Updated June 7, 2023

How Analytics.JS Works?
Analytics.JS – Every analyst should have good knowledge in two core skills to become an expert in the field of digital analytics. One statistics and the other JavaScript.
JavaScript is the most useful programming language.
All the measurements or tags are written in JavaScript. JavaScript is used to have a control over the behaviour of HTML, CSS and web browsers.
The Google analytics.js is a JavaScript library that is used to measure how the users interact with your website. This is a legacy library. If you are using Google Analytics then you should use the latest tracking library analytics.js.
How to add analytics.js to your site?
There are three ways to add JavaScript to a HTML document.
- Inline JavaScript
- Embedded JavaScript
- External JavaScript
The easiest way to start with analytics.js is to add the code to your site template. The script should be added within the </head> tag and the tracking ID should be provided in place of the string of the Google analytics which you wish to track.
Inline JavaScript
Inline JavaScript is the one added to the HTML tag
For example
<a Click="ga('send', 'blog', 'Twitter','Share',window.location.href);">….</a>‘Click’ in this example is an event handler which is used in Inline JavaScript.
Embedded JavaScript
Embedded JavaScript is added to the HTML document. It uses the <script> tag but without the ‘src’ attribute.
A simple example is given below
<html>
<head>
<script language = "javascript1">
function greet () {
alert ('hi);
}
</script>
</head>
</html>The italic font text are JavaScript code.
External JavaScript
External JavaScript is added to the HTML document using <script> tag with src attribute.
Example is
<script type="text/javascript" src="minescript.js"></script>External JavaScript is the best method to use as it has the following advantages over the other two methods.
- It does not interfere with the other codes in the page
- It is easy to maintain, understand and use
- It can speed up the loading time of the pages
Customizations can also be made to the JavaScript Tracking snippet. The code which loads analyticcs.js and starts the ga() function should not be changed.
What does the tracking snippet do?
By adding either of the above-mentioned tracking snippet you can get page views for each page your users visit. Google analytics can give you information regarding
- The time spent on each user on your site
- The time spent by each user on each page and in what order they have navigated between the pages
- What are the internal links which were clicked by the users
When a new tracker is created using analytics.js it is used to find out the following
- Geographical location of the user
- Through which operating system or browser they have visited your site
- What is their screen size and whether they have installed Java or Flash
- Their referring site
JavaScript Statements
JavaScript statement is an instruction that is executed by web browsers. Each JavaScript statement should end with a semicolon. Google analytics tracking code contains a bunch of JavaScript statements. An example is given below.
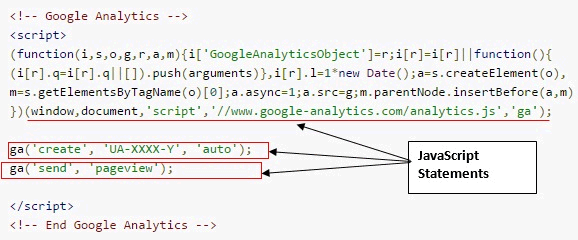
Order of execution
JavaScript statements are executed from top to bottom in the order they are written.
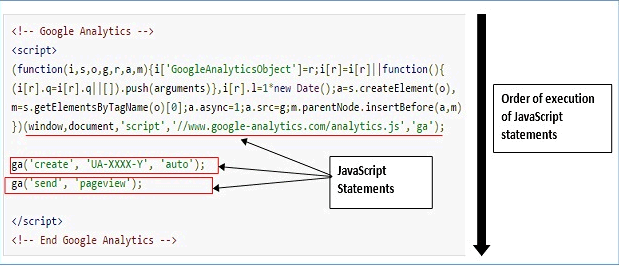
If the order is changed then the code will either behave differently or it will stop working.
JavaScript and White Spaces
JS ignores multiple white spaces. It is always recommended to add spaces around the operators to increase the readability of the code. Extra spaces if used in a string can create problems.
Comments in JavaScript
Comments are used to add a note to a JavaScript. There are 2 main types – Single line and Multiple line comment.
