Updated March 3, 2023
Introduction to uigetfile Matlab
‘uigetfile’ is one of the important functions from the file operations domain, which is used to access the file dialog box. Whenever we run or execute this function we get one dialog box which shows a list of files on screen. By using this function we can directly open the file from any location, and if we don’t know the exact location of a specific file then we can brown the file and check the location on the command window. Whenever we execute the command we can observe two types of output one is if we don’t choose any file and canceled the execution and the other is by choosing the file with file location. All the information related to file and variables get stored in the workspace automatically.
Syntax:
- [ input, file _location ] = uigetfile ( ‘ * . m ‘)
[ file variable name, file location variable name ] = uigetfile ( ‘*. file extension ’ )
- [ input, file _ location, index] = uigetfile
[ file variable name, file location variable name, index variable ] = uigetfile
Why we use uigetfile in Matlab?
Uigefile function helps the user to access the files from the current folder or other folders. When we execute the command it shows one dialog box where we can choose a file by selecting the file or by typing the name of the file. If out file is not available in a current folder then we can browse the folders from the dialog box on left side of the dialog box. It gives results in form of 0 and 1. if we select specific files then it gives the result as 1 and if we don’t then it gives output at 0.
Examples
Let us discuss examples of uigetfile Matlab.
Example #1
Let us consider one simple example to access the file. File is stored variable input and path is stored in variable file _location. As we know uigetfile function gives results in form of 1 and 0. Therefore if the output is 0 then it will show the message as ‘canceled open file operation which is illustrated in example 1 ( a ). And if we select one file then it will give output as 1along with file location, which is illustrated in example 1 ( b ). In this particular example, we also mentioned a type of file accessible by program .here the type or extension of is ‘.m’. ‘.m’ is an extension for Matlab file. So that we can select only Matlab files.
Matlab program for Example 1 ( a ) –
clc ;
clear all ;
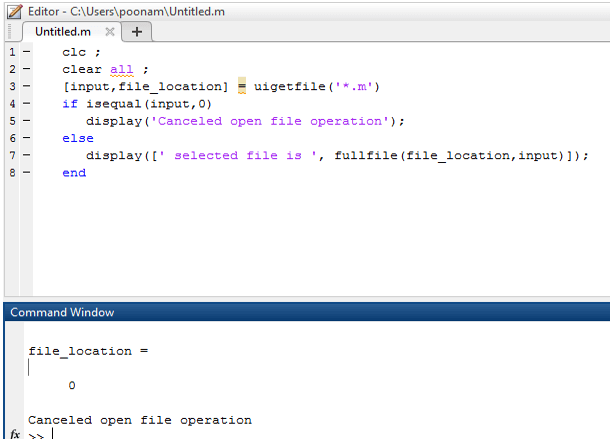
[ input, file_location ] = uigetfile ( ' * .m')
if input == 0
display ( ' Canceled open file operation ' ) ;
else
display ( [ ' selected file is ', fullfile(file_location, input) ] ) ;
end
Output:
Matlab program of Example 2 ( b ) –
clc ;
clear all ;
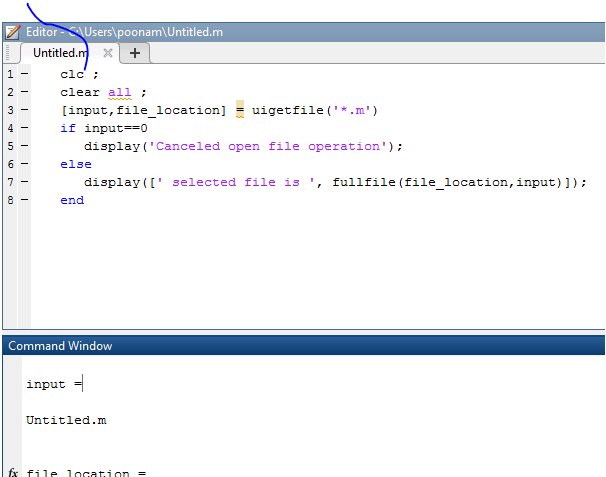
[ input, file_location] = uigetfile ('*.m')
if input == 0
display ( ' Canceled open file operation ' ) ;
else
display ( [ ' selected file is ', fullfile (file _location, input) ] ) ;
end
Output:
Example #2
In the second example, there are three parameters in assigned by uigetfile. File is stored variable input and path is stored in variable file _location and the third parameter is an index which shows result in form of 0 and 1. Therefore if the output is 0 then it will show the message as ‘canceled open file operation which is illustrated in example 2 (a). And if we select one file then it will give output as 1and other information like index, file location, and filter index, which is illustrated in example 2 (b). In example 2 we did not mention any type or extension of a file along with uigetfile function, so we can access or open any type of file from the dialog box including pictures.
