per the above “vi” editor, we are able to edit the “/etc/hosts” file. Once we have rebooted the machine. The new hostname entry was enabled.
Output :
Screenshot 1 (a)
Screenshot 1 (b)
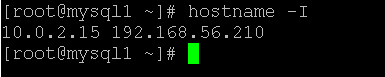
- CentOS hostname: Get Associated IP address
In the hostname command, we are able to get the number of IP address associated with the machine.
Command :
hostname -I
Explanation :
As per the above command, we are using the “I” option with the hostname. It will print all the IP address associated with the machine, i.e. the two IP addresses we have seen on the output “10.0.2.15 192.168.56.210”.
Output :
- CentOS hostname: Get the Domain Name
In the CentOS environment, we are able to list out the machine domain name.
Command :
hostname -d
Explanation :
As per the above command, we are list out the domain name associated with the machine. The “db.com” domain is associated with it.
Output:
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of the “CentOS change hostname” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. For the proper communication of all the instances in the network, it is good to set the hostname to every instance. It will help to trace out the machine or the instances through their hostname. Here, no need to remember the machine IP addresses.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to CentOS Change Hostname. Here we discuss Introduction, How CentOS change hostname Command Works? examples with commands, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –