Updated July 20, 2023
Definition of Dividend Growth Rate
The dividend growth rate is defined as the rate of growth of a company’s dividend over a period of time which is generally expressed in a percentage form. It is generally calculated on a yearly basis but is required the calculation can also be done on a monthly or quarterly basis too.
Explanation
The dividend growth rate of a company is defined as the rate in which the dividend issued by the company is growing which is typically expressed in a percentage form calculated on an annual basis but at times may be calculated on a monthly or quarterly basis too. This is a very important number because it provides helps to determine the profitability of the company on a long-term basis. As it is understood that as dividends are given from the source of retained earnings of the company, the dividend growth analysis over a period of time, can give us significant information about both the company’s profitability and sustainability. It also acts as an important factor in security pricing too because it acts as one of the important variables in dividend discount modeling
Formula to Calculate Dividend Growth Rate
The formulas is as follows:
Generally we need two periods for the computation of the dividend growth rate. It can be either two year or two quarters or even two months. Generally it is preferable to take two years as most companies generally follow annual dividend policy. So here in this case let us take for example dividend issued in first year as D1 and similarly dividend issues in the next year as D2. To compute the rate we need to divide the dividend issues in second year with the dividend issued in first year and subtract the resultant by 1.
formula to use to calculate compounded growth:
Here the n determine the number of period. Dn is the final dividend and D0 is the initial dividend.
Examples of Dividend Growth Rate (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
It can be calculated either on the basis of arithmetic mean model or on the basis of compounded mean model. Here we are going to demonstrate the same in both the ways, the practice files are also available in excel format.
Example #1 – Arithmetic Mean Model
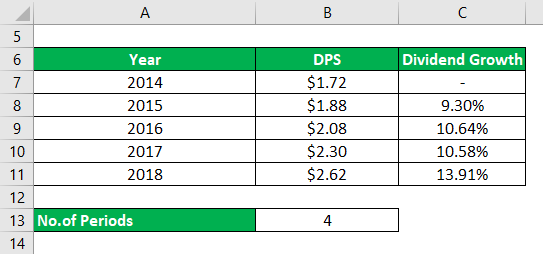
Let us take an example of an IT sector company to demonstrate the computation of dividend growth rate using arithmetic mean model. In the year 2014 the company distributed $1.72 as dividend and accordingly there has been a steady growth in its dividend to $2.62 in 2018. Now if we want to calculate the growth rate between 2014- 2018 we need to find each individual year growth rate. So growth rate for each year is computed by taking into consideration two consecutive years. In 2015 growth rate was 9.30%, 2016 had growth rate of 10.64%, 2017 had 10.58% and finally 2018 had 13.91%. Hence to calculate the annualized growth rate we need to apply the arithmetic mean of the growth rate.
Solution:
Thus, total number of period = 2018 – 2014 = 4
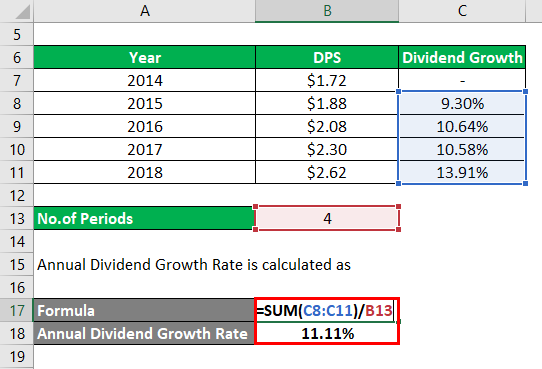
Annual Dividend Growth Rate is calculated as
- Annual Dividend Growth Rate = (9.30 + 10.64 + 10.58 + 13.91)/4
= 11.11%
This means the dividend is growing 11.11% on an annualized basis for the past 4 years.
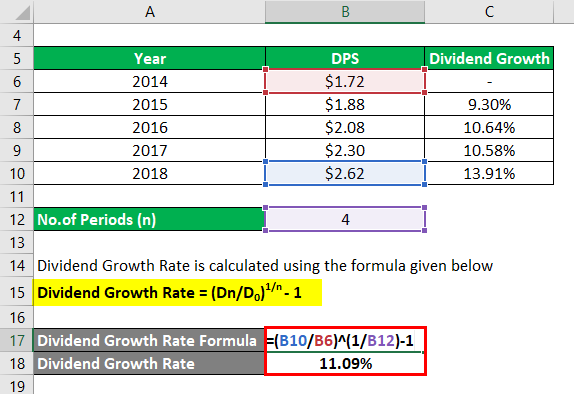
Example #2 – Compounded Mean Model
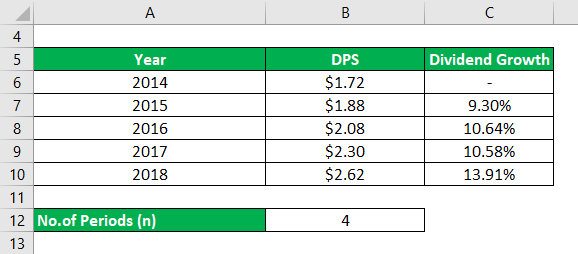
Let us take an example of the same IT sector company to demonstrate the computation of dividend growth rate using a compounded mean model. Here even if there is lot number of years we are only concerned about the final year and initial year. Thus we see 2018 had a growth rate of 13.91% and 2015 had a growth rate of 9.30%. These are the two rates we will apply to our computation. The formula to compute the same used is (D Final Year/D Initial Year) ^ (1/N)-1.
Solution:
Here N is the number of period which is 4 years.
Dividend Growth Rate is calculated using the formula given below
Dividend Growth Rate = (Dn/D0)1/n – 1
- Dividend Growth Rate = (13.91/9.30) ^ (1/4) – 1
= 11.09%
Importance
Dividend growth rate is a very important number that every investor look for. This determines the long term profitability and sustainability of the company. Investors are always interested at stocks that offer more dividends. More than the quantity or the amount of dividend it is the growth rate which one should look for. The growth rate signifies the rate at which the dividend has been growing or sinking. Thus this is a very important metric to look for. Stocks giving growing dividends are generally considered to be healthy and also resemble the potential to even grow further in the near future Thus investors specifically look for such stocks based on the growth rate. A shrinking dividend associated with a stock can, however, point to be a negative signal or a warning signal and forces an investor to think twice before investing and the investor also needs to do a fundamental analysis of the stock before investing.
It has been generally observed based on the trend that dividend growth stocks have seem to outperform the stock market over a period of time. Companies having a steady growth rate is considered to be lesser volatile and have been outperforming their estimates. Thus, it typically helps us to look out for such stocks in the market. Dividend growth stocks because they are less volatile and thus earn a good return no matter what the stock market is performing. Thus, the rate is an important factor to scrounge for these stocks. Investors use this to do research based on a specific time frame and pick stock accordingly.
It comes very useful in the dividend discount model too when it comes to security pricing analysis. A history of dividend growth signals future profitability and long term growth of the stock. When dividend growth is calculated the best part is the user can use any interval of time to arrive at the number. It can be between two consecutive years or a period of years which may not be on a consecutive basis. The best part of the dividend growth rate is that it can be calculated using several methods. It can be calculated either on a least square method or by generally taking the annualized number over a specific period of time. It solely depends on the investor which method one needs to adhere to and for what time frame he/she is looking into the analysis. The rate can also be a trigger if we see it other way round about the company’s retained earnings. If a company has a higher rate of dividend growth it generally tends to mean that the company is more into the distribution of profit rather than investing in other avenues or expansion and that it has lower retained earnings. Thus a thorough analysis of the number is very important for the investor to dig into the policies of the company and understand better the financials.
Conclusion
Thus is a very important metric for every investor. It signifies how the money invested can reap benefits in the form of dividends which many investors are crucially looking at. Every investor is in look out for value additive stocks and dividend can be one of the attribute for such stocks. Thus, the rate then comes handy when picking up such value investment stocks from the market and compare which one is the best among them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Dividend Growth Rate. Here we discuss how to calculate dividend growth rate along with practical examples. we also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –