Updated April 15, 2023
Introduction to XML XSD
XML Schema Definition is defined as a language to describe the structure of the XML document. It means that all the XML Standards are defined in the XSD and they are written in XML. It is recommended by W3C to replace the Document Type Definition (DTD). The schema defines their types or built-in types. XML Schema is also allowed to check whether a given XML document is valid with syntactic Confirmation. W3C recommended XML-Schema with 1.0 and 1.1 version.
How XSD works in XML?
A separated file is created for XSD and this document is linked with the respective XML document. With XML Schema Specification a method is specified which is to be included in the root of the XML Document.
<xs: schemaxmlns: xs=http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="filename.xs"
Here the first statement is the Namespace Declaration.
xs is the namespace Prefix used within the elements a document element of XML Schemas and takes the attribute. The first statement describes the elements and attributes used in the code are defined in the above namespace. Next fragments say that the schema must be namespace-qualified.
The second statement denotes XML-Schema-instance i.e. xi which prefers to use schema Location and namespace which is sometimes made optional.
XSD defines two types of data types.
- Simple Type
- Complex Type
1. Simple Type
This type permits text-based Elements with fewer attributes and child names.
Some of the Simple types and its description is given below:
- Element: It contains simple element as well as other element content.
- Attribute: It’s a type used in Simple data types.
- Restriction: It has acceptable values in the respective XML document.
a. Elements: Elements being an important part in the Document that contains the data.
The elements are defined in XSD as follows :
<xs : element name = “ hgfhj” type = “ xxxx” />
So, this is the name property and holds the description about the element. This includes few pre-defined types like xs : integer, xs : date, xs : string, xs : Boolean. The appearance of an element is defined by a cardinality which are specified using attributes like minOccurs and maxOccurs.
Example:
For the XML like:
<manuf_date> 2019 - 05 – 12 </manuf_date>
<Product_company><br />
New jersey <br />
</ Product_company>
The XSD is:
<xs: element name=" manuf_date>"<br />
type="xs: date"/>
<xs: element name=" Product_company "<br />
type="xs: string"/>
The element takes two values which is reflected in the XML document that is fixed and default.
- Default is used when there is no specific value assigned in the XML document, XML parser assigns the default that is specified in the XSD.
- Fixed is assigned when the value of the XML document matches XSD value in the element.
b. Attributes: The attribute by itself declares it has simple types. If an element has specified attributes then it is a complex type.
Syntax of attribute:
<xs : attribute name =” order” type =” string/integer/Boolean”/>
An XML document with attribute.
<product id = “2123” > Body Wash </product>
XSD line for the above XML document.
<xs :attribute name =” product “ type =xs :int”/>
If attributes are needed then it is important to assign the keyword ‘use’ to the statement.
<xs :attribute name =” product “ type =xs :int” use=”required” />
c. Restriction: The elements which have some restrictions are called facets. It defines the accepting elements. It takes data types like enumeration, length, max inclusive, exclusive.
Example:
<xs:element name="bookno">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:integer">
<xs:pattern value="[1-81-8][1-8][1-8]"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
So, here an element name book accepts only four-digit between the range [ 1- 8]. Even restrictions can be done on a series of values with strings.
2. Complex Type
This type holds multiple elements and attributes as well and could have empty elements. It can be structured as a container element which allows us to define all the child element within it. Complex type is made global which has a name and can be re-used with the schema. The compositors of Complex types are sequence, all, choice.
<xs:element name="delivery">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="mobile" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:element name="location" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
The child element for delivery are mobile and location.
Examples to Implement XSD in XML
XML file using Schema Definition.
Example #1
College detail with root element followed by child elements.
Here individual Schema file is created with the perschema.xsd that should be included as the namespace in the XML document.
Code:
pre.xml
<?XML version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Result xmlns="College" xsi: schemaLocation="perschema.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<College noOfWorkers="-4420">
<Principal>
<SurName>string</SurName>
<Idno>string</Idno>
</Principal>
<Faculty>
<FullName>string</FullName>
<SurName>string</SurName>
<Address>string</Address>
<Idno>string</Idno>
</Faculty>
<Dept>string</Dept>
</College>
</Result>
Creating a Schema File.
Code:
perschema.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="College" targetNamespace="College" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="Faculty" type="FacultyType"/>
<xs:element name="Result">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="College" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="College">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="Faculty" type="FacultyType"/>
<xs:element name="Principal" type="FacultyType"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:element name="Dept" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="noOfWorkers" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="FacultyType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="FullName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="SurName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="Address" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="Idno" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="YearsOfExperience" type="xs:int" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
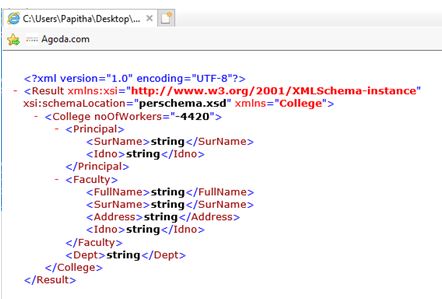
Output:
Example #2
Order details.
Code:
ord.xml
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<Orderdetails>
<Customer id="011">
<cname>Mark Lewis</cname>
<destination Country ="Australia" Delivdate=" 6 days">Free Delivery</destination>
<eid>[email protected]</eid>
</Customer>
<Customer id="022">
<fname from="jersey">Loafther cris</fname>
<destination Country ="USA" Delivdate=" 11 days">Shipping Charges</destination>
<eid>[email protected]</eid>
</Customer>
<Customer id="033">
<cname>Amal Raj</cname>
<destination Country ="Thailand" Delivdate=" 6 days">Shipping Charges</destination>
<email>[email protected]</email>
</Customer>
</Orderdetails>
Code:
ord.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xs:schema attributeFormDefault="unqualified" elementFormDefault="qualified" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="Orderdetails">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" name="Customer">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" name="fname">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="from" type="xs:string" use="required" />
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" name="cname" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="destination">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="Country" type="xs:string" use="required" />
<xs:attribute name="Delivdate" type="xs:string" use="required" />
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" name="email" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" name="eid" type="xs:string" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:unsignedByte" use="required" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
Conclusion
In this article, we saw Schema building formats which are highly evolving as the most important facets in the XML world. Schema is a collection of standard rules that designs how a document is put together. Therefore, to conclude we have seen schema definition for a XML document with an implementation.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XML XSD. Here we discuss how XSD works in XML? and examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –