Updated April 12, 2023
Definition on C++ vector vs list
Vector in C++ is nothing but a container to store the elements in the computer memory. It is implemented as a dynamic array internally which can resize itself upon the successful insertion and deletion of elements. As it is implemented as an array so the elements are stored in the contiguous memory locations and can be traversed easily using the iterator and accessed through random access by providing the index. Default memory is pre-allocated for the array in case of working with the Vector. Insertion of an element in the Vector by default takes place at the end of an array.
List in C++ is also a container (data structure) and stores the elements in non-contiguous memory locations. List implements the doubly linked list to store the elements having the address (pointed out by the pointers) for the next and previous elements in order for the easy backward and forward traversal. For every new insertion of the element, memory is dynamically allocated and is linked with the nodes of other elements through pointers. So there is no need for the default memory allocation in the case of List.
Head to Head Comparison Between C++ vector vs list (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between C++ vector vs list.
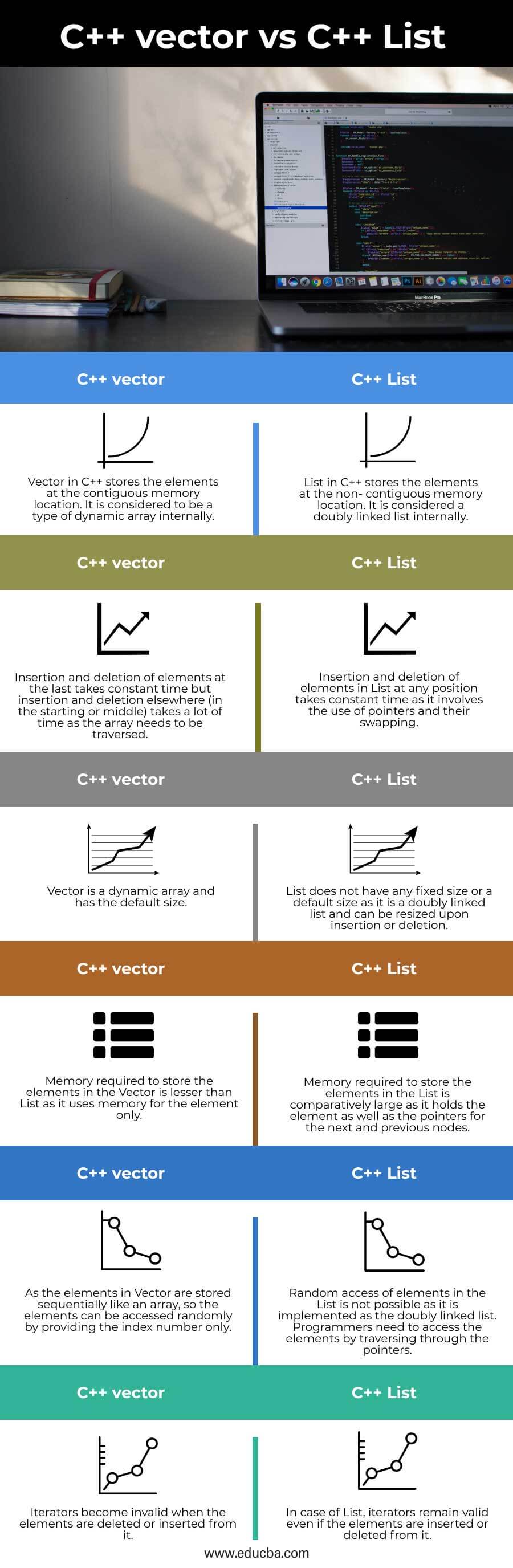
Key differences between C++ vector vs list
Below given are the key differences between the C++ Vector and List:
- As the elements in the Vector are stored in the contiguous memory locations so they are synchronized whereas the elements in the List are stored randomly and connected with each other through the links (pointers) so they are non- synchronized.
- When it comes to the insertion and deletion, List is more effective as a comparison to Vectors as insertion/ deletion at any position takes the same time and following the same procedure of swapping of pointers whereas insertion/ deletion in Vectors at the last position is simple (by default it inserts/ deletes elements at the last) but in the middle or starting requires the traversing of the whole array, inserting new element and shifting the rest of elements.
- As the memory of the Vector is pre-allocated, in case of insertion if the memory becomes insufficient, new contiguous memory needs to be allocated and the elements are shifted in it whereas there is no issue of memory insufficiency in List as the memory is allocated dynamically.
- One of the most important advantages of Vector is that it is thread-safe whereas the List in C++ is not thread-safe.
- When talking about the memory efficiency, Vector is considered to be more effective as it needs memory for the element to be stored only whereas in the case of List, (implemented as a doubly-linked list) memory required to hold the single element is very large as the memory for the pointers to hold the address of preceding and succeeding node is also required.
- As per the programmer’s perspective, dealing with the pointers is tricky and requires higher-level coding knowledge (especially for the newbies) so working on the List is comparatively more difficult than the Vectors which deals with the normal array operations.
- For a small number of elements, the vector is comparatively much faster than the List as the searching and the insertion becomes very easy and the array which is implemented in the Vector can be traversed and accessed easily.
C++ vector vs list Comparison Table
Below given is the comparison table of C++ vector vs list:
| C++ List | C++ Vector |
| List in C++ stores the elements at the non-contiguous memory location. It is considered a doubly linked list internally. | A vector in C++ stores the elements at the contiguous memory location. It is considered to be a type of dynamic array internally. |
| Insertion and deletion of elements in List at any position take constant time as it involves the use of pointers and their swapping. | Insertion and deletion of elements at the last take constant time but insertion and deletion elsewhere (in the starting or middle) takes a lot of time as the array needs to be traversed. |
| List does not have any fixed size or a default size as it is a doubly-linked list and can be resized upon insertion or deletion. | Vector is a dynamic array and has the default size. |
| Memory required to store the elements in the List is comparatively large as it holds the element as well as the pointers for the next and previous nodes. | Memory required to store the elements in the Vector is lesser than List as it uses memory for the element only. |
| Random access of elements in the List is not possible as it is implemented as the doubly linked list. Programmers need to access the elements by traversing through the pointers. | As the elements in Vector are stored sequentially like an array, so the elements can be accessed randomly by providing the index number only. |
| In case of List, iterators remain valid even if the elements are inserted or deleted from it. | Iterators become invalid when the elements are deleted or inserted from it. |
Examples
Let us discuss examples of C++ vector vs list.
Example #1 – Vector
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 5; i <= 15; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
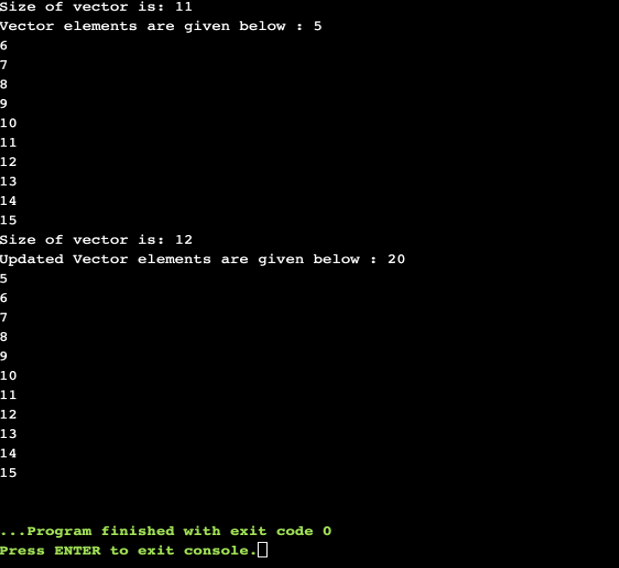
cout<< "Size of vector is: " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "Vector elements are given below : ";
for (auto i = vec.begin(); i != vec.end(); i++)
cout << *i << endl;
vec.insert(vec.begin(), 20);
cout<< "Size of vector is: " << vec.size() << endl;
cout << "Updated Vector elements are given below : ";
for (auto i = vec.begin(); i != vec.end(); i++)
cout << *i << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2 – List
Code:
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
//function to display the elements of list using iterator 'itr'
void display(list <int> x)
{
list <int> :: iterator itr;
for(itr = x.begin(); itr != x.end(); itr++)
cout << *itr << endl;
}
int main()
{
list <int> list1, list2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
list1.push_back(i * 10);
list2.push_front(i + 4);
}
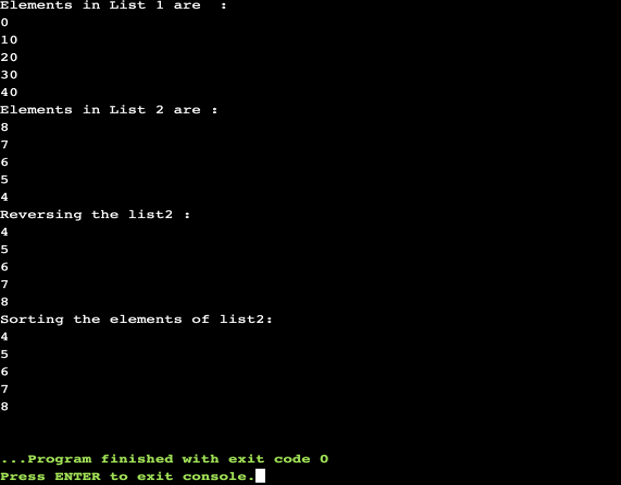
cout << "Elements in List 1 are: "<< endl;
display(list1);
cout << "Elements in List 2 are : " << endl;
display(list2);
cout << "Reversing the list2 : "<< endl;
list2.reverse();
display(list2);
cout << "Sorting the elements of list2:"<< endl;
list2.sort();
display(list2);
return 0;Output:
Conclusion
Above description clearly explains what is vector and List in C++ and the major differences between the two. Both are the containers in the C++ used widely to store the elements sequentially. Though both perform the same task having both advantages and disadvantages at a certain level their implementations are different. It depends on the choice of programmer to implement any one of them according to the specific requirements.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to the top differences between C++ vector vs list. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles –


