Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Apache Spark Architecture
Apache Spark Architecture is an open-source framework-based component that are used to process a large amount of unstructured, semi-structured and structured data for analytics. Spark Architecture is considered as an alternative to Hadoop and map-reduce architecture for big data processing. Spark architecture associated with Resilient Distributed Datasets(RDD) and Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) for data storage and processing. Also, It has four components that are part of the architecture such as spark driver, Executors, Cluster managers, Worker Nodes. Spark uses the Dataset and data frames as the primary data storage component that helps to optimize the Spark process and the big data computation.
Apache Spark Architecture
The Architecture of Apache spark has loosely coupled components. Spark consider the master/worker process in the architecture and all the task works on the top of the Hadoop distributed file system. Apache spark makes use of Hadoop for data processing and data storage processes. They are considered to be in-memory data processing engine and makes their applications run on Hadoop clusters faster than a memory. Having in-memory processing prevents the failure of disk I/O. Spark allows the heterogeneous job to work with the same data. Spark divides its data into partitions, the size of the split partitions depends on the given data source.
Below are the two main implementations of Apache Spark Architecture:
1. Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD)
It is responsible for providing API for controlling caching and partitioning. It’s an important toolset for data computation. It helps in recomputing elements in case of failures and is considered to be immutable data and acts as an interface. Transformations and actions are the two operations done by RDD.
2. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
It forms a sequence connection from one node to another. The driver converts the program into DAG for each job. The Apache Spark Eco-system has various components like API core, Spark SQL, Streaming and real-time processing, MLIB, and Graph X. Some terminologies that to be learned here is Spark shell which helps in reading large volumes of data, Spark context -cancel, run a job, task ( a work), job( computation)
Components of Apache Spark Architecture
The Four main components of Spark are given below and it is necessary to understand them for the complete framework.
- Spark Driver
- Executors
- Cluster manager
- Worker Nodes
The following diagram shows the Architecture and Components of spark:
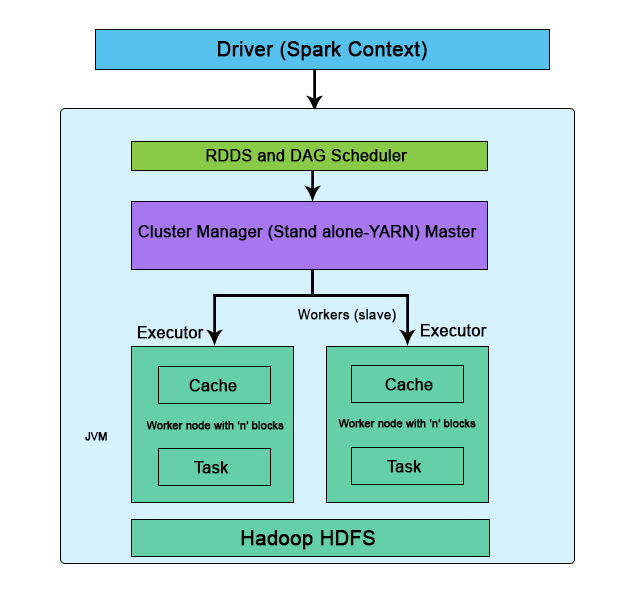
Fig: Standalone mode of Apache Spark Architecture
The execution flow begins as follows:
1. Spark Driver
The driver’s responsibility is to coordinate the tasks and the workers for management. It’s an Application JVM process and is considered a master node. A driver splits the spark into tasks and schedules to execute on executors in the clusters. In the diagram, the driver programs invoke the main application and create a spark context (acts as a gateway) collectively monitor the job working within the given cluster and connect to a Spark cluster All the functionalities and the commands are done through the spark context.
Spark context is an entry for each session. Spark driver has more components to execute jobs in the clusters. Spark clusters get connected to different types of cluster managers and simultaneously context acquires worker nodes to execute and store data. In the cluster, when we execute the process their job is subdivided into stages with gain stages into scheduled tasks.
2. Executor
It is responsible for the execution of a job and stores data in a cache. At the very initial stage, executors register with the drivers. This executor has a number of time slots to run the application concurrently. Executors perform read/ write process on external sources. The executor runs the job when it has loaded data and they are been removed in the idle mode. The executor is enabled by dynamic allocation and they are constantly included and excluded depending on the duration. During the execution of the tasks, the executors are monitored by a driver program. Executors execute users’ task in java process.
3. Cluster Manager
It helps in managing the clusters which have one master and number of slaves. There are two types of cluster managers like YARN and standalone both these are managed by Resource Manager and Node. cluster work on Stand-alone requires Spark Master and worker node as their roles. The responsibility of the cluster manager is to allocate resources and to execute the task,
4. Worker Nodes
They are the slave nodes; the main responsibility is to execute the tasks and the output of them is returned back to the spark context. They communicate with the master node about the availability of the resources. Spark context executes it and issues to the worker nodes. Each worker nodes are been assigned one spark worker for monitoring. They make the computation very simply by increasing the worker nodes (1 to n no of workers) so that all the tasks are performed parallel by dividing the job into partitions on multiple systems. The other element task is considered to be a unit of work and assigned to one executor, for each partition spark runs one task.
Conclusion
Therefore, by understanding Apache Spark Architecture, it signifies how to implement big data in an easy manner. Ultimately, we have learned their accessibility and their components roles which is very beneficial for cluster computing and big data technology. Spark computes the desired results in an easier way and is preferred in batch processing.
Spark’s distinctive features like datasets and data frames help to optimize the users’ code. An important feature like SQL engine promotes execution speed and makes this software versatile. Therefore, we have seen spark applications run locally or distributed in a cluster. Apache Spark is considered to be a great complement in a wide range of industries like big data. To sum up, spark helps in resolving high computational tasks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Apache Spark Architecture. Here we discuss the Introduction to Apache Spark Architecture along with the Components and the block diagram of Apache Spark. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–