Single line comment starts with two forward slashes. An example is given below
ga('create' , 'UA-XXXX-Y', 'auto' ); // creates a trackerMultiple line comment starts with /* and ends with */. An example is given below
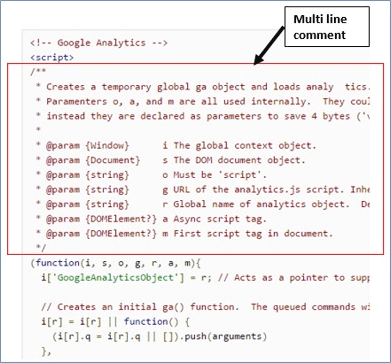
Comments are also used to stop a statement from being executed.
JavaScript Variables
Creating variable in JavaScript is known as declaring a variable. Variables are used to store values. Variables can be created in JavaScript using the keyword ‘var’. It is recommended to create variables at the beginning of a code.
var_gaq ; // create a variable and name it _gaqYou can also assign a value to the variable. To use the value of the variable you should use the variable name without including it inside the quotes. If you include it within the quotes then it is considered as a string.
Naming JavaScript variables
There are six important features of variable names in JavaScript
- They are case sensitive
var pagetracker;
var Pagetracker;
- Variable names can be alphanumeric
var alpha46;
- Spaces are not allowed in a variable name
var first name = ‘Nirmal’; // not valid
- It is recommended to use lower cases for variable names
- Special characters are not allowed in a variable name except $ and underscore
var first-name = “Nirmal”; // hyphen is not allowed
var_first name = “Peter”;// underscore is allowed
- Variable name cannot begin with a number
var 46alpha;
- Variable name cannot be a keyword name
- It is best to use underscore or camel casing to separate words in variable name
JavaScript Keywords
A keyword is a word that carries a special meaning
Following are some of the keywords used in JavaScript
- var
- function
- return
- for
- true
- false
- if
JavaScript Values
Variables are used to store values of any type of data. It can include the following type of data
- Numeric Value
- String Value
- Boolean Value
- Undefined Value
- Null value
- Array
- Object
- Array of objects
Strings in JavaScript
String is a series of characters of any length. Strings must be written within single or double quotes.
var name = 'Nirmal Sharma';A string can be any character including white spaces. Numbers are also considered as a string if it is included within quotes either single or double.
You can use back slash to use quotes inside a string that match the quotes outside the string.
JavaScript Arrays
Array is a special variable that is used to store multiple elements of either same or varied data types.
Arrays can be strings, numeric values, undefined values, a boolean value, other arrays or objects.
Array can be created using ‘new Array()’ function or through array literal notation.
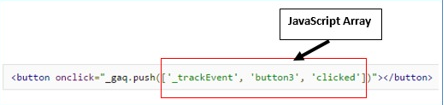
Examples are listed below
var bus = new Array();
var bus = [];Objects in JavaScript
Object is another special variable that contains properties and methods. In object, property can be a string or identifier.
Datalayer is an example of array with one or more objects. The syntax for creating object is mentioned below
ObjectName={'property10':value10, 'property11':value11, …..'propertyN':valueN};
Functions in JavaScript
Function is a set of code that is used to perform a specific task when it is executed. A function needs to be called in order to be executed. The keyword used to create a function in JavaScript is ‘function’.
The structure for creating function is as follows:
function <functionName>(parameter1, parameter2,….) {
Java Script Statement10
Java Script Statement11
.
.
Java Script StatementN
}Parameters are names listed to define a function. Arguments are the values for calling a particular function.

‘ga’ Function
‘ga’ is the Google Analytics’ in built function. It performs many tasks in Google Analytics. The first argument of ‘ga’ function is a command. It is explained in the picture below
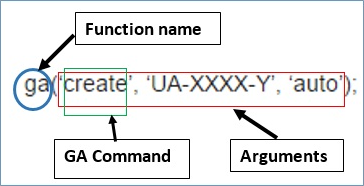
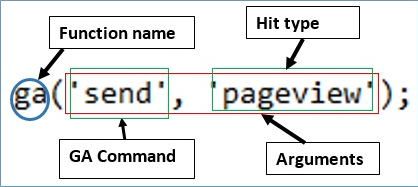
Each function has only a particular number of parameters allowed to be added.
Each function can accept only certain data type.
Important points to remember
- Use correct structure or arrangement for all the functions
- Use only the active methods or functions found
- Never add quotes unnecessarily
- Refer to the documentation
How does analytics.js works?
Here we have discussed the working of analytics.js.
The ga command queue
The ga function is also called the command queue as it does not execute the commands immediately and it adds the commands to the queue to execute it until the library is fully loaded.
In JavaScript functions are otherwise known as objects as it also contains properties. The tracking snippet defines a q property on the ga() function which acts as an empty array.
Adding commands to the queue
All the calls to the ga() function queue share a common feature. The command which acts as the first parameter is a string that helps to identify a particular analytics.js method. Any additional parameter are considered as arguments that gets through the method.
The term method here indicates either a global method like ‘create’ or an instance method like ‘send’. If the ga() command queue gets any command it automatically calls the ga() function as it will not return any error.
Command Parameters
Most of the commands and the methods in analytics.js accept parameters in a different type of formats. This makes it easy to pass commonly used fields to particular methods.
For example take the two commands below
ga('create', 'UA-XXXXX-Y', 'auto');
ga('send', 'pageview');In the first command ‘create’ it accepts the fields ‘trackingId’, ‘cookieDomain’ and ‘name’. In the second command ‘send’ it accepts hitType second parameter as an option.
All commands undertake a ‘fieldsObject’ parameter that can be used for specifying any fields.
Creating Trackers
Trackers are objects that can collect and store data. It can then send that data to Google Analytics. To create a new tracker you must specify a tracking ID and a cookie domain which will be used to specify how cookies need to be stored.
If for a particular domain a cookie does not exist then for that domain a new client ID is created and stored in the cookie. Here the user is recognized as new. If a client ID already exists for that domain then the user is recognized as returning.
Once it is created tracker objects start collecting information about the browsing content such as the page title and URL, screen resolution, viewport size and others. Later when the need arises the tracker sends all the information which is stored to the Google Analytics.
Create Method
Analytics.js offers different ways to create trackers but the most frequently used way is the ‘create’ command and the tracking ID and cookie domain fields are used as the second and third parameters. An example is given below
ga('create', 'UA-XXXXX-Y', 'auto');Naming Trackers
You can name the tracker using the name field as the fourth argument in the create command. It is a must to name the tracker when there are more than one tracker in a single page. A tracker without a name field is known as the default tracker and it is internally allotted with the name “t0”.
ga('create', 'UA-XXXXX-Y', 'auto', 'myTracker');Specifying fields at creation time
Another Fields object can also be added which allows you to set any of the fields at the creation time. They will be stored on the tracker and applied to all hits that are sent. The fields object can be used to specify all the fields while calling the ga() functions.
Working with Multiple trackers
Where there are more than one owner for a site then you need to send data to multiple properties from a single page. In such cases you need to create two separate trackers and one should be a named tracker.
To run the commands for a specific tracker you should always prefix the command name with the tracker name which has to be followed by a dot. The command to send pageviews is given below
ga('send', 'pageview');
ga('clientTracker.send', 'pageview');Important tips to remember about Google Analytics Tracking Code
- Every page on your site should contain Google Analytics Tracking Code (GATC)
- You should not copy-paste the GATC from any document
- It is recommended to avoid customization of GATC as it will break the code and as a result the code will stop working
- Try to avoid using multiple versions of GATC code as it becomes unreliable for the users. Use single version of GATC on a page at a time.
- Insert the GATC inside the head section of the page of your site.
- Make sure that you are adding the correct GATC which belongs to that particular site
- Even if you place the GATC in an external file Google Analytics will collect the data
- Once the GATC code is executed it sends HTTP response to the GA server
Conclusion
Now we just know how to get started easily with analytics.js. There are also lot more to explore about analytics.js. The information you collect can be used to improve your marketing campaigns and develop your website to provide best user experience.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to How Analytics.JS Works?. Here we have discussed the basic concept, working, how to add analytics.js to your site along with important tips to remember about Google Analytics Tracking Code. You may look at the following articles to learn more –


