Updated April 19, 2023
Introduction to XSLT Format Date
XSLT format date is specified using XSLT 2.0 this offers format date as a string data type with the improved establishment. This was done using a template called format date for the date elements. Format date is used much in web development frequently for manipulation. The format date on XSLT Technique uses a template dealing with Gregorian Time and Internationalization.
Syntax:
<xsl:attribute name="feed>
<xsl:value-of select =" format-date(function name) (inpvalue, 'MMM dd, yyyy')"/>
<xsl:attribute>
// using category declaration
<xsl:date-format name = xname
language = xxtoken
calendar = xname />
The parameter for this date function is a picture string that encloses code in square brackets(D[07]). The name attributes declare date format or default date. It should be declared only once.
How to Format Date in XSLT?
XSLT offers three functions to specify a date:
- format-DateTime() for combined date and time.
- format-date() for a date.
- format-time() for a time.
The above three functions are collectively termed as date formatting functions and it works well in multiple ways. The second function format date specifies time zone arguments as optional and replaces already parsed XML Standard Date Format Specification on java based format. The format-date function uses picture strings with the Specifiers like Y for Year, M-month in a year, D for Day in a week. The time zone patterns are included in the tokens as (z and Z) respectively.
Few sample representation on time zone are given below:
For all these, we should add years or reduce years, month, hours, minutes with these functions.
1. Conversion using GMT date “2010/11/02 11:30:10”
<xsl:value-of select=”s: format-date (‘2010/11/02 11:30:10’, ‘yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss’)”/>
2. E.g. Convert a GMT or BST date time “2004/04/05 12:34:11”
<xsl:value-of select=”s: format-date (‘2004/04/05 12:34:11’, ‘yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss’, ‘GMT/BST’)”/>
3. E.g. Convert a GMT+2:00 date time “2005/07/01 11:30:11”
<xsl:value-of select=”s: format-date (‘2005/07/01 11:30:11’, ‘yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss’, ‘GMT+2:00’)”/>
4. E.g. Convert a date time specified as milliseconds specified as “247856955545”
<xsl:value-of select=”s: format-date (‘247856955545’)”/>
Time zone must be declared as per the rules mentioned in simple DateFormat under general time zone syntax.
Next the ISO dates is given in absolute days and is formatted as year-week-day as shown below:
<xsl:template name=”iuju:absolute-day-to-iso-date”>
<xsl:param name=”a-date”/>
We can also do a comparison between two dates in XSLT with few cases while transforming XML document to another format.
Examples of XSLT Format Date
Given below are the examples mentioned:
We write code in an XML file.
The implementation of date format functions in XSLT uses the parameters as follows:
- XML file which takes date element.
- XSLT for transformation and using attributes value of select for the date function.
- Finally, an output in XML file or HTML file.
Example #1
Code:
tt.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<scheduled date="2006-08-29">
</scheduled>
tt.xslt
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<html xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xsl:version="2.0">
<head>
<title>Time Management Task</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<xsl:value-of
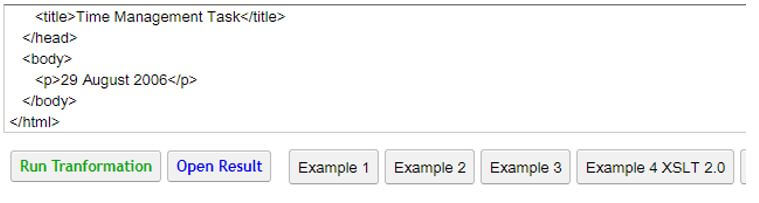
select="format-date(/scheduled/@date, '[D1] [MNn] [Y1]')" />
</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
- Here the date function is specified in select attribute and the strings are specified in the square brackets.
Output:
Example #2
Code:
dt.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<file>
<date_file>Feb-18-2008 09:50:20</date_file>
</file>
dt.xsl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="/">
<file>
<xsl:element name="newdate">
<xsl:call-template name="FormatDate">
<xsl:with-param name="DateTime" select="file/date_file"/>
</xsl:call-template>
</xsl:element>
</file>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template name="FormatDate">
<xsl:param name="DateTime" />
<!-- new date format 2008-02-18T09:50:20 -->
<xsl:variable name="month">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($DateTime,1,3)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="day-t">
<xsl:value-of select="substring-after($DateTime,'-')" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="day">
<xsl:value-of select="substring-before($day-t,'-')" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="year-t">
<xsl:value-of select="substring-after($day-t,'-')" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="year">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($year-t,1,4)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="time">
<xsl:value-of select="substring-after($year-t,' ')" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="hr">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($time,1,2)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="minute">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($time,4,2)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="sec">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($time,7,2)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:value-of select="$year"/>
<xsl:value-of select="'-'"/>
<xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Jan'">01</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Feb'">02</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Mar'">03</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Apr'">04</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'May'">05</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Jun'">06</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Jul'">07</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Aug'">08</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Sep'">09</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Oct'">10</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Nov'">11</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="$month = 'Dec'">12</xsl:when>
</xsl:choose>
<xsl:value-of select="'-'"/>
<xsl:if test="(string-length($day) < 2)">
<xsl:value-of select="0"/>
</xsl:if>
<xsl:value-of select="$day"/>
<xsl:value-of select="'T'"/>
<xsl:value-of select="$hr"/>
<xsl:value-of select="':'"/>
<xsl:value-of select="$minute"/>
<xsl:value-of select="':'"/>
<xsl:value-of select="$sec"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation:
- In this example, we have assigned a substring to add the ‘/’ between the dates in the output.
Output:
Example #3
Code:
file.xml
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<XMLdemo xml:space="preserve"
xmlns:dt="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:datatypes">
<Filedata>
<Audit>Richie ray</Audit>
<Date dt:dt="datetime">2019-03-12T14:56:00</Date>
</Filedata>
</XMLdemo>
file.xslt
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:ms="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xslt"
xmlns:dt="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:datatypes">
<xsl:template match="/">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<xsl:for-each select="XMLdemo/Filedata/Date">
<DIV>
Edited Date VAlue
<xsl:value-of select="."/>
</DIV>
<DIV>
Date After The function:
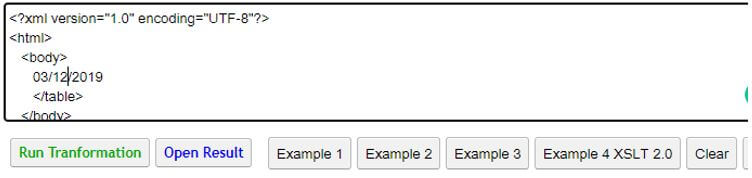
<xsl:value-of select="ms:format-date(., 'MMM dd, yyyy')"/>
</DIV>
</xsl:for-each>
</BODY>
</HTML>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation:
- This is where we can use format date() to define the dates so that the end-users receive the exact date structure in the output.
Output:
Example #4
Code:
<TRdatabase>
<CustomerQuery>
<CustomerNumber>554</CustomerNumber>
<CName>Rana Chtarabosh</CName>
<SchDate>2017-04-06T18:51:01.60+04:30</SchDate>
<AmountFair>900</AmountFair>
<TeamName>Monica raawt</TeamName>
<JobNumber>2545</JobNumber>
<SectorNO>1224</SectorNO>
<Obligations>remarks</Obligations>
<TravelCost>1500</TravelCost>
<Mode>international</Mode>
</CustomerQuery>
<CustomerQuery>
<CustomerNumber>550</CustomerNumber>
<CName>Rana Chtarabosh</CName>
<SchDate>2019-05-04T18:52:01.60+04:30</SchDate>
<AmountFair>1100</AmountFair>
<TeamName>Atul raawt</TeamName>
<JobNumber>1234</JobNumber>
<SectorNO>1234</SectorNO>
<Obligations>remarks</Obligations>
<TravelCost>1500</TravelCost>
<Mode>international</Mode>
</CustomerQuery>
</TRdatabase>
.xsl
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="xml" indent="yes"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<body>
<table border="1">
<xsl:apply-templates select="TRdatabase/CustomerQuery"/>
</table>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="SchDate">
<td>
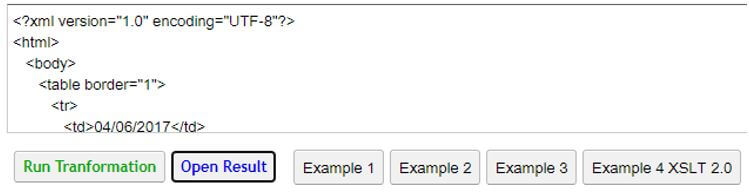
<xsl:value-of select="format-dateTime(.,'[M01]/[D01]/[Y0001]')" />
</td>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="CustomerQuery">
<tr>
<xsl:apply-templates select="SchDate"/>
</tr>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation:
- Here we have applied a filter condition ‘select’ parameter as shown below with the date format.
- The above example maps single date format with month/date/year.
Output:
Example #5
Code:
spr.xml
<schedulesheet>
<date>08022012</date>
</schedulesheet>
spr.xsl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="xml" />
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:apply-templates />
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="date">
<xsl:element name="date">
<xsl:call-template name="formatdate">
<xsl:with-param name="dts" select="."/>
</xsl:call-template>
</xsl:element>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template name="formatdate">
<xsl:param name="dts" />
<xsl:variable name="aa">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($dts,1,2)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="min">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($dts,3,2)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name="yr">
<xsl:value-of select="substring($dts,5,4)" />
</xsl:variable>
<xsl:value-of select="$aa" />
<xsl:value-of select="'/'" />
<xsl:value-of select="$min" />
<xsl:value-of select="'/'" />
<xsl:value-of select="$yr" />
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="node()|@*">
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="@*|node()"/>
</xsl:copy>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Explanation:
- This works in XSLT 2.0 with format date function. Here the XML file has a data on the elements and when we apply stylesheets on it. The strings are manipulated with the param name which selects the perfect date strings.
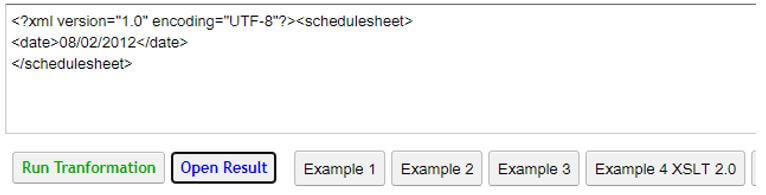
- The input format in the XML file is given as ddmmyy but the output file shows dd/mm/yy format.
- The output of the above transformation is given below.
Output:
Conclusion
Therefore using XSLT we can achieve date format pattern in the result which is the part of date-time development. XSLT 2.0 makes it easier to support date and time. To be precise, XSLT doesn’t allow suffixes in the date text.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XSLT Format Date. Here we discuss the introduction, how to format date in XSLT? and examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –