Updated July 5, 2023
Variable Declaration in VBA
Although is not mandatory to declare the variable at the very first step of VBA Coding. We can shift or move this process later in between the code before calling the values stored in that variable. But it is always advisable to declare at the beginning of the code. So, we will be having the idea which and all variables need to get assigned any value.
In VBA, we have 2 types of data. Fixed and Variable. Variables are those data types whose values will always be changing and can be changed. Variables in VBA are those data types which consist of some value or memories in them. Whatever we feed into a variable gets stored somewhere in memory of variables.
While declaring any variable we can be choosing any name for that. It can be an alphabet or word. It is always recommended to declare the variable with the name we are performing for that code. Suppose, we are creating macro for a database of contact detail. Then for defining the variable, we can choose FirstName or FName to define that variable as String. This will give the impression of what kind of values we need to store in that variable.
There are some commonly used data types for declaring any variables as;
- Integers
- String
- Double
- Long, etc.
How to Use Excel VBA Variable Declaration?
Now let us try with some examples on VBA Variable Declaration in Excel.
Example #1 – VBA Variable Declaration
In this example, we will see how to use a variable with an Integer data type. For this, we would need a module where we will be writing the code.
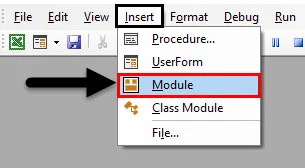
Step 1: So, go to the Insert menu and select Module as shown below.
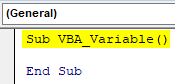
Step 2: Now insert a Subcategory better in the name of the performed function as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable() End Sub
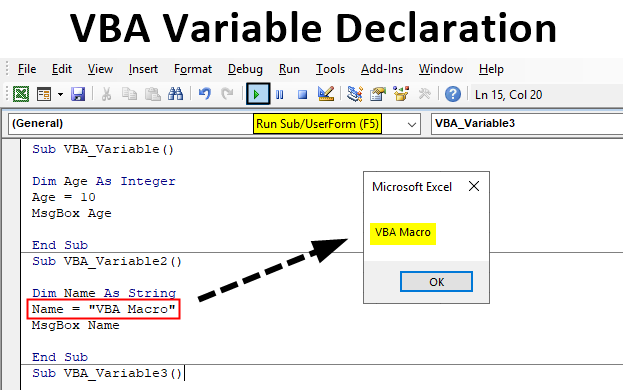
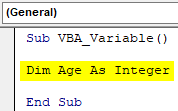
Step 3: Here we will print the age numbers. So as per that, define any variable such as Age with data type Integer as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable() Dim Age As Integer End Sub
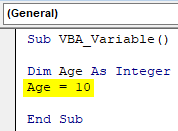
Step 4: Integer can store the value from the range -32768 to +32767 appx. Now assign a value to declared variable Age, Let’s say it is 10.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable() Dim Age As Integer Age = 10 End Sub
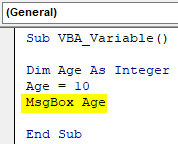
Step 5: Now to see the value stored in the variable Age, we will use MsgBox as shown below. This will print the value stored in any assigned variable.
Code:
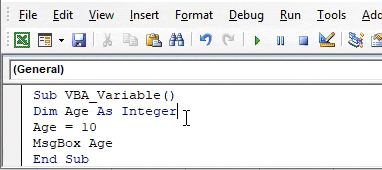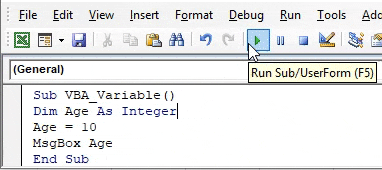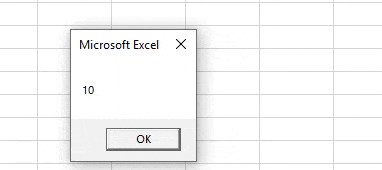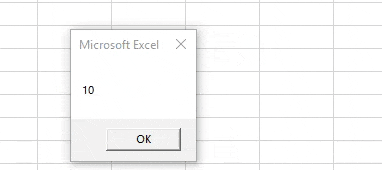
Sub VBA_Variable() Dim Age As Integer Age = 10 MsgBox Age End Sub
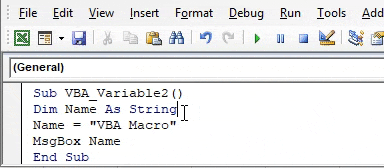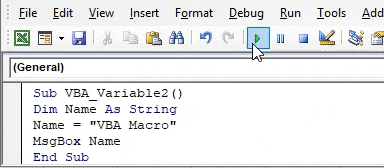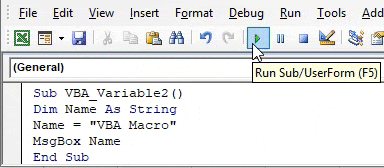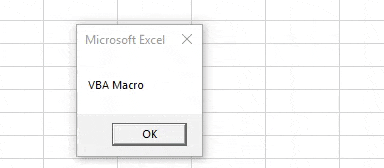
Step 6: Now, at last, compile the code and run it by clicking on the Play button which is below the menu bar or press F5 function key. We will see the message box containing the Age number as 10 which is under the range of Integer limit.
Example #2 – VBA Variable Declaration
In a similar way, we will use the String data type. A string data type is used for storing the text or alphabetical values. Suppose if we are creating the database of First name and Last name then we would need to declare the variable for it.
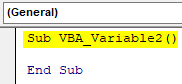
Step 1: First, open a module and write the subcategory there as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable2() End Sub
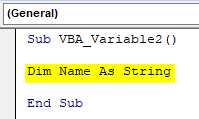
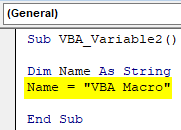
Step 2: Now define a variable as Name and give it a data type as String as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable2() Dim Name As String End Sub
Step 3: Then in the defined variable Name, assign any text value in it. Let say that value is “VBA Macro” as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable2() Dim Name As String Name = "VBA Macro" End Sub
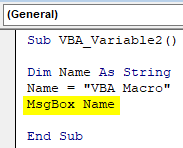
Step 4: To get the value stored in variable Name, we will use msgbox to print the value as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable2() Dim Name As String Name = "VBA Macro" MsgBox Name End Sub
Step 5: Now compile the code and run. We will see in the message box “VBA Macro” is printed.
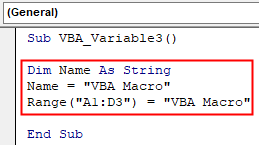
Step 6: Also, instead of MsgBox, we will choose the range of cells as well, where we need to print the value. For this purpose, select function Range as assign the location cells where we want to print the values stored in a defined variable. Let’s consider those cells from A1 to D3 and then put the value stored in the variable as shown below.
Code:
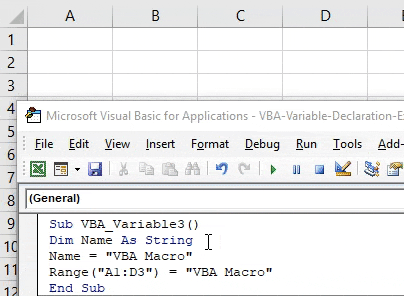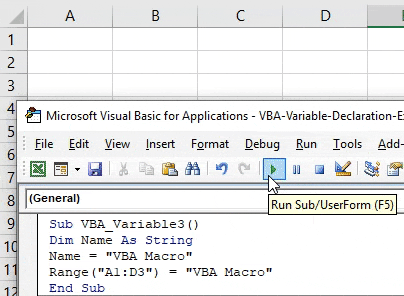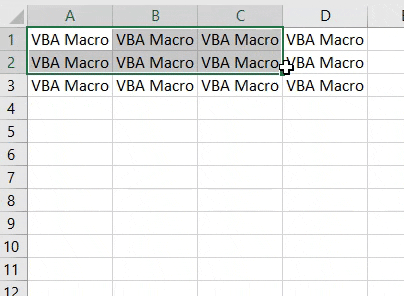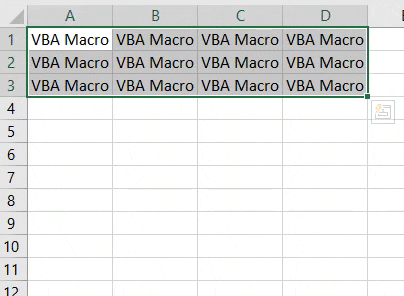
Sub VBA_Variable3() Dim Name As String Name = "VBA Macro" Range("A1:D3") = "VBA Macro" End Sub
Step 7: Now again run the code. We will see, text “VBA Macro” will get printed from cell A1 to D3 as shown below.
Example #3 – VBA Variable Declaration
In this example, we will use a Long data type and see how the values which cross the range of Integer (which is -32768 to +32767). Suppose, we want to store the value of Memory which is more than an Integer can allow. For this,
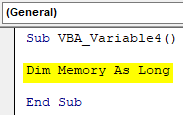
Step 1: Open a new module create the subcategory. And define a variable as Memory assign it the Long data type in it as shown below.
Code:
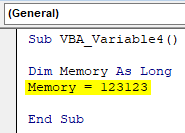
Sub VBA_Variable4() Dim Memory As Long End Sub
Step 2: Now assign any large value, let’s say 123123, which is beyond the range of Integer as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable4() Dim Memory As Long Memory = 123123 End Sub
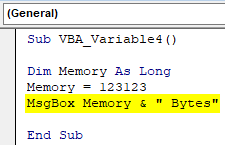
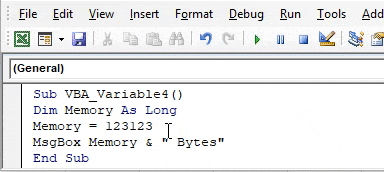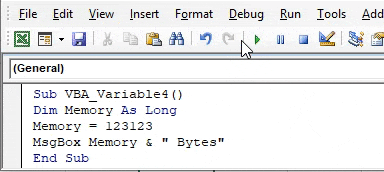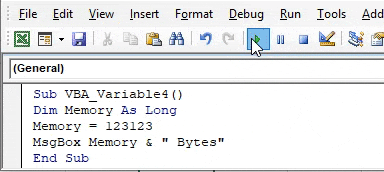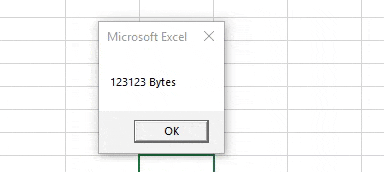
Step 3: Now use MsgBox to print the value stored in variable Memory as shown below with the unit of Memory as “Bytes”
Code:
Sub VBA_Variable4() Dim Memory As Long Memory = 123123 MsgBox Memory & " Bytes" End Sub
Step 4: Now run the code. We will get the message box with the message “123123 Bytes” as the value stored in variable Memory.
Pros of VBA Variable Declaration
- Variable gives the identity to the type of variable we want to declare.
- If we declare any variable at the starting of the code, then it is quite a reminder that we will be considering to store the values in it.
- We can store any type of values in variables but the data type should be of that kind.
Things to Remember
- There is a limit of writing the name of the variable which should not be more than 255
- Always declare the variable at the beginning of the code.
- Variables are not case sensitive but there should not be any space between the variable names.
- It should not contain any special character.
- A variable should start with text or alphabet, not with any number.
- Once a macro is created, save the file as Macro enable excel to avoid losing the code.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Variable Declaration. Here we discuss how to use Excel VBA Variable Declaration along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –