Updated March 2, 2023
Introduction to Random Forest
At the first, let us throw some big words at you all and we would explain to you bit by bit so that at the end of an article we would be no longer calling the previously called “jargons” as difficult terminology or “jargons” anymore! Random Forest in the world of data science is a machine learning algorithm that would be able to provide an exceptionally “great” result even without hyper-tuning parameters. It is a supervised classification algorithm, which essentially means that we need a variable to which we can match our output and compare it to. The supervised algorithm essentially means that there would be some variable that will try to match to another variable which we call as an output. Now Random Forest is essentially a collection of decision trees working together to present output. Now having talked about decision trees, we haven’t quite introduced that term yet. Let’s do that first.
How does Random Forest work?
Decision Tree is a tree-like a structured algorithm that keeps on segregating the entire dataset into branches which then again segregates it into branches and finally having a leaf, which can’t be split further. Essentially the dataset in the leaf denotes some range of similarity which is essentially decided by what data are we trying to split. Once we have a trained Decision tree, we can feed that with a new data point and the tree will lead to the leaf, which has a similar kind of attribute with the new data point. For example, let’s say we have a list of celebrities, and the tree is trained in such a way with the variable attributes that at one leaf node we have all cricketers. Now, we introduce a new data point of Sachin Tendulkar, “the god of cricket!”, the tree would automatically lead to the leaf which consists of a group of cricketers.
Now that we have a fair understanding of what Random Forest is and how Random Forest and Decision Trees are related to each other, let us try to understand the working of the decision tree, and then we would take a leap to understand the working of the Random Forest.
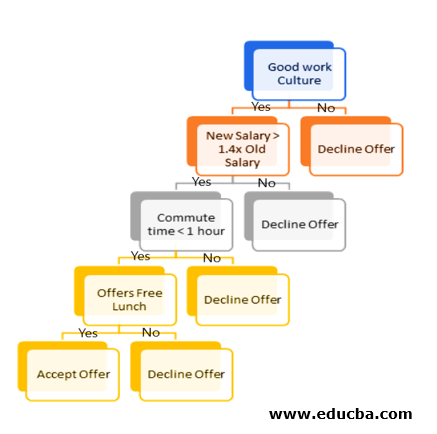
Let us take an example of a job offer to understand the working of the decision tree and then we would use the same example to better understand the working of Random Forest. Now, let us say you have a job offer in hand, and you ask one of your friends who is working there about the company and he replies that the work culture in the organization is awesome! You would eventually go ahead and think to take up this offer along with some more validation points like: is the company offering 40% more salary than the current organization, how far is the office location, whether it offers free lunch and many such more. The decision tree for this example would look like the one shown below:
Now, if a new offer rolls in we would do the same kind of hierarchical decision making in choosing whether to go ahead with accepting the offer or not. This methodology of decision making by the use of trees to come to a final leaf is what decision tree methodology is.
Now, while going through the explanation, did you encounter something weird about the methodology. If not, let us explain it. What if the friend you asked has some personal gain to say “yes” to you or maybe “No” because he or she is too frustrated with the organization? This creates a biasness towards the final decision you would make. Now, in this dilemma, we would ask a number of other friends or friends of friends about the decision and we would maybe rank the one which most of the people’s individual tree would point the result to.
Thus, in the example of a decision tree, choosing or declining an offer is the “target” variable. The salary, time to commute, work environment, etc. are the variables needed to decide and a new offer coming in is a new data point. For random forest, asking a lot of other friends is basically what tree creation is and for Data Science, the different decision trees created are random in nature.
Classification of Random Forest
Now, let us look at a methodology that is widely used in the industry and that is in cases of the classification problem. We call the usage of the random forest for classification as an ensemble methodology and by the ensemble, we mean that different decision trees’ votes will be aggregated, and the final class of the new data will be portrayed. In the case of random forest, we would train a lot of decision trees and then take “Majority-Voting” to finally decide the class the data falls into. Majority voting essentially means that the class in which the majority of the decision tree represents is adjudged as the final class for the data points.
From the example from the previous section of this article, in case of an offer from an organization, let us assume we have around 9 decision trees in the random forest, and the majority of the trees’ output is to join the organization. Hence it would obviously give the candidate confidence to pursue the opportunity in the next organization.
Advantages of Random Forest
We can now well appreciate why Random Forest is one of the most widely used algorithms, especially for classification problems.
Let’s look at the advantages it provides in pointers below:
- Random forest builds highly accurate classifiers.
- Running on large databases is efficient for the random forest.
- A lot of input variables can be handled without any variable deletion.
- Variable importance estimation can be obtained as a part of the process of Random Forest.
- The generalization error is estimated in an unbiased way in the way this algorithm is built.
- We can also use Random Forest for estimating the missing data wherever necessary.
Conclusion
In the following article, we assume that we were able to break down the jargon of random forest is been eased out and one can now use random forest with confidence in their data science projects. This algorithm provides a quicker way of analyzing data and eventually builds a model for quick turnaround cases. Also, this algorithm provides an indication of the important features. All in all this algorithm is surely a way to ease out the complications in a big dataset.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Random Forest. Here we discuss an introduction to Random Forest, how does it work, classification, and advantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –