Updated July 3, 2023
Introduction to MATLAB Colon
‘Colon’ is used as an operator in MATLAB programming and is one of the frequently used operators. This operator comes into the picture to create vectors defining with simple expressions, specifying‘for’ iterations or subscribing arrays, or getting access to a set of elements of an existing vector in a sequence. When the colon operator is used to create a vector for indexing into a cell or structure-type array in MATLAB, the resulting operation can produce multiple outputs. This is achieved by using the syntax ‘cellName{:}’ or ‘structName(:).fieldName.’
Syntax
Various forms of syntax are supported to use the operator ‘:.’ The functionalities of different syntaxes are described below:
|
Syntax |
Description |
| li = j:k | This syntax is used to create a unit-spaced vector list i.e. values with increment value ‘1’, consisting of the elements as [j,j+1,…,k]. |
| li= j:i:k | This syntax creates a regularly-spaced vector list ‘li’ using values with increment value ‘i’, consisting of the elements [j,j+1,…,k]. |
| M(:,n) | This syntax is used to store the nth column of matrix M. |
| M(m,:) | This syntax is used to store the mthrow of matrix M. |
| M(:) | This syntax can be used to reshape the element ‘M’ into a vector containing a single column. |
| M(j:k) | This syntax can be used to apply the vector list having the elements: to index into matrix M.
This is equivalent to forming a vector as [M(j), M(j+1), …, M(k)]. |
| M(:,:,p) | This syntax can be used to store/extract the data from a three-dimensional array A set on the pth page. |
| M(:,:) | This syntax can be used to reshape the elements of matrix ‘M’ into a two-dimensional matrix. |
| M(:,j:k) | This syntax can be used to include the subscripts present in the first dimension and to use the vector having elements j:k for indexing the second dimension. This results in a matrix having columns as [M(:,j), M(:,j+1), …, M(:,k)]. |
Examples to Implement MATLAB Colon
Below are some examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
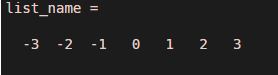
list_name = -3:3
Output:
Explanation: The command has generated a list of values from -3 to 3 having different between 2 consecutive elements as ‘1’.
Example #2
Code:
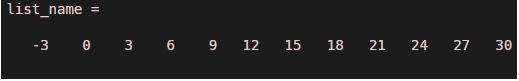
list_name = -3:3:30
Output:
Explanation: The command has generated a list of values from -3 to 30 having different between 2 consecutive elements as ‘3’.
Example #3
Code:
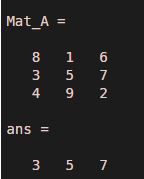
Mat_A = magic(3)Mat_A(2,:)
Output:
Explanation: The command has displayed the elements from the second row of the matrix ‘Mat_A’
Example #4
Code:
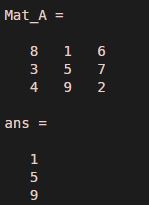
Mat_A = magic(3)Mat_A(:,2)
Output:
Explanation: The command has displayed the elements from the second column of the matrix ‘Mat_A’
Example #5
Code:
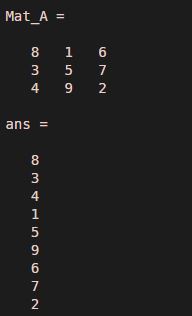
Mat_A = magic(3)Mat_A(:)
Output:
Explanation: The command has displayed the elements of the matrix ‘Mat_A’ in a single column.
Example #6
Code:
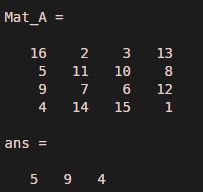
Mat_A = magic(4)Mat_A(2:4)
Output:
Explanation: The command has displayed the elements of the matrix ‘Mat_A’ indexed between 2 to 4.
Application of MATLAB Colon
Below are the applications:
1. Using colon to create a list
A vector with evenly-spaced numbers can be generated using a colon operator.
Code:
Mat_A =1:2:10
Output:
2. Creating a vector with only column format
The colon operator can be used to transform the input of the row vector type to that of the column vector type. The colon operator can also be used to create a column vector with reshaping or permute functions.
Code:
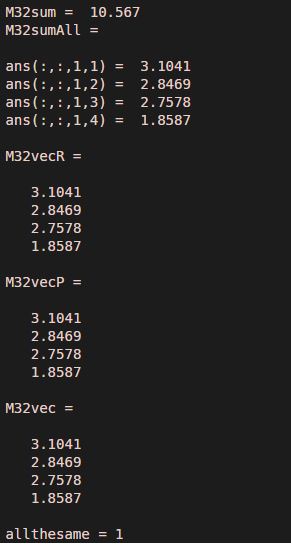
M = rand(3,2,6,4);
M32sum = sum(M(3,2,:))
M32sumAll = sum(M(3,2,:,:))
%Creating column vector using reshape method
M32vecR = reshape(M32sumAll,[],1)
%Creating column vector using %permute method
M32vecP = permute(M32sumAll, [4 1:3])
%Creating column vector using only colon operator
M32vec = M32sumAll(:)
allthesame = isequal(M32vec, M32vecP, M32vecR)
Output:
3. Maintaining the shape of an array during assignment operation
The application of the assignment operator in the assignment operation on the input matrix assures the shape of the array remains unchanged.
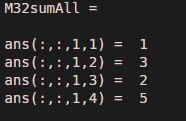
Code:
M32sumAll(:) = [1 2; 3 5]
Output:
4. Working with all the entries in specified dimensions
The colon operator can also be used to manipulate specific dimensions of the input array.
Code:
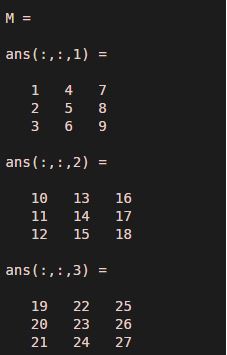
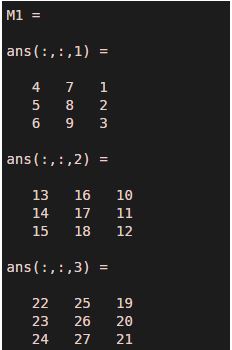
M = zeros(3,3,3)M(:) = 1:numel(M)M1 = M(:,[2:size(M,2) 1],:)
Output:
Explanation: The colon operator is used to redefine the indices of the elements in the input matrix ‘M’ and create a new input matrix ‘M1’.
5. Create Unit-Spaced Vector
Using a colon operator, a vector having a list of consecutive numbers within a specified range can be generated using the syntax li=j: k.
Code:
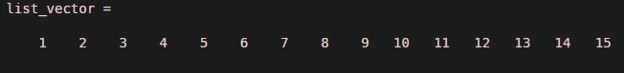
list_vector = 1:15
Output:
Explanation: Using a colon operator, a list of numbers from 1 to 15 is generated from the MATLAB command.
6. Create a Vector with a Specified Increment
Using the colon operator, a vector with a list of numbers having an equal difference between two consecutive numbers within a specified range can be generated using the syntax li=j:i: k.
Code:
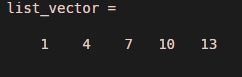
list_vector = 1:3:15
Output:
Explanation: Using a colon operator, a list of numbers from 1 to 15 with a common difference of 3 is generated from the MATLAB command.
7. Specify for-loop Iterations
Colon operator is also used in designing the looping operation in MATLAB programming.
Code:
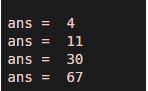
for m = 1:4
m^3+3
end
Output:
Additional point:
In case I being a non-integer and k is not equal to j+m*i, in the command form of li=j:i:k, floating-point arithmetic determines about colon, including the endpoint k or not.
If no scalar array is specified, then MATLAB assumes i:k as j(1): i(1):k(1).
li = colon(j,k) and li = colon(j,i,k) are rarely used alternate ways for the commands li=j:k and li=j:i:k respectively.While implementing class, these syntaxes can be used to apply operator overloading.
Linspaceexhibit similar behavior to that of colon operator. Logspace, the sibling function, is used to generate values being logarithmically spaced.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MATLAB Colon. Here we discuss an introduction to MATLAB Colon, syntax, examples, and application. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –