Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to TypeScript namespace
The following article provides an outline for TypeScript NameSpace. The Namespace comes up with a way of grouping functionalities logically. A logical grouping of functionalities is how typescript organizes and encapsulates the features that share the same characteristics throughout the flow. Basically, it encapsulates the objects sharing the same relationship in the script. It has different modules such as Interface, class, and Function that support this functionality in typescript. They are inbuilt into TypeScript means any declaration will go on the global scope variable. They are also called internal Modules. Naming collisions are resolved using the Typescript Namespaces.
Syntax
The syntax for TypeScript NameSpace is :-
A namespace can be created using the keyword namespace by the namespace name.
A curly brace is used that contains the information inside that. Be it Class, Interface, etc.
Syntax:
Namespace <name>
{
//Interface , class , etc.
}Working of TypeScript namespace
The NameSpace provides the space to encapsulate the logical data by writing it in a function. A namespace with a unique name makes a logical grouping of functions with the desired functions, making it accessible to use throughout TypeScript.
When these function, interfaces that we write inside that namespace provides with a logical meaning by combination and those can be used to write down the code line.
We use the keyword Export that exports the namespace function, making it visible outside the scope of the namespace. Once using the export statement, we can place it anywhere in the code and can work accordingly.
namespace abc {
export function Uppercase(str: string): string {
return str.toUpperCase();
}
}Using export will have this reference outside the scope of TypeScript.
Output:
declare namespace abc {
function Uppercase(str: string): string;
}ScreenShot:
Without Using export:
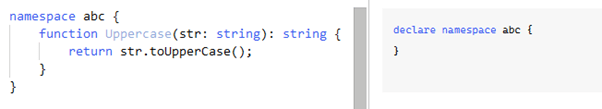
Using Export to change the scope:

To use the namespace components in another place, we first need to include the namespace using a pattern, i.e., inserting the reference path with ///.
We can also have a nested namespace; this allows us to define one namespace into another. We can access the member of the nested namespace using the dot(.) operator.
Example:
namespace Demo {
export namespace NestedDemo {
export class NestedClass {
public function1(p: number) {
return p + .60;
}
}
}
}ScreenShot:

Example
Let us see TypeScript NameSpace with some Example:-
Let us now create an interface in TypeScript with the name of Demo1.
This interface will have a method that can be used in the post or outside the scope of Typescript.
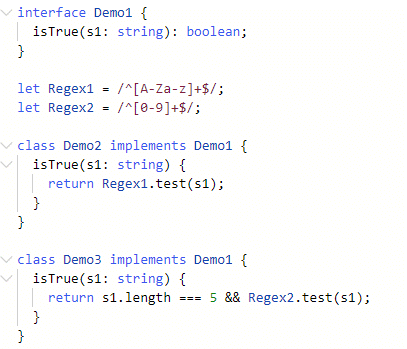
interface Demo1 {
isTrue(s1: string): boolean;
}Let’s create a Regex variable.
let Regex1 = /^[A-Za-z]+$/;
let Regex2 = /^[0-9]+$/;Create a class that implements the interface in the same namespace.
Demo2 is the name of the first class, and Demo3 being the name of the second one.
class Demo2 implements Demo1 {
isTrue(s1: string) {
return Regex1.test(s1);
}
}The first one checks the String with the regex, whether true or not, and the latter one checks it with a value.
class Demo3 implements Demo1 {
isTrue(s1: string) {
return s1.length === 5 && Regex2.test(s1);
}
}Screenshot:
Now let us create an object of the classes and check whether the string given input is matched or not.
We will make the object of both classes. And then, the object name is matched with the input, and the result is printed.
A for loop will help us match the elements in this.
let Demo4: { [s1: string]: Demo1 } = {};
Demo4["Number"] = new Demo3();
Demo4["Letters"] = new Demo2();
let sampleTest = ["This", "9333", "333"];
for (let s1 of sampleTest) {
for (let name in Demo4) {
let Matched = Demo4[name].isTrue(s1);
console.log(`'${s1}' ${Matched ? "matches" : "no match"} '${name}'.`);
}
}Screenshot:

This will print the matched elements in the console log of the type Script.
Output:
[LOG]: "'This' no match 'Number'."
[LOG]: "'This' matches 'Letters'."
[LOG]: "'9333' no match 'Number'."
[LOG]: "'9333' no match 'Letters'."
[LOG]: "'333' no match 'Number'."
[LOG]: "'333' no match 'Letters'."Full Code ScreenShot:

From this, we saw how a namespace works in TypeScript.
Rules and Regulation for namespace
Let us look over the rules and regulations required for writing a namespace in TypeScript.
- A namespace should have a unique name associated with it.
- It must start with the keyword namespace.
- It contains interfaces, functions giving a logical meaning.
- Use the export Keyword to use the function outside the scope of namespace.
- We can also merge namespace with another type of Decelerations. We can merge them with class, function, enum.
- The codes are organized in a TypeScript NameSpace.
- Namespaces are inbuilt in type Script, so variables are into the global scope.
- A namespace can span in multiple files.
- It removes the naming collisions.
We can also split the codes and encapsulate the code in TypeScript.
From the above article, we saw the rule for writing the code in TypeScript.
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw the use of NameSpace in TypeScript. We tried to understand how the namespace function works in TypeScript and what are uses at the programming level from various examples and classification.
We also saw the internal working and the advantages of having a namespace that we define for various programming purposes. Also, the syntax and examples helped us to understand much precisely the function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript namespace” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

