Updated June 2, 2023
Introduction to Timestamp to Date in MySQL
The following article provides an outline for Timestamp to Date in MySQL. Using various methods, you can convert a timestamp value into a date format in SQL. Some include using the FROM_UNIXTIME () function and the format function. The timestamp value can be an integer number that represents the number of seconds that have been passed from a particular date considered as the standard date for reference, which is the midnight time 12:00 of 1 January 1970, which does not involve the consideration of leap seconds in the calculation and is called as an epoch.
The integer value of the timestamp is converted in the date format of YYYY DD MM format by using a function called FROM_UNIXTIME (). Here we will see how we can implement the FROM_UNIXTIME () function to convert a value stored in a particular table in timestamp format and try to retrieve the corresponding date of that timestamp in MySQL with the help of an example.
Syntax of Timestamp to Date in MySQL
The syntax of the FROM_UNIXTIME () function in MySQL is as shown below:
FROM_UNIXTIME (UNIX timestamp value [, required format])In the above syntax, the terminologies specified are as described below:
- UNIX timestamp value: The UNIX timestamp value is the integer value that represents the timestamp of a particular time in seconds starting from the standard time of the first January 1970 and is treated internally in the database for timestamp value. This integer can also be the function UNIX_TIMESTAMP () output as this function also returns the UNIX timestamp value.
- required format: The required format is the optional parameter that can be supplied specifying the format of the date or time desired as the output. When not set, the default format considered is “YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss”, or it can be YYYYMMDDhhmmss. The retrieved default format depends on whether the FROM_UNIXTIME () function is used in the string context or numeric context.
Output:
The output of the FROM_UNIXTIME () function has the current session’s time zone considered as the time zone while displaying the date and time values.
Points to be considered:
In case we are using the FROM_UNIXTIME () function and the UNIX_TIMESTAMP () function together while trying to convert to date value from timestamp values in non-UTC time zones, there is a possibility of losing the data as the data might not get mapped properly as there is no mapping in a one-to-one way for both the directions.
How to Convert Timestamp to Date in MySQL?
- In order to convert the timestamp value in MySQL to a date value, we can make the use of FROM_UNIXTIME () function. In the first step, you can take one static integer value representing the UNIX timestamp value which means the number of seconds since 1 Jan 1970.
- Alternatively, you can take one column whose datatype is unix timestamp, storing this integer value of seconds. To convert these values of a column of static ones, we will need to specify the second parameter of the FROM_UNIXTIME () function to ‘%Y %D %M’ as we want the output to be in date format.
- The first argument will be the column’s name or static timestamp value that needs to be converted. The returned output value will be the string value consisting of the date value of the supplied timestamp value.
Example of Timestamp to Date in MySQL
Given below are the example of Timestamp to Date in MySQL:
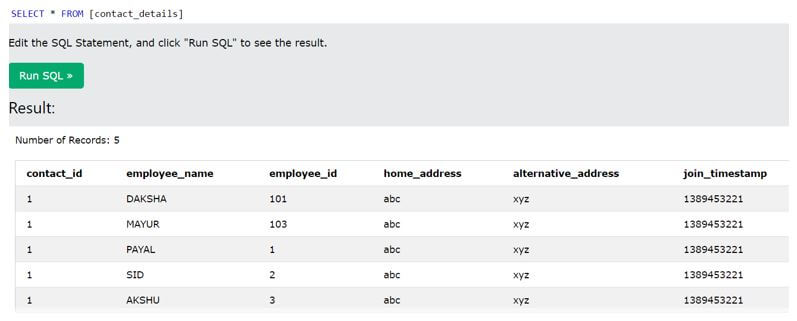
Let us consider one table with the name contact_details with one column named join_timestamp, which stores the integer value of the number format. The first step will be to retrieve all the values of the contact_details table to check its contents using the following query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM [contact_details] ;Output:
As we can see, the column join_timestamp contains all the integer values representing the UNIX timestamp value, which is the number of seconds from 1 Jan 1970. Thus, the FROM_UNIXTIME () function, when applied on the same column, gives the following output, and our query statement becomes as shown below.
Code:
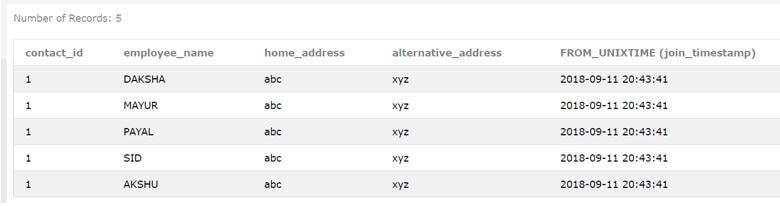
SELECT contact_id, employee_name, home_address, alternative_address, FROM_UNIXTIME (join_timestamp) FROM [contact_details] ;The output of the above query statement is as shown below, showing the default date time format value of the corresponding timestamp value stored in the join_timestamp column.
Output:
Now, we will see how we can retrieve only the date value from the timestamp value by using the FROM_UNIXTIME () function. This can be done by specifying the required format argument, which is the second optional argument to the FROM_UNIXTIME () function giving the date format as shown below.
Code:
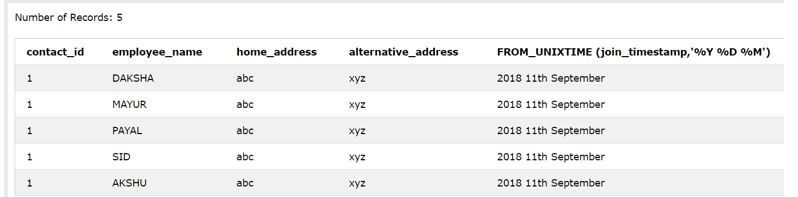
SELECT contact_id, employee_name, home_address, alternative_address, FROM_UNIXTIME (join_timestamp,'%Y %D %M') FROM [contact_details] ;The %Y is for the year, %D is for the date value, and the %M is for the month value in the date format. The output of the above query statement is as shown below, which retrieves only the date value of the timestamp value stored in the join_timestamp column of the contact details table.
Output:
We can also change the date format in which the date value needs to be retrieved. Let’s consider another example where we must convert the same value in the join_timestamp column into a different date format. The required format is the month, date, and year values. The month should be in string format displaying the month’s name and not the number.
Our query statement now changes to as shown below.
Code:
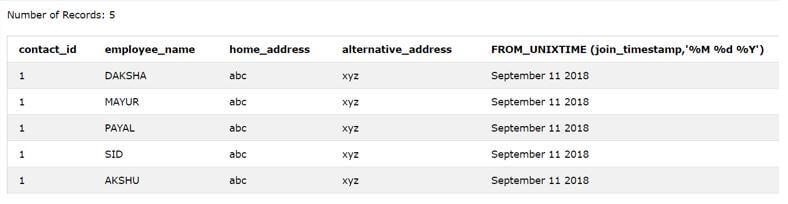
SELECT contact_id, employee_name, home_address, alternative_address, FROM_UNIXTIME (join_timestamp,'%M %d %Y') FROM [contact_details] ;The output of the above query statement is as shown below, with the date value retrieved in the required format.
Output:
Hence, our mission was achieved: to retrieve the date value from the time stamp in MySQL.
Conclusion
The FROM_UNIXTIME () function converts UTC’s timestamp value to the date value by specifying the appropriate date format as its second argument. The timestamp value should be a UNIX timestamp consisting of an integer representation of several seconds till the current time value from the standard timestamp of 1 January 1970.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Timestamp to Date in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.