Updated February 27, 2023

Introduction of xlsread Matlab
‘xls’ command is used in Matlab to import and export excel files into Matlab. We can create the excel files by using this command as well as we can read the excel files by using this commands. there are two operation in Matlab one is to create excel files and other is to read or open excel files. These commands are xlsread and xlswrite. Xlsread command is used to read or open the existing excel files in Matlab. Xlswrite command is used to write or create excel files in Matlab.by using xlswrite command we can also modify content of existing excel files. This command improves the adaptability of Matlab language by accessing data in other formats.
Syntax:
xlsread (filename)
xlsread (filename, parameters list)
xlsread (filename, [data])
xlsread (filename, sheet name)
xlsread (filename, range for columns or row)
How does xlsread Work in Matlab?
To read any excel file in Matlab first we need to create that file with some data in to it. There are various ways to write and read the excel files. These files can be written by sing parameter list, direct data, by giving sheet name, or by giving a range of the columns or rows.
Steps to read excel file in Matlab –
- Clear workspace
- Declare and assign data
- Write into excel file by using ‘xlsread’ syntax( xlswrite (filename,[data])
- Declare variable to read a file
- Use xlsread read command by using syntax. ( xlsread (filename ) ).
Examples of xlsread Matlab
Following are the examples are given below:
Example #1
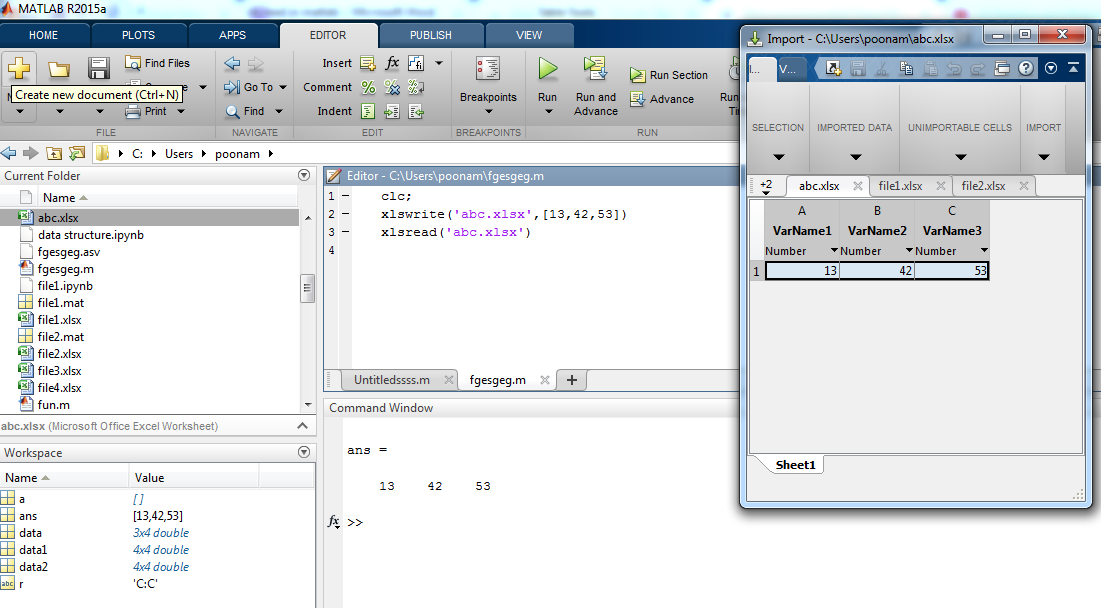
In this example, excel file is ‘abc.xlsx’ and data added to the file is [ 13 ,42, 53 ]. So it create one excel file in current directory.
| Matlab Editor | Command window |
| Clc ;
xlswrite(‘abc.xlsx ‘,[13, 42, 53]) xlsread (‘ abc.xlsx ‘) |
ans =
13 42 53 |
Output:
Example #2
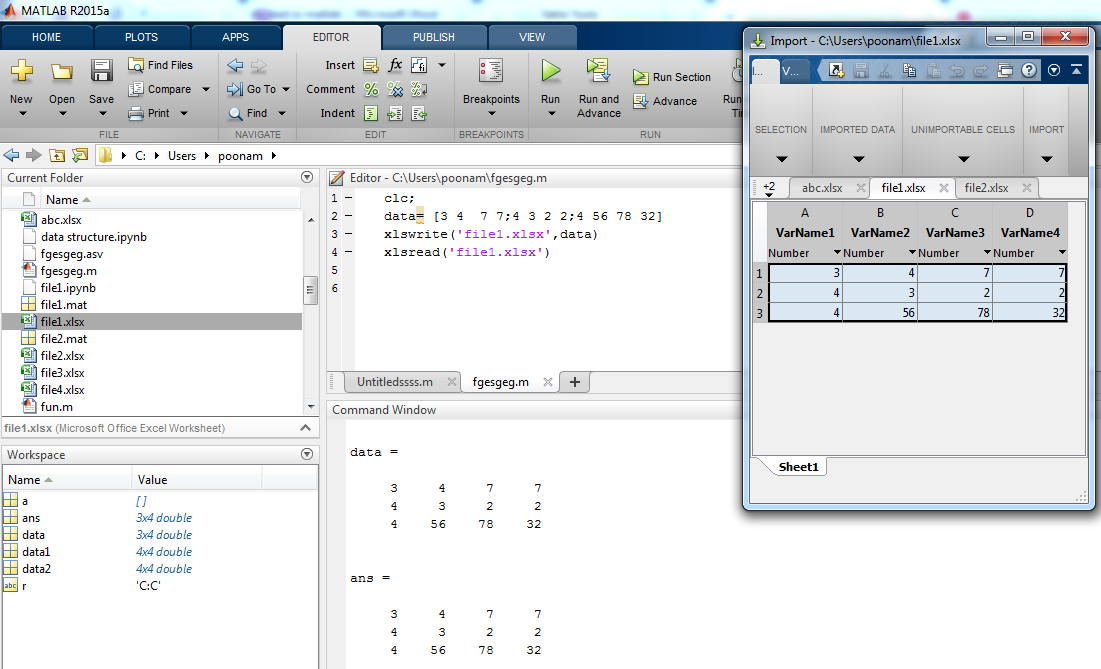
In this example input data is declared by using another variable, which is ‘data’ (data= [3 4 7 7;4 3 2 2;4 56 78 32]) . Data is written in ‘file1’.
| Matlab Editor | Command Window |
| Clc ;
Data = [3 4 7 7 ; 4 3 2 2 ; 4 56 78 32] xlswrite(‘ file1.xlsx ‘, data) xlsread (‘ file1.xlsx ’) |
data =
3 4 7 7 4 3 2 2 4 56 78 32 ans = 3 4 7 7 4 3 2 2 4 56 78 32 |
Output:
Example #3
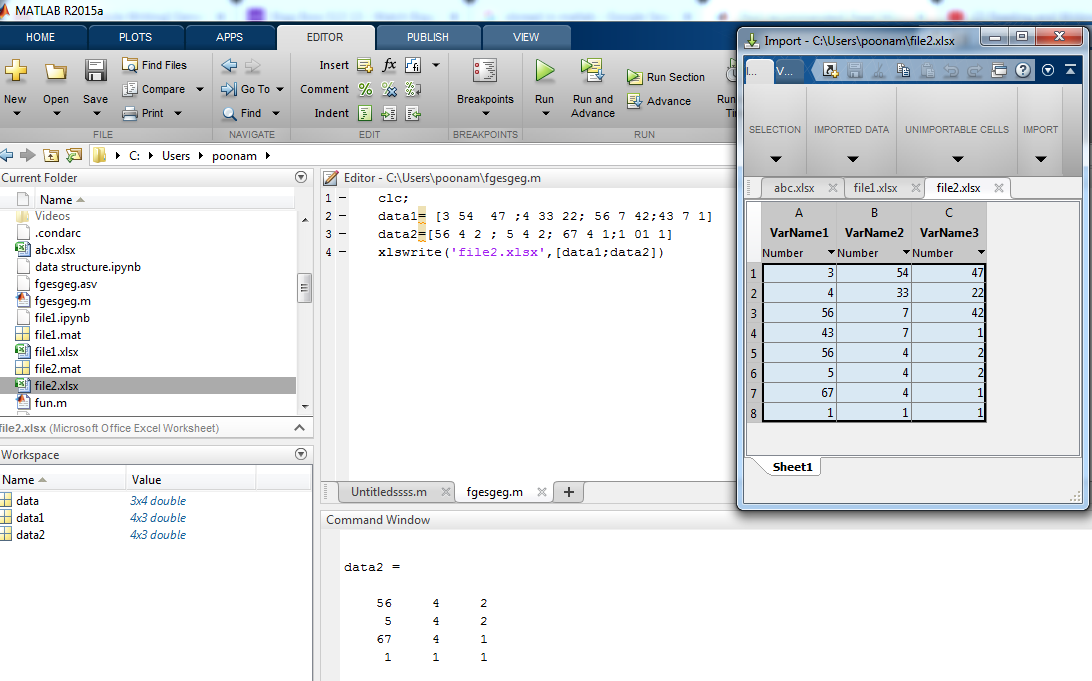
In this example input data is declared by using another two variables, which is ‘data’ (data1= [3 54 47 ;4 33 22; 56 7 42;43 7 1] and data2=[56 4 2 ; 5 4 2; 67 4 1;1 01 1]. Data is written in ‘file2’.
| Matlab Editor | Command Window |
| Clc ;
data1= [3 54 47 ; 4 33 22; 56 7 42 ; 43 7 1] data2 = [56 4 2 ; 5 4 2 ; 67 4 1 ; 1 01 1] xlswrite(‘ file2.xlsx ‘ , [data1 ; data2]) xlsread(‘ file2.xlsx ‘)
|
data1 =
3 54 47 4 33 22 56 7 42 43 7 1 data2 = 56 4 2 5 4 2 67 4 1 1 1 1 ans = 3 54 47 4 33 22 56 7 42 43 7 1 56 4 2 5 4 2 67 4 1 1 1 1 |
Output:
Example #4
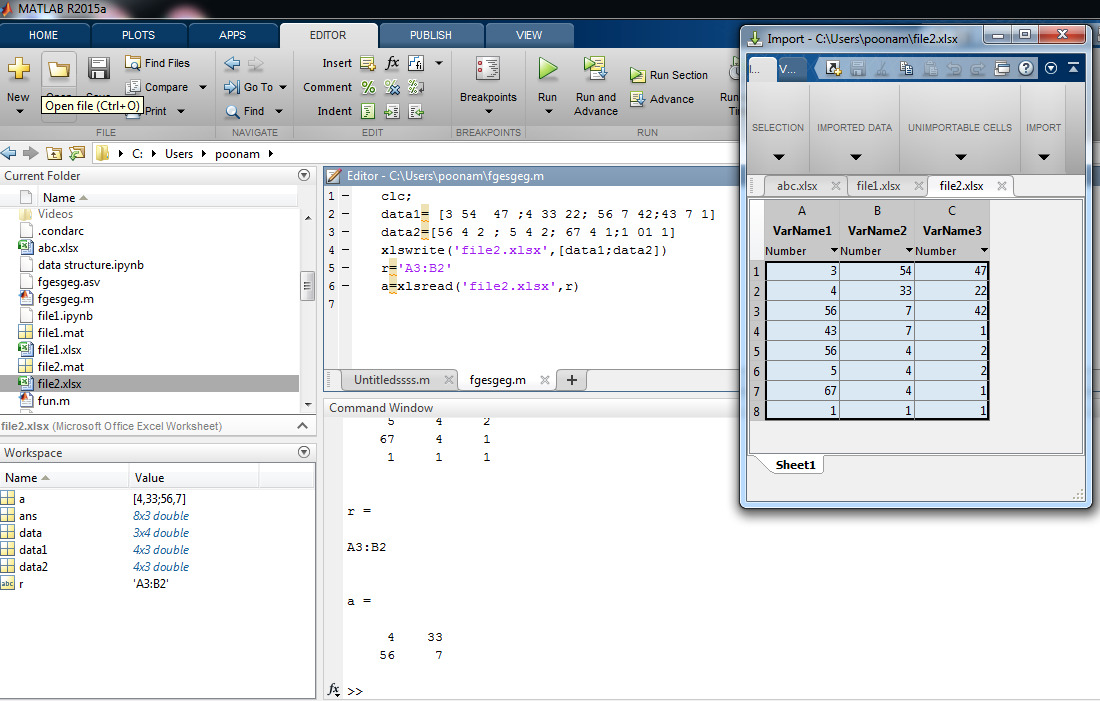
In this example input data is declared by using another two variables , which is ‘data’ (data1= [3 54 47 ;4 33 22; 56 7 42;43 7 1]and data2=[56 4 2 ; 5 4 2; 67 4 1;1 01 1]). Data is written in ‘file1’.to read the file we use range function. By giving range to the specific file we can display only important data.
| Matlab Editor | Command Window |
| Clc ;
data1 = [3 54 47 ;4 33 22; 56 7 42;43 7 1] data2 = [56 4 2 ; 5 4 2 ; 67 4 1 ; 1 01 1] xlswrite(‘file2.xlsx’,[data1 ; data2]) r = ‘ A3 : B2 ‘ a = xlsread(‘file2.xlsx’, r )
|
data1 =
3 54 47 4 33 22 56 7 42 43 7 1 data2 = 56 4 2 5 4 2 67 4 1 1 1 1 r = A3:B2 a = 4 33 56 7 |
Output:
Example #5
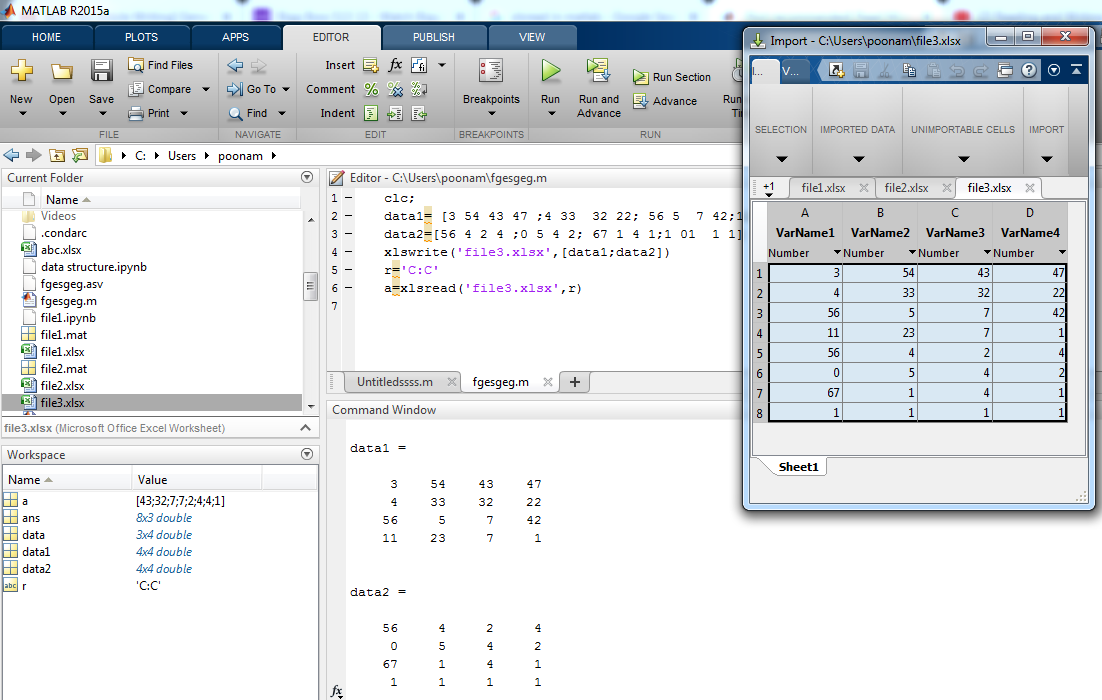
In this example input data is declared by using another two variables , which is ‘data’ (data1= [3 54 43 47 ; 4 33 32 22 ; 56 5 7 42 ; 11 23 7 1] and data2 =[56 4 2 4 ;0 5 4 2; 67 1 4 1;1 01 1 1 ]). Data is written in ‘file3’.to read the file we use range function. By giving range to the specific file we can display only important data. Here start range value and end range value is same to we can display only specific row or column by using this method.
| Matlab Editor | Command Window |
| clc;
data1= [3 54 43 47 ;4 33 32 22; 56 5 7 42;11 23 7 1] data2=[56 4 2 4 ;0 5 4 2; 67 1 4 1;1 01 1 1] xlswrite(‘file3.xlsx’,[data1;data2]) r=’C:C’ a=xlsread(‘file3.xlsx’,r)
|
data1 =
3 54 43 47 4 33 32 22 56 5 7 42 11 23 7 1 data2 = 56 4 2 4 0 5 4 2 67 1 4 1 1 1 1 1 r = C:C a = 43 32 7 7 2 4 4 1 |
Output:
Conclusion
We know that nowadays a, most of the data comes in excel format only, therefore to deal with excel files is little difficult. But by using Matlab we can easily import and export the data from excel to Matlab or Matlab to excel. We can read the excel data in various ways as per our need and as per application need. Matlab operates on excel data very effectively and efficiently.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to xlsread Matlab. Here we also discuss the introduction and how does xlsread work in matlab? along with different examples and its code implementation. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –