Differences Between Java Vector vs ArrayList
Java Vector and ArrayList both hold object references. If the array is fully occupied and if we want to add a new object after fully occupied, now in both the cases, size will increase, but the main difference comes in size in ArrayList if the size is not specified, it can increase by half of the current array, but a vector can double the size of the increment value is not specified. We can create a vector with the initial size or with the default initial size.
We will see the code for default initial size or initial size:
- To create a Vector with default initial size
Vector v = new Vector(); - To Create a Vector with an initial size
Vector v = new Vector(300);
Common Methods
Below are the common vector methods::
- add(o)
- clear()
- firstElement(i)
- listIterator()
- size()
- toArray(Object[])
Java ArrayList is one of the simplest and most used data structures in the Java API library’s implementation classes. The main important thing is it uses a dynamic array for storing the elements. We should remember that while creating arrays, they are of fixed length; once these are created, we cannot do any modifications.
Below are the Constructors:
- ArrayList( ): It helps in building the empty array list.
- ArrayList(Collection c): It helps in building a list of constructive elements in a pre-specified collection.
- ArrayList(int capacity): It helps in constructing an empty list.
Below are the most commonly used methods:
- boolean add(E obj)
- void add(int index, E obj)
- E get(int index)
- boolean contains(Object obj)
- boolean isEmpty()
Java was introduced with a new collection of API in Java 2.0 to provide uniform structured classes. When a new API introduced, there will be changes in the methods. Now here we will see some of the old and new methods changed at the time of API change.
| Old Method | New Method |
| Object elementAt(int) | Object get(int) |
| void insertElementAt(Object, int) | void add(index, Object) |
| void addElement(Object) | boolean add(Object) |
| void setElementAt(int) | Object set(int, Object) |
| void removeElementAt(int) | void remove(int) |
| void removeAllElements() | void clear() |
Head to Head Comparison Between Java Vector vs ArrayList (Infographics)
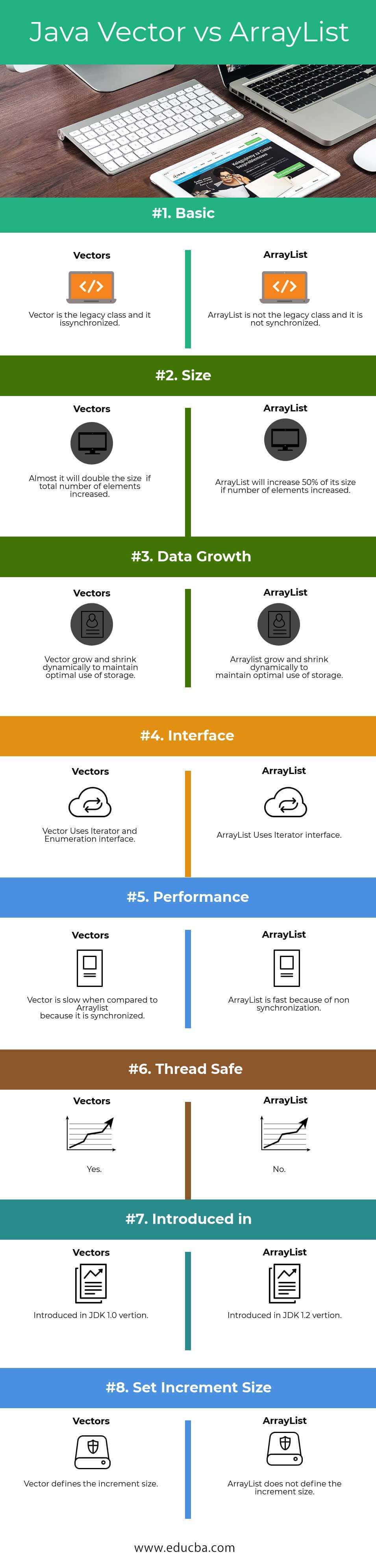
Below is the Top 8 comparison between Java Vector and ArrayList:
Key Differences Between Java Vector and ArrayList
Below are the lists of points, describe the key differences between Java Vector and ArrayList:
- ArrayList is Non-synchronized and not thread-safe, but Vector is synchronized and having one thread to call methods at a time. But when coming to safety is a single-threaded case, ArrayList is the only choice, but if we are working on multithreading, we need to prefer the Vectors. If we have any doubt or confusion in data, then we can select vector because, in vector, we can set the increment value.
- A vector can use both Enumeration and Iterator interface for traversing over elements, but ArrayList can only use the Iterator interface for traversing. In vector, If you are using the Integer wrapper, you will not be able to change the integer value. In the vector, the two most used methods have Next() and next(). ArrayLists are created with initial size because if objects are adding, it will increase the size, and objects are removing size will be decreasing automatically.
- The vector class in Java implements a dynamic array of objects. It is exactly identical to the array; it contains elements accessible using a simple integer index. However, a Vector’s size can grow or shrink to accommodate adding and removing items on an as-needed basis.
- Java Vector and ArrayList both provide a re-sizable array that means an array that can increase the space. Java provides vector class to provide dynamic size, Generic and useful predefined methods (we already saw the methods on page1). Use an array if the size is fixed; use Vector if the size may change. Both Java Vector and ArrayList are index-based and use the array internally, and both Java Vector vs ArrayList maintain the insertion order of elements. Java offers an ArrayList class to provide similar features as Vector dynamic, generic and useful predefined methods.
- Java Vector and ArrayList both classes used for dynamic usage of arrays. Class ArrayList<E> — E specifies the type of objects that an array can hold. Here created array is a variable one, and it can increase or decrease based on the object allocation. Vector:: class Vector<E> — E represents the type of object that will be stored in the array.
Java Vector and ArrayList Comparison Table
Following is the comparison table between the Java Vector and ArrayList.
| Basis of Comparison | Vectors | ArrayList |
| Basic | Vector is the legacy class, and it is synchronized | ArrayList is not the legacy class, and it is not synchronized. |
| Size | Almost it will double the size of the total number of elements increased. | ArrayList would increase by 50% of its size if the number of elements increased. |
| Data Growth | Vector grow and shrink dynamically to maintain optimal use of storage | ArrayList grow and shrink dynamically to maintain optimal use of storage |
| Interface | Vector Uses Iterator and Enumeration interface | ArrayList Uses Iterator interface |
| Performance | Vector is slow when compared to ArrayList because it is synchronized | ArrayList is fast because of non-synchronization |
| Thread Safe | Yes | No |
| Introduced in | Introduced in JDK 1.0 version | Introduced in JDK 1.2 version |
| Set Increment Size | Vector defines the increment size | ArrayList does not define the increment size |
Conclusion
Java vector vs ArrayList both is having advantages and disadvantages. Both are very successful in the market. ArrayList is the recent once if we compare it with Vector. ArrayList is preferred if you do not need synchronization. When using Vector or ArrayList, always try to initialize the largest capacity that your program will need because expanding the array is costly.
I finally conclude by saying that I always prefer to use ArrayList. Why because ArrayList performs faster and better when compared to Vector.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Vector vs ArrayList.Here we also discuss their meaning head-to-head Comparison, key differences, along with infographics and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –