Updated July 17, 2023
Definition of Box Spread
A box spread is a concept from options trading format, wherein a combination of positions enters in such a way that it entails buying a bull (long) call spread and hedging against a matching bear (short) put spread. It requires a certain amount of payoff to create a neutral interest rate position in the market.
Explanation
This is an arbitrage strategy in that traders enter by buying a call spread and a put spread. In such an arrangement, the difference in both these spreads will be the net payoff for the box spread.
It needs to be highlighted that every trade or transaction entails a commission. Similarly, even in this trading, there will be a commission charge, and it becomes of utmost importance to consider the same while arriving at a profit when entering into box spreads.
How Does It Work?
To explain the whole concept, it needs to understand that this arbitrage strategy involves buying an In The Money (ITM) call and putting and simultaneously selling an Out The Money (OTM) call and put.
With this strategy, the trader aims to achieve a risk-free profit, provided the commissions on buying and selling the option contracts are lesser than the profit derived.
Example of Box Spread
Let’s take an example to understand the concept a little better.
Suppose Amazon Inc. stocks are currently trading at a price of $100. Further, consider that each leg of the box is for 100 stocks. Based on the below given box spread strategy, find out the estimated profitability of the box spread.
- Buy ITM call of 99 @ 400 per option contract
- Sell OTM call of 105 @ 90 per option contract
- Buy ITM put of 105 @ 200 per option contract
- SellOTM put of 99 @ 80 per option contract
First, let us find out the cost incurred in this box spread. Total cost before any commission will be: $400 – $90 + $200 – $80 = $430. The strike prices spread will be $105 – $99 = $6. Therefore per contract, the spread will be $6*100 = $600.
Based on the above calculation, we can see that the box spread gives us a profit of $170 (before commissions). Assuming commissions to be $10 per contract, our net profit will be $130.
| Strike Price | Call | Put | Spread | Strike Price Spread |
| 99 | 400 | 80 | 320 | 9,900 |
| 105 | 200 | 90 | 110 | 10,500 |
| Net Spread | 430 | 600 | ||
| Commission @ $10 per contract | 40 | |||
| Net Profit | 130 |
Box Spreads in Futures Trading
Futures trading is a contract or agreement to buy or sell a stock or commodity or an underlying asset at a future date at a predetermined price. Box spread can be equally applied to the future as well. However, it is said that in the case of futures trading, prices don’t really to a significant extent. Futures mostly have a range and move in that range. Accordingly, the strategy needs to be molded for futures trading.
Since options are more volatile, you see that many traders generally apply a box spread strategy in options trading compared to futures trading.
Risk of Box Spread
On the face of it, box spread looks risk free. Here’s the catch. It is not risk free. Certain concerns attached to the box spread strategy are given below.
- Box spread strategies entail entering into four positions, meaning you end up paying commissions on all four contracts you need to enter into. Furthermore, you need to ensure that the profits you earn at least cover the commission and charges you pay before you can call in a profit.
- If you go for short option positions, remember there is always a risk of early assignment. In a box spread, you have two short positions. Thus, the risk of early assignment and possible additional charges from your broker.
- Knowledge plays a very important role in planning a box spread strategy. Until and unless you are a seasoned and well-versed trader, be prepared to handle many difficulties in handling such spreads.
- Time and timing concerns. The arbitraging opportunities last for hardly a few seconds, literally, and maybe a few minutes. You need to be quick to plan a spread and execute it well to profit from it.
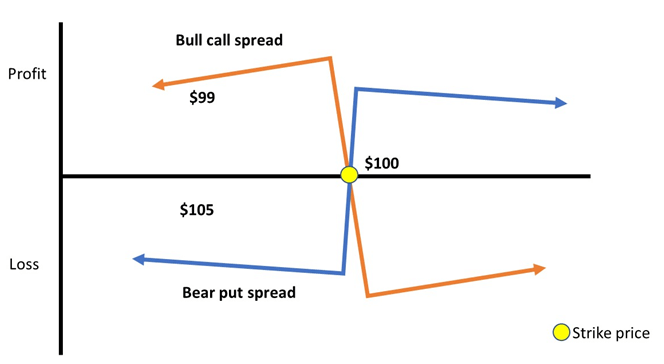
Box Spread Graph
Continuing the above example, we will show you the box spread in a graph format for a visual understanding.
We can see that the yellow circle shows the strike of $100. As the strike price moves, the values of call and put options will keep changing, and accordingly, the profit will change.
Considering that the trader will buy the call and put option, any upward movement in the strike price will entail a positive movement in the call option. In contrast, any downward movement in the strike price will entail a positive movement in the put option. Thus, this strategy will enable the trader to arbitrage and eventually earn some profit out of the trade.
Advantages
Certain benefits are achieved with the use of box spread as listed below:
- Risk-free profit
- Expiry value is better than spread value
- The direction in which the stock price moves doesn’t affect the strategy
- The strategy is neutral from a delta perspective
- The chances of incurring loss are very minimal
Disadvantages
Below are some of the disadvantages :
- Minimal profits earned
- Huge amounts go into commissions
- Experience in markets and its knowledge required
- Buying options requires maintaining margin money
- A huge amount of money is blocked from holding the positions
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Box Spread. Here we also discuss the definition and how box spread works. Along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –