Updated March 28, 2023
Difference Between Solr vs Elasticsearch
Solr vs Elasticsearch both are an open-source search engine, Solr(pronounced as solar), built on Apache Lucene Library, which is in Java. It is developed in Java. It consists of HTTP/XML web API interfaces. Solr queries are in the form of JSON documents. Elasticsearch is highly scalable analytics and search engine. It is developed in Java and is basically a wrapper on Apache Lucene Library. It consists of an HTTP web API interface. It has no schema with JSON documents where all the data is stored.
Head to Head Comparison between Solr vs Elasticsearch (Infographics)
Below are the top 9 comparisons between Solr vs Elasticsearch:
Key differences between Solr vs Elasticsearch
Let us discuss some key differences between Solr vs Elasticsearch in the following points:
- Solr has been in the industry since 2004, and it is safe to say that it is a mature product, and it has a huge community. Elasticsearch is relatively new to the industry. Solr is truly open source in the sense that anyone can contribute to the product, whereas Elastic is slightly restricted. All the contributions made makes it to the product only when the development team of elasticsearch approves it.
- Elasticsearch talks in terms of JSON. Solr also supports JSON, but this feature was added recently. When Solr was built initially, its main language was XML.
- Solr’s a focus is mainly on text search and related operations. Elasticsearch is a step ahead in this by analyzing logs and visualization along with basic text queries.
- Solr has a special feature, facet search. Faceting is a process that enables users to narrow down the query results. It can be considered as guided navigation.
- Search engines, by default, work with huge data sets. To improve efficiency, it is recommended that they are modular and scalable. Elasticsearch is scalable and is very flexible when it comes to data clusters. Solr itself is not very scalable, but SolrCloud, managed by a zookeeper, does the job.
- Solr allows the addition of shards on the go based on the requirements of the applications. Elastic search actually discourages this practice. It has a fixed number of primary shards that cannot be altered. This is done to increase the query efficiency as the number of shards/indexes increase, latency in fetching the results increase.
- Elastic search exposes multiple metrics to the users for monitoring, visualization, etc. Solr also exposes metrics and APIs but not as extensive as Elasticsearch.
- Caching plays a major role in search engines for faster responses. Elastic search caches at a segment level, which mean changes in a segment don’t affect others. Solr caches at a global level. Whenever there is a change, the whole shard instance becomes invalid, and indexing with respect to new data should be done again. Each has its own advantages based on the application.
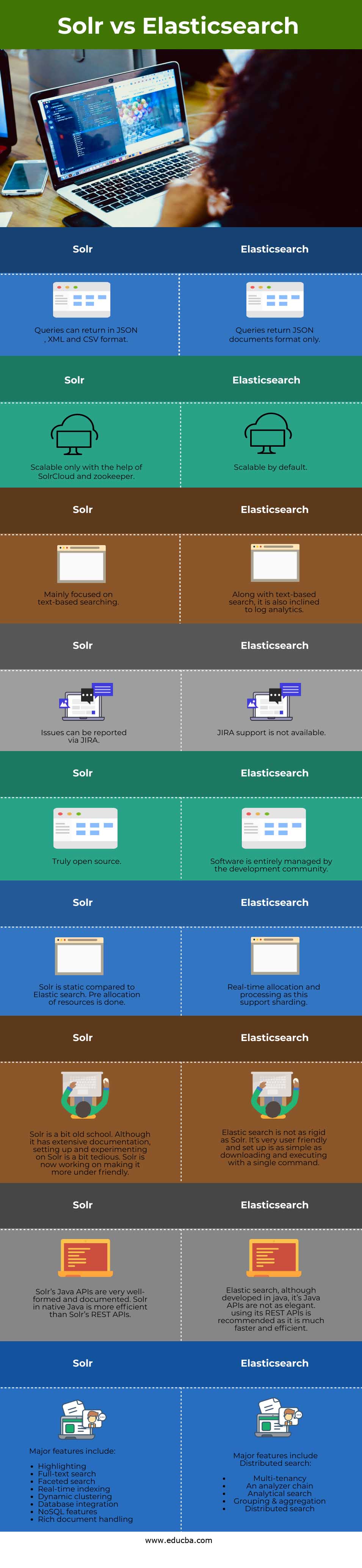
Comparison Table of Solr vs Elasticsearch
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Solr vs Elasticsearch:
| Solr | Elasticsearch |
| Queries can return in JSON , XML and CSV format. | Queries return JSON documents format only. |
| Scalable only with the help of SolrCloud and zookeeper. | Scalable by default. |
| Mainly focused on text-based searching. | Along with text-based search, it is also inclined to log analytics. |
| Issues can be reported via JIRA. | JIRA support is not available. |
| Truly open source. | The development community entirely manages software. |
| Solr is static compared to Elastic search. Pre allocation of resources is done. | Real-time allocation and processing as this support sharding. |
| Solr is a bit old school. Although it has extensive documentation, setting up and experimenting on Solr is a bit tedious. Solr is now working on making it more under friendly. | Elastic search is not as rigid as Solr. It’s very user friendly, and the set up is as simple as downloading and executing with a single command. |
| Solr’s Java APIs are very well-formed and documented. Solr in native Java is more efficient than Solr’s REST APIs. | Elastic search, although developed in java, it’s Java APIs are not as elegant. Using its REST APIs is recommended as it is much faster and efficient. |
Major features include:
|
Major features include Distributed search:
|
Studies on the performance of both the search engines are ongoing. The results from the existing studies are not concrete. That being said, some studies have shown that both engines are almost similar when it comes to performance.
Conclusion
Overall, Solr and Elasticsearch seem similar in working but are different in a few areas like scalability, functionalities, ease of deployment, etc. Choosing either one is entirely dependent on the organizations and their applications. A detailed description of the pros and cons is given above to get a brief understanding of both entities.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Solr vs Elasticsearch. Here we discuss the Solr vs Elasticsearch key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –