What is Equal Employment Opportunity?
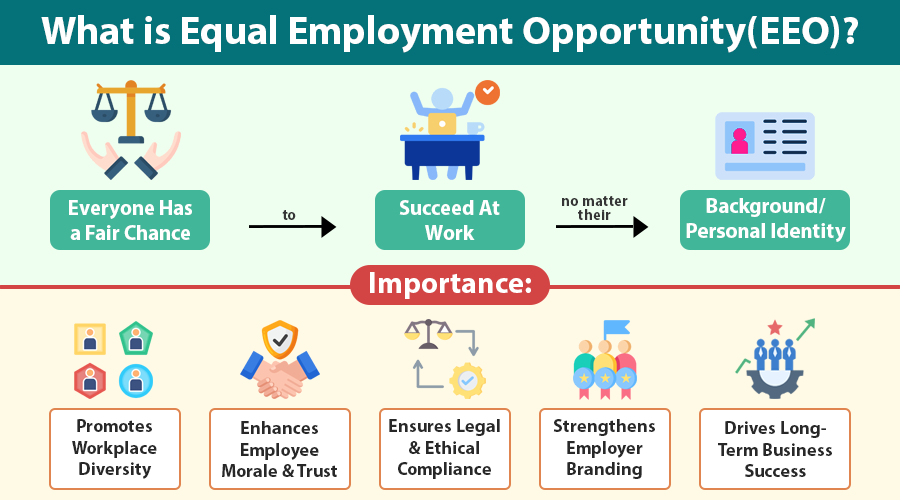
Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) means every person should have a fair chance to succeed in the workplace, regardless of background, personal identity, or circumstances. EEO promotes fairness, inclusivity, and non-discrimination.
Under the Equal Employment Opportunity, employers must make decisions based on job-related factors, such as skills, experience, performance, and potential, rather than personal attributes. For example:
- A company cannot reject a qualified candidate because of their gender or religion.
- An older employee should not be denied training opportunities solely because of age.
- Employers must provide employees with disabilities the necessary accommodations to perform their jobs effectively.
At its core, EEO creates a level playing field where individuals are judged by their abilities and contributions, not by stereotypes or prejudices.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Importance
- EEO Laws
- Principles
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Best Practices
- Role of Employers and Employees
Importance of Equal Employment Opportunity
Equal Employment Opportunity is crucial for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. We can understand its importance across several dimensions:
1. Promotes Workplace Diversity
Organizations that embrace EEO attract talent from various backgrounds. Diverse teams bring fresh ideas, cultural awareness, and innovative solutions to business challenges.
2. Enhances Employee Morale and Trust
Employees feel motivated and respected when they know promotions, pay, and recognition depend on performance rather than favoritism or bias. This builds trust in leadership.
3. Ensures Legal and Ethical Compliance
Adhering to EEO laws prevents lawsuits, penalties, and reputational harm. It also demonstrates a company’s commitment to ethical standards.
4. Strengthens Employer Branding
Job seekers actively seek organizations with inclusive cultures. People perceive companies that prioritize EEO as progressive, fair, and socially responsible.
5. Drives Long-Term Business Success
Fair workplaces foster collaboration, reduce turnover, and boost innovation. Studies show that companies embracing diversity and inclusion often achieve better results than those that do not.
Equal Employment Opportunity Laws
EEO laws vary across countries but share a common goal: protecting workers from discrimination. Below are key examples from the United States, with parallels found worldwide:
- Civil Rights Act of 1964 (Title VII – U.S.): This law forbids employers with 15 or more employees from discriminating against anyone based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA): Protects workers aged 40 and above from age-related discrimination in hiring, training, or promotions.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Employers should offer reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, unless doing so would result in undue hardship.
- Equal Pay Act of 1963: Ensures men and women receive equal pay for substantially similar work.
- Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA): It prevents discrimination in employment and health insurance based on an individual’s genetic information.
Beyond U.S. laws, international frameworks, such as the International Labour Organization (ILO) Conventions, uphold global standards for equal opportunity and non-discrimination.
Principles of Equal Employment Opportunity
The success of EEO lies in implementing its guiding principles consistently:
- Non-discrimination: Employers must make employment decisions based solely on an individual’s skills and qualifications, without regard to personal traits or protected characteristics.
- Fair compensation: Employees must receive equal pay for work of equal value. Salary structures should be transparent and unbiased.
- Workplace accessibility: Employers must adapt the workplace to be inclusive, such as by providing wheelchair access or flexible work arrangements for caregivers.
- Harassment-free environment: Employers must protect employees from bullying, sexual harassment, and retaliation for reporting issues.
- Transparency and accountability: Organizations uphold principles consistently by enforcing clear policies, implementing effective grievance mechanisms, and conducting regular audits.
Benefits of Equal Employment Opportunity
Organizations that actively enforce EEO policies enjoy a range of benefits:
- Increased productivity: Employees work better when they are valued and respected.
- Better retention rates: Fair treatment reduces turnover, saving organizations the cost of hiring and training.
- Broader talent pool: By using inclusive recruitment, employers can tap into highly skilled candidates who might otherwise be overlooked.
- Improved problem-solving: Diverse teams bring unique perspectives, resulting in more creative solutions.
- Positive public image: Companies recognized for their fairness and inclusivity strengthen their corporate reputation.
Challenges in Implementing EEO
Despite progress, organizations face challenges in making EEO a reality:
- Unconscious bias: Hiring managers may unintentionally favor candidates who resemble themselves.
- Cultural resistance: Some employees may resist diversity initiatives due to stereotypes or traditional mindsets.
- Limited resources: Small businesses often lack dedicated HR teams to effectively enforce EEO policies.
- Inconsistent enforcement: Policies exist on paper but are not consistently applied.
- Intersectionality issues: Employees belonging to multiple marginalized groups (e.g., women with disabilities) face compounded discrimination.
To overcome these challenges, organizations must invest in training, establish accountability mechanisms, and demonstrate a strong commitment to inclusivity.
Best Practices for Promoting EEO
These are actionable steps organizations can follow to promote EEO.
- Develop inclusive policies: Draft and communicate clear anti-discrimination policies that are consistently applied and enforced.
- Conduct diversity and sensitivity training: Help employees and managers recognize unconscious bias and foster respect.
- Implement blind recruitment: Remove names, gender, and personal identifiers from applications to ensure a merit-based hiring process.
- Create mentorship programs: Offer growth opportunities for underrepresented groups.
- Monitor diversity metrics: Track recruitment, promotions, and pay equity to measure progress and ensure ongoing improvement.
- Encourage open dialogue: Provide channels for employees to voice concerns without fear of retaliation.
- Leadership commitment: Senior leaders should model inclusive behavior and hold teams accountable.
Role of Employers and Employees in EEO
- Employers’ role: Employers must enforce fair policies, provide training, ensure accessibility, and take swift action against discrimination. They should also create performance-based systems for hiring and promotions.
- Employees’ role: Employees must respect differences, refrain from discriminatory behavior, and foster a culture of inclusivity. Reporting unfair practices through appropriate channels also helps maintain accountability.
When both employers and employees actively contribute, organizations build sustainable cultures of fairness and equality.
Final Thoughts
Equal Employment Opportunity is not just about avoiding lawsuits; it is about building a workplace culture where fairness, inclusivity, and respect thrive. Organizations that embrace EEO see higher employee engagement, innovation, and long-term business success.
By enforcing laws, following principles, and adopting best practices, companies can create workplaces where talent is recognized and rewarded without bias. Ultimately, EEO benefits not only employees but also organizations and society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is Equal Employment Opportunity different from workplace diversity?
Answer: EEO focuses on ensuring fair treatment and non-discrimination in all workplace practices. Diversity refers to having employees with diverse backgrounds, experiences, and viewpoints. While EEO ensures fairness, diversity emphasizes representation and inclusion.
Q2. Can an employee report a violation if they believe EEO laws have been broken?
Answer: Yes. Employees who face discrimination or unfair treatment can report it to their HR department, grievance channels, or external agencies, such as the EEOC in the U.S. Reporting promptly helps resolve issues and ensures EEO compliance.
Q3. What are common signs of EEO violations in the workplace?
Answer: Common signs include unequal pay for similar work, discriminatory hiring or promotion decisions, inadequate accommodations for disabilities, harassment based on personal characteristics, or inconsistent enforcement of company policies.
Q4. How do cultural differences affect how EEO is applied around the world?
Answer: Cultural norms and local laws influence the application of EEO policies in different countries. Global organizations must adapt their EEO strategies to respect local customs while maintaining core principles of fairness, non-discrimination, and inclusivity.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Equal Employment Opportunity helped you understand its importance in creating fair and inclusive workplaces. Explore our related articles on:

