
Introduction to SQL Server
SQL Server is an application software for Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), from Microsoft, that can be used for creating, maintaining, managing, and implementing the RDBMS systems. It is an extensively used application as it enables multiple users simultaneously to work on the database systems, where users can range from minor office-based machines to huge Internet-based servers. Provisions any variety of SQL programming extending from ANSI SQL (for traditional SQL) through SQL to T-SQL (Transact-SQL) used for advanced relational databases.
It is the relational database management system developed by Microsoft back in 1988. It is actually a backend application that allows us to store and process data. In simple terms, it offers us a platform where we can update, change, and manage the data. It is called the relational database management system due to its nature to store the data in tables where the tables store the data about the same entity.
How does SQL Server make Working so Easy?
- It is very helpful when it comes to storing the data in the backend in order to process it. It has a very easy interface that helps the backend developer to focus much on taking care of the data rather than getting afraid of its working.
- As it is the product of Microsoft, the .Net framework could be easily integrated with it as it also belongs to the same organization.
- In comparison to the other mean of storing data like Excel, text and so on, the database is always preferred due to its magnificent power to process data, to offer high security and mainly due to its capacity to store large data.
Installing SQL Server in OS
This section will give you an idea about how we can set up SQL Server in a Windows operating system in order to use it.
So below are the steps that we have to follow to complete this installation in our system.
- Step 1: Go to https://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/sql-server/sql-server-downloads.
- Step 2: Download the Developer version.
- Step 3: After downloading the setup open it by clicking twice and select Download media.
- Step 4: Choose the ISO file and select the path and click Download.
- Step 5: Extract the downloaded file and open the folder.
- Step 6: Click on setup.exe and then click on the first link.
- Step 7: You will need to click the next button a couple of times.
- Step 8: At last, accept the term and choose to Install the only option.
- Step 9: Wait for around 10-15 minutes to get it installed.
- Step 10: Go to https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms?view=sql-server-2017.
- Step 11: Download the SQL server management studio and run the setup.
- Step 12: Once it is installed, restart the system and we are done.
Using these easy steps we can download and set up the SQL in our operating system. Once it is installed we will be able to use it for data storage and data processing.
Working with SQL Server
After installation, we can open the SQL Server management studio to begin the work. The studio provides us the interaction platform to work with the database. So to work with we will be using a language called SQL (Structured query language).
So once we open this management studio for the first time, we have to select the server on which we will be working.
Below is how the studio looks like.
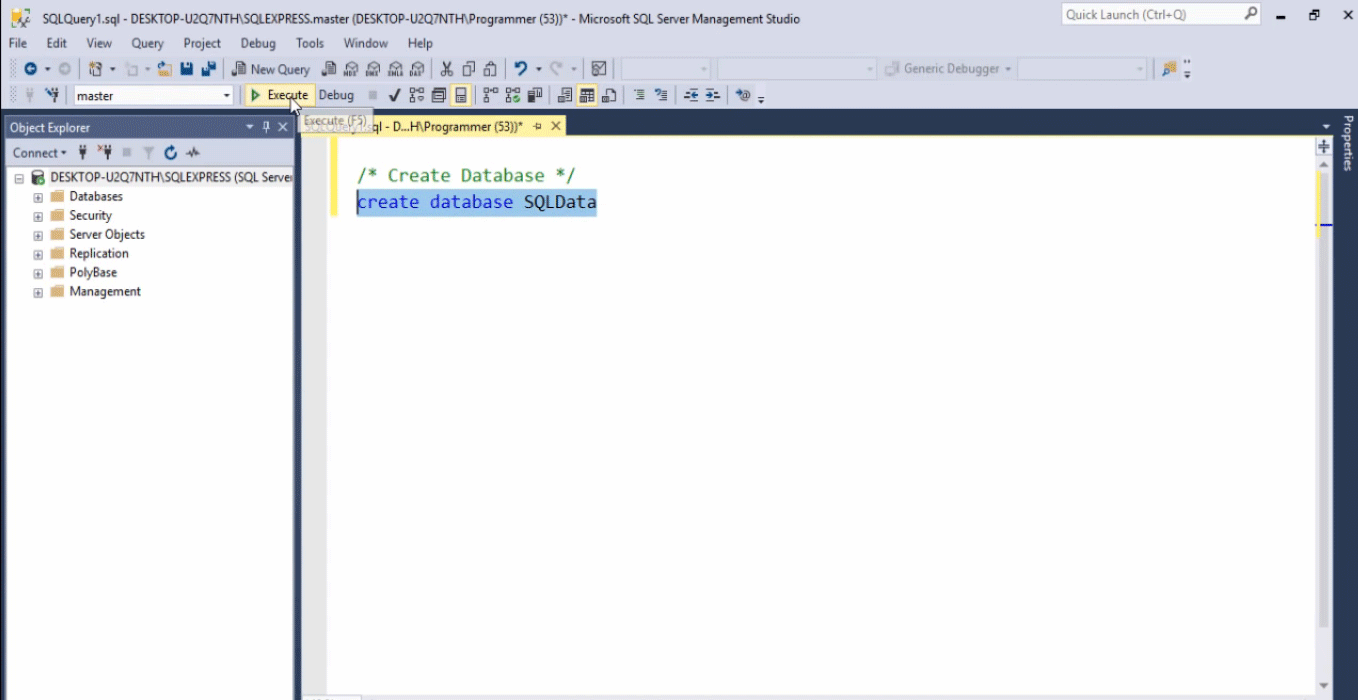
In this picture:
- The left pane shows the name of a server that we have chosen and below the server name, which are some folders like Database, security, etc that come with the by default existing files.
- The right pane shows the area where the SQL codes have to be written in order to work with the database.
- In order to run the code, first, you have to write and then select it and eventually click on the Execute button to have the query executed. The execute button is highlighted here.
- If the code is executed successfully, it will give the message below “Commands completed successfully”.
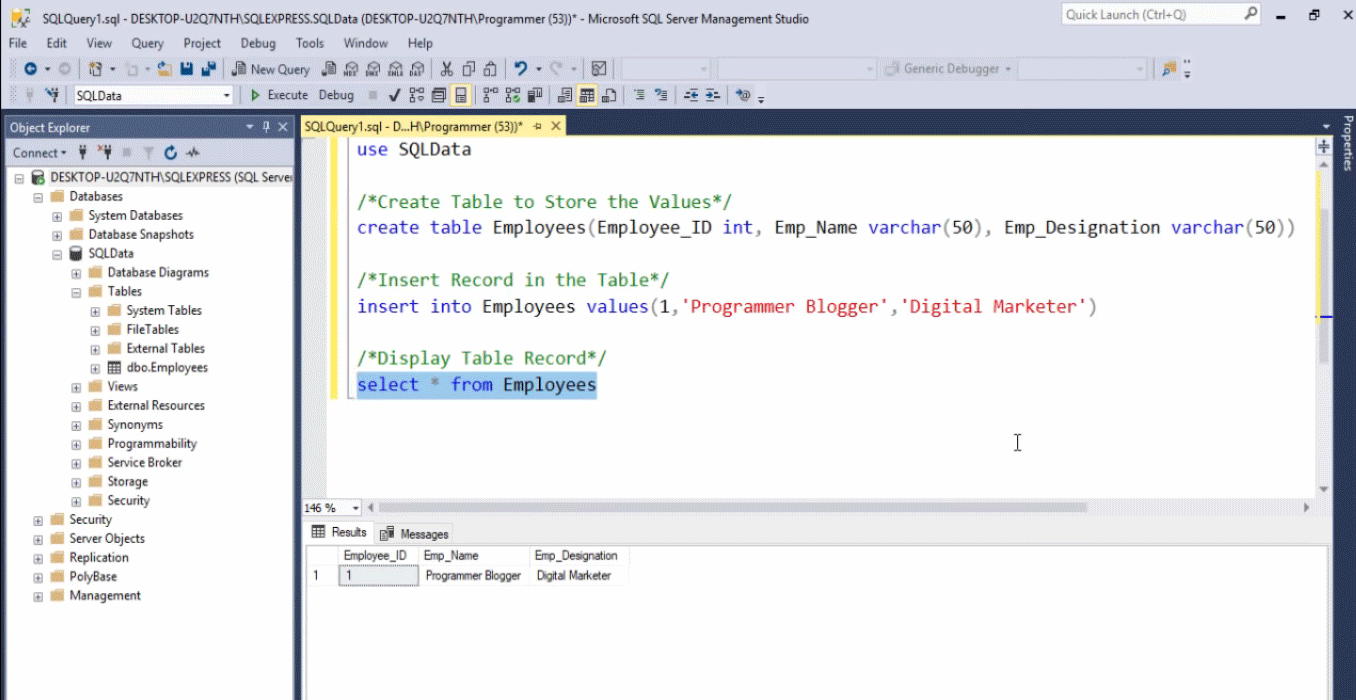
Below is one more program to create a table in the database, to insert some value in it, and then to retrieve the values stored in the table.
Advantages
There are several plus points of using SQL server over other means of data storage.
- Data processing: It allows us to process the data stores in order to generate the desired output. The data could be computed using SQL server.
- High storage: We can store a large number of data in the SQL server. Due to its high storage capacity, it is considered best while data storing in organizations.
- Integration with front-end: It could also be integrated with the frontend application to offer the mechanism of dynamically data change. It is very frequently used in integration with web applications.
- Easy to connect with.Net: As SQL server and.Net framework both belong to Microsoft, both are very easy to be connected. It works very fine or smooth when merged with an application developed on .Net.
Who is the Right Audience for Learning SQL Server Technologies?
- Folks who are interested in growing their career in backend development could be a great audience for diving deep into SQL server technology.
- This technology offers fantastic growth opportunities as well which is expected to be kept on increasing with the exponential increase in e-commerce and social media.
Conclusion
In very short and crisp words, the SQL Server is the tool used to implement the mechanism of a relational database management system. It allows the developers to work with data in order to offer a good experience to the user. In organizations, it is the most preferred mean of data processing as it is highly capable to deal with a large pool of data.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is SQL Server. Here we discussed the working and advantages of SQL server. Also how and where this technology can help in career growth. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

