Updated May 2, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Data Types
PostgreSQL Data Types are the supported data types that are defined while creating the database tables. There are several types of data types available with PostgreSQL, such as numeric, monetary, character, binary, Boolean, date/time and enumerated types. Each of the data types is used to store and process specific types of data. It supports both single-value data types such as integer and character, float and Boolean and mufti value or complex data types such as arrays, JSON, and interval. The enumerated data type has specific functionality to create a set of static values data set, such as defining months of a year.
Every application that works with data requires a database to store all the data-related to the application. Since data is a critical part of any system, a platform must exist to aid in processing and managing the data. The data type may be defined as a kind of data. In simple terms, the variable that is assigned with one of the data types can store the value of that data type only. For instance, if any variable is supposed to store the integer values only, then in all the cases, it will store the integer value only. If the user tries to feed the value of different data types in that variable, it will lead to an error.
Different PostgreSQL Data Types
Given below are different PostgreSQL Types:
- Numeric data types
- Monetary data types
- Character data types
- Binary data types
- Date/Time data types
- Boolean data types
- Enumerated data types
1. Numeric Data Types
It mainly provides two distinct types of numeric data types.
- Integer
- Floating point numbers
Integer Data Type
The variable defined with the integer data type can only store the integer value. The value must be the integer value else; it will end up with throwing the error. For example, if a variable named i is supposed to store the integer value, it will only hold the integer value.
Example: – 1,200,459,354 etc.
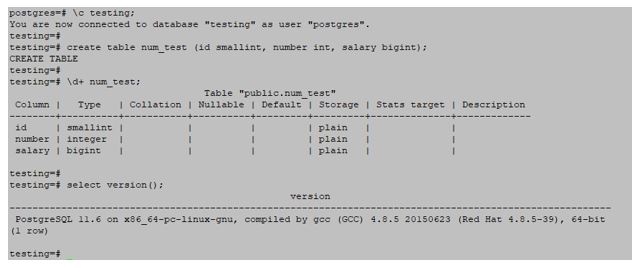
In PostgreSQL, basically, three kinds of integer present are as follows:
- Small Integer: The storage size of the small integer is 2 bytes.
The range of small integer is -32768 to +32767
- Integer: The storage size of the integer is 4 bytes.
The range of integer is -2147483648 to +2147483647
- Big Integer: The storage size of big integer is 8 bytes.
The range of big integer is -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807
Code:
# create table num_test (id smallint, number int, salary bigint);Output:
Floating point number
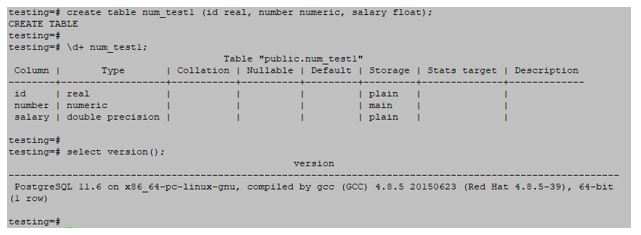
Floating-point numbers mainly divide into three types are as follows:
- Float
- Numeric
- Real or float8
Float: This is floating point number precision in PostgreSQL. Range if floating point is at least n and a maximum of 8 bytes. It is also called double-precision data types.
Numeric: This is a real number data type in PostgreSQL. Numeric p and s are the exact numbers in numeric data types.
Real: It is a 4-byte floating point no in PostgreSQL data types.
Code:
# create table num_test1 (id real, number numeric, salary float);Output:
2. Monetary Data Types
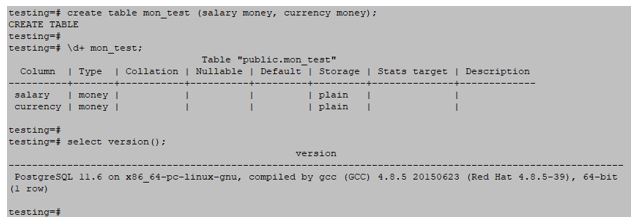
Monetary data types in PostgreSQL stores the current amount with a fractional fixed precision number. The range of monetary data type in PostgreSQL is -92233720368547758.08 to +92233720368547758.07
Code:
# create table mon_test (salary money, currency money);Output:
3. Character Data Types
In this, there are mainly three distinct character data types available.
- Char
- Varchar
- Text
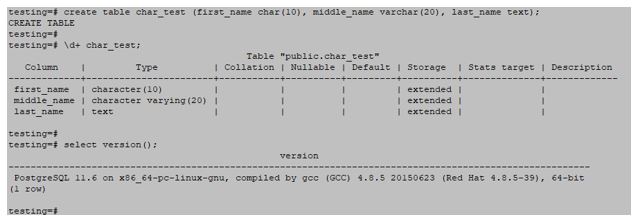
Char Data Type: The char data type stores a single character value and is typically preferred when only a single character needs to be stored. If the user tries to put more than one character in this, it will lead to an error. The variable storing the char values occupies very little space of the storage.
Example: ‘A’, ‘a’, ‘m’ etc
Text Data Type: The variable with data type as the text can store the long string values. In all the cases where the length of the text that has to be stored is unknown, one can use the text data type. PostgreSQL refers to this as a variable-length character string. In this data type, character strings with an unlimited number of records are referred to as text data.
Example: “Hello”, “Congrats” etc
Varchar(n) Data Type: Varchar data type with some number written along with it denotes that it can store or hold only the number of characters written next to it. In these data types, we can store n number of characters.
For example, if we write varchar(9), it means that the variable will only be able to hold the maximum of nice characters.
Example: “ABCDEFGHI”, “Hello Hey”
Code:
# create table char_test (first_name char(10), middle_name varchar(20), last_name text);Output:
4. Binary Data Types
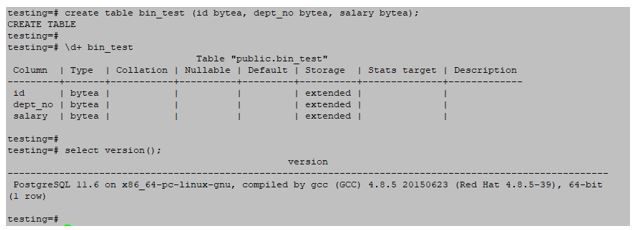
PostgreSQL binary data types allow the storage of binary string in PostgreSQL. Its variable length is binary data types.
Code:
# create table bin_test (id bytea, dept_no bytea, salary bytea);Output:
5. Date/Time data Types
Variables meant to store only time values are assigned the time data type. There should be some particular format of time that has to be stored in the time data type variable. It is one of the most important data types in PostgreSQL as it is used to keep track of transactions.
Example: 12:00:36, 01:06:56
Below is the date/time data types available in PostgreSQL are as follows:
- Date
- Time
- Timestamp
- Timestamptz
- Interval
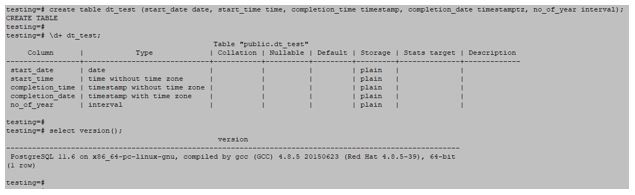
Date: This data type only stores date. It will not store any time. The low value of this data type is 4713 BC, and the highest value is 294276 AD.
Time: This data type only stores time. It will not store any date. The low value of this data type is 4713 BC, and the highest value is 5874897 AD.
Timestamp: This data type stores the date and time. It will not store any timestamp. The low value of this data type is 4713 BC, and the highest value is 294276 AD.
Timestamptz: This data type stores the date and time with the timestamp. The low value of this data type is 4713 BC, and the highest value is 294276 AD.
Interval: The storage size of these data types is 12 bytes. It will describe the time interval value.
Code:
testing=# create table dt_test (start_date date, start_time time, completion_time timestamp, completion_date timestamptz, no_of_year interval);Output:
6. Boolean Data Types
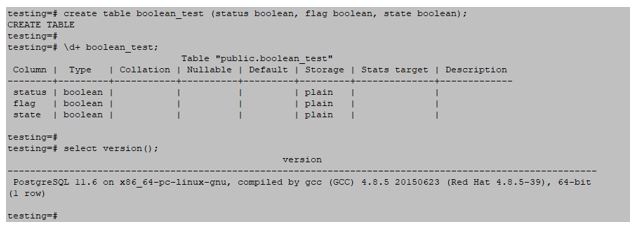
Boolean is one of the data types supported by PostgreSQL. This data type can store two values only that are “True” and “False”. In usual cases, the Boolean values are used to verify if the statement is correct as when the statement is correct, it returns the true value; else, the value will be false. This data type is also utilized in decision-making, where the program needs to make a choice based on one of two values.
Example: “True”, “False”
Code:
# create table boolean_test (status boolean, flag boolean, state boolean);Output:
7. Enumerated Data Types
It comprises a static order set of values.This closely resembles the enum data type supported in programming languages. Enumerated data type in PostgreSQL creates using create type command. In this, if we create enumerated data types once, it will use in any other type.
Code:
# CREATE TYPE year AS ENUM ('JAN', 'FEB', 'MAR', 'APR', 'MAY', 'JUN', 'JUL', 'AUG', 'SEP', 'OCT', 'NOV', 'DEC');Output:
Some other Data Types in PostgreSQL
Below is a list of additional data types available in PostgreSQL.
- Interval Data Type: The interval data type can be assigned to a variable and is capable of storing a specific time interval. It focuses on time and can be used to measure time in various scenarios. The database diligently records which transaction occurred at what interval, and this data type aids in managing the intervals.Example – ‘7 months ago, ‘2 years 5 hours 40 minutes.
- Array: We use arrays to store a set of strings or any values, with the restriction that all array values must be of the same data type. Using arrays makes the program more convenient to understand for those who were not involved in its development Example – ARRAY [ 408)-589-5846′,'(408)-589-5555′ ]
- UUID Data Type: The UUID data type is responsible for storing Universally Unique Identifiers, which programs use to identify anything uniquely. High-level programming languages do not support this special type of data. Example – 0e37df36-f698-11e6-8dd4–cb9ced3df976, a81bc81b-dead-4e5d-abff-90865d1e13b1
- JSON Data Type: Variables that store JSON values are assigned the JSON data type, which is essential in PostgreSQL and capable of handling complex JSON data. Example – { “client”: “Doe”, “items”: {“product”: “Application”,”qty”: 7}}
Conclusion
Any application that deals with data can benefit greatly from using PostgreSQL database management. PostgreSQL supports various essential data types, such as time, date, and interval, for tracking transactions. In some of the operating systems like Kali Linux, it is available inbuilt. It makes it very easy for the developers to integrate their application with the database. Users can also utilize the various types of data available in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Data Types” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.