Updated July 31, 2023
Difference Between Annuity vs IRA
An annuity is an option in which periodic withdrawals are made. This is an agreement made between the investor and the third party where the investor pays the entire amount to the company and receives an installment amount once the retirement age has reached. Thus, the annuity provides a steady income after the retirement age. In an IRA, investors invest some amount of money for retirement savings in an account by the inventor’s employer. They are similar to annuities in the way that money is allocated to different asset classes. This account contains a sum of money kept aside from the taxable accounts.
What is an Annuity, and How Does it Work?
Annuities are insurance products designed to provide investors with an income stream. There are annuities that also provide death benefits and provide the beneficiaries with the pre-decided amount in case of sudden death before the end of the tenure. Annuities can be brought with the money held in the taxable account. Annuities can be jointly owned.
What is IRA, and How Does it Work?
Money can be on a pre-tax basis, and there will be no taxes until any withdrawal. After that, a 10% tax is applied as a penalty on withdrawals. However, there are exceptions to these cases, like buying a house for the first time, and there is no penalty required. IRA is also based on income, and individuals below a certain income may not be eligible.
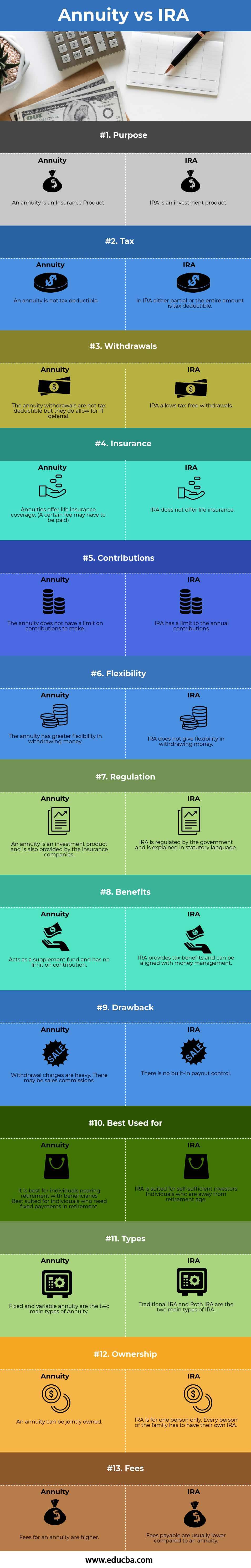
Head To Head Comparison Between Annuity vs IRA (Infographics)
Below is the top 13 difference between Annuity vs IRA:
Key Differences Between Annuity vs IRA
Annuities vs IRAs are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Difference Between Annuity vs IRAs.
- An annuity is not tax-deductible, while the IRA is either partial or the entire amount is tax-deductible.
- The annuity withdrawals are not tax-deductible, but they do allow for IT deferral, while IRA withdrawals are tax-free.
- Annuities offer life insurance coverage. (A certain fee may be necessary). IRA has a limit to annual contributions.
- It is best for individuals nearing retirement with beneficiaries. And is best for individuals who need fixed payments in retirement. IRA is good for self-sufficient investors and individuals away from retirement age.
- Fees for managing annuities are higher, while fees to manage IRAs are comparatively lower.
- The following are the main types of annuities.
Fixed Annuities
These types of annuities are not affected by changes in interest rates or market fluctuations and are, thus, the safest types of annuities. Types of fixed annuities are Immediate Annuity and Deferred Annuity. In an immediate annuity, the investor receives payments as soon as he makes the first investment. In a deferred annuity, the money is accumulates for a predetermined period before the payments begin.
Variable Annuities
As the name suggests, these annuities are variable in nature and allow investors to generate a high rate of returns by investing in equity or bonds. Income will depend on the performance of these assets. This is perfect for investors who are ready to take risks.
The following are the main types of IRAs.
1. Traditional IRA: Funds are not subject to any tax unless they are withdrawn. A 10% penalty is charged if they are withdrawn before retirement.
2. Roth IRA: In the case of Roth, IRA funds are taxable yearly. Annual contributions are important after tax. Therefore, there will be no charge during the retirement period. This option is considered to be more beneficial than the traditional IRA.
- An annuity can be jointly owned, while the IRA is for one person only. Every person in the family has to have their own IRA.
- Withdrawal charges are heavy. There may be sales commissions. There is no built-in payout control.
Annuity vs IRA Comparison Table
Let’s look at the top 13 Comparisons between Annuity vs IRA.
| The Basis of Comparison |
Annuity |
IRA |
| Purpose | An annuity is an Insurance Product. | IRA is an investment product |
| Tax | An annuity is not tax-deductible | In IRA, either partial or the entire amount is tax-deductible. |
| Withdrawals | The annuity withdrawals are not tax-deductible, but they do allow for IT deferral. | IRA allows tax-free withdrawals |
| Insurance | Annuities offer life insurance coverage. (A certain fee may be necessary) | IRA does not offer life insurance |
| Contributions | The annuity does not have a limit on contributions to make | IRA has a limit to the annual contributions |
| Flexibility | The annuity has greater flexibility in withdrawing money. | IRA does not give flexibility in withdrawing money |
| Regulation | An annuity is an investment product and is also provided by insurance companies. | IRA is regulated by the government and is explained in statutory language |
| Benefits | It acts as a supplement fund and has no limit on contribution | IRA provides tax benefits and can be in sync with money management |
| Drawback | Withdrawal charges are heavy. There may be sales commissions. | There is no built-in payout control. |
| Best Used for | It is best for individuals nearing retirement with beneficiaries.
Best suited for individuals who need fixed payments in retirement. |
IRA is best for self-sufficient investors
Individuals who are away from retirement age |
| Types | Fixed and variable annuities are the two main types of Annuities. | Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs are the two main types of IRAs. |
| Ownership | An annuity can be jointly owned. | Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs are the two main types of IRAs. |
| Fees | Annuity fees are higher. | Fees payable are usually lower than an annuity. |
Conclusion
Both Annuity vs IRA provides sound retirement plans if managed properly. The annuity has a large number of options, while IRA, as specified, has two types of options Traditional and Roth. The main difference between Annuity vs IRA schemes lies in the amount contribution limit. Contributions in IRA have limited funds, while the annuity is away from such limitations. Both Annuity vs IRA products provides the chance to increase and grow your investment on a tax-deferred basis. An important point to note is that these investments are not mutually exclusive, and an investor can invest in both these products if he wishes to. However, there is no reason why an individual should opt for both, especially if they have exhausted the tax-advantaged accounts.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Annuity vs IRA. Here, we also discuss the Annuity vs IRA key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.