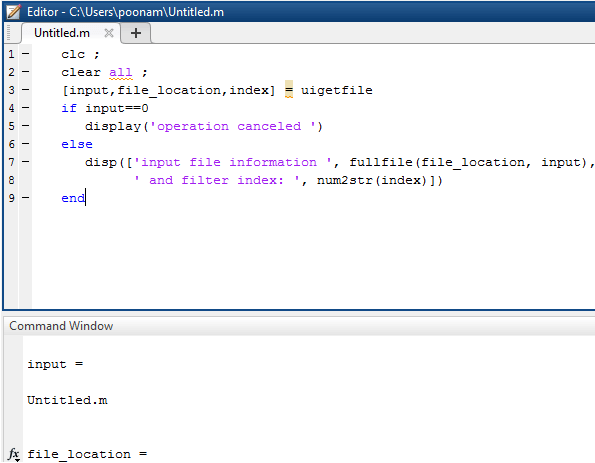
Matlab program of Example 2 (a) –
clc ;
clear all ;
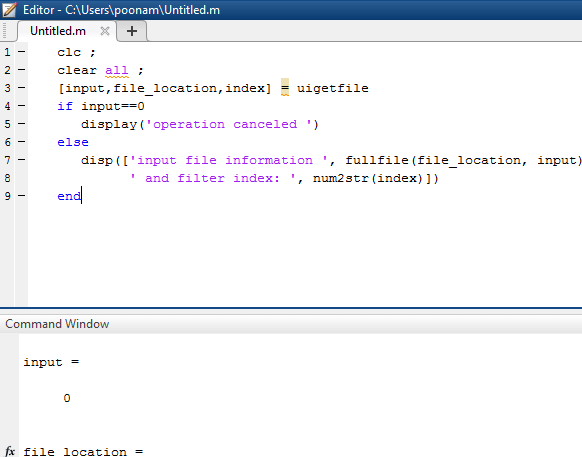
[ input, file_location, index ] = uigetfile
if input == 0
display ( ' operation canceled ' )
else
disp ( [ ' input file information ', fullfile (file _location, input),...
' and filter index: ', num2str(index)])
end
Output:
Matlab program of Example 2 ( b ) –
clc ;
clear all ;
[ input, file_location, index ] = uigetfile
if input == 0
display ( ' operation canceled ' )
else
display ( [ ' input file information ', fullfile(file_location, input),...
' and filter index: ', num2str(index)])
end
Output:
Conclusion
As we have seen in this article how to access the files from the Matlab function without using direct options. From the Matlab window, we can open single as well as multiple Matlab files from the dialog box. We can also open other types of files also like .txt, .doc, .xls, .png, .jpg and many more. There is one more option to open the files which is dir command but uigetfile is much effective. Along with the file accessibility, we can also check file specification and other information in the command window. We can also apply filters in parameters of uigetfile function so it will be easy for users to browse the file.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to uigetfile Matlab. Here we discuss the Introduction, syntax, Why we use uigetfile in Matlab, and examples along with code implementation respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –