Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to C# nameof
To avoid the hardcoded string in the code, we make use of an operator called nameof operator in C# which accepts the elements of the code names and returns the same element’s string literal and a class name, all the members of the class like variables, methods, constants can be passed as parameters to the nameof operator and a string literal is returned and this string literal returned from using nameof operator is a special kind of string literal because the given name is checked by the compiler to see if something exists by that name and if it is referred by the visual studio.
The syntax of the nameof operator in C# is as follows:
nameof(Expression)Working of nameof operator in C#
- The nameof operator in C# is often overlooked but it is one of the very useful operators in C#.
- It is an operator without which we can perform coding but to point out certain errors during the compile-time, the nameof operator is very essential.
- Names of different code artifacts are returned by the nameof operator in C#.
- Consider the below program to demonstrate the use of nameof operator in C#:
Code:
using System;
//a namespace called name is defined
namespace Name
{
//a class called check is defined
class Check
{
//main method is called
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//nameof operator is used
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Name));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Check));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Check.Main));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Main));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(args));
}
}
}Output:
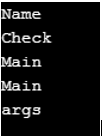
In the above program, a namespace called name is defined. Then a class called check is defined. Then the main method is called. Then the nameof operator is used to identify the name of the namespace, name of the program, the main method, and its arguments. The point of using the nameof operator here is that if any of the items of the code names are changed, then we must change all the nameof operators used in the code otherwise failure of build occurs. If we are using the nameof operator, then the compiler will point out the bugs otherwise these will be found when the program is used in production.
Examples of C# nameof
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1
Program to demonstrate the nameof operator.
Code:
using System;
//a namespace called Features is defined
namespace Features
{
//a class called Example is defined
class Example
{
//an integer array called array is defined
int[] array = new int[5];
//main method is called
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//an instance of the class Example is created
Example ex1 = new Example();
//try and catch block is defined
try
{
//the showop method is called using the instance of the Example class
ex1.showop(ex1.array);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
//the method that throws the exception is displayed
Console.WriteLine("The name of the method is: "+nameof(ex1.showop));
}
}
int showop(int[] x)
{
x[5] = 12;
return x[5];
}
}
}Output:
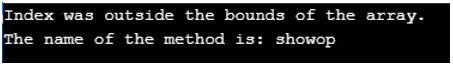
In the above program, a namespace called Features is defined. Then a class called Example is defined. Then an integer array called array is defined. Then the main method is called. Then an instance of the class Example is created. Then try and catch block is defined. Then the showop method is called using the instance of the Example class. Then the method that throws the exception is displayed. The point of using the nameof operator here is that if any of the items of the code names are changed, then we must change all the nameof operators used in the code otherwise failure of build occurs. If we are using the nameof operator, then the compiler will point out the bugs otherwise these will be found when the program is used in production.
Example #2
Program to demonstrate the use of the nameof operator.
Code:
using System;
//a class called check is defined
public class Check
{
//DateTime Function is used to find the current data and To LocalTime
private static DateTime Today = DateTime.Now;
//get and set functions are used
public string Name { get; set; }
//main method is called
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//a variable called local_Time is defined to obtain the current date and To LocalTime
var local_Time = DateTime.Now.ToLocalTime();
//nameof operator is used to obtain the local_time, args, Systme information, main method, program name.
Console.WriteLine(nameof(local_Time));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(args));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(System.IO));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Main));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Check));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Check.Today));
Console.WriteLine(nameof(Check.Name));
}
}Output:
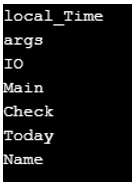
In the above program, a class called Check is defined. Then the DateTime Function is used to find the current date and LocalTime. Then get and set functions are used. Then the main method is called. Then a variable called local_Time is defined to obtain the current date and LocalTime. Then the nameof operator is used to obtain the local_time, args, System information, main method, program name. The point of using the nameof operator here is that if any of the items of the code names are changed, then we must change all the nameof operators used in the code otherwise failure of build occurs. If we are using the nameof operator, then the compiler will point out the bugs otherwise these will be found when the program is used in production.
Example #3
Program to demonstrate the nameof operator.
Code:
using System;
//a class called check is defined
class Check
{
//a method called taste is defined
static void Taste(int argu)
{
//nameof operator is used
Console.WriteLine(nameof(argu));
Console.WriteLine(argu);
//nameof operator is used on the defined variable
var plane = "Shobha";
Console.WriteLine(nameof(plane));
}
//main method is called
static void Main()
{
//the method taste is called along with passing a parameter
Taste(200);
}
}Output:
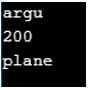
In the above program, a class called check is defined. Then a method called taste is defined within the class in which the nameof operator is used. Then a variable is defined on which the nameof operator is used again. Then the main method is called from which the defined method Taste is called along with passing the parameter. The point of using the nameof operator here is that if any of the items of the code names are changed, then we must change all the nameof operators used in the code otherwise failure of build occurs. If we are using the nameof operator, then the compiler will point out the bugs otherwise these will be found when the program is used in production.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we understand the concept of nameof operator in C# through definition, the syntax of nameof operator in C#, working of nameof operator in C# through examples, and their outputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C# nameof. Here we discuss the working of nameof operator in C# and examples for better understanding. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


