Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Performance Tuning
MySQL Performance Tuning is a MySQL technique to enhance the MySQL queries to improve the database’s speed and performance. In MySQL, the special language SQL (Structured Query Language) is used to write commands or do programming in the server so that we can create, insert, update, modify, delete, and fetch data records from the MySQL database. SQL programming is implemented and found to be applied in many relational databases such as MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, Postgres, and others.
Applying the SQL query statements allows a programmer to easily perform functional server operations like CRUD events on data, creating triggers, etc. Therefore, it is beneficial to optimize MySQL databases properly as the quantity of data grows, and the technology gets progressively complex. This will ensure to bring end-user understanding and will minimize the substructure costs.
How to Perform Performance Tuning in MySQL?
- With the growing data dimensions that have given workload complexity, MySQL Performance tuning and database query enhancement are essential to maximizing system presentation and resource consumption.
- There may be several motives why the MySQL tuning process will be a bit difficult for the developers because, initially, it may require broad technical proficiency to code and recognize several execution strategies. It is the task of one who can utilize the knowledge while scripting clean and comprehensive MySQL statements.
- Besides its complication, the tuning is considered to be very time overwhelming. There are various benefits to it. Once the MySQL Tuning is done properly, the database will result in sensible performance and excessive functionalities with quick data retrieval, which ultimately reduces the cost and improves the data storage in the server. This performance tuning will improve the memory bandwidth, Disk seeks, reading and writing, CPU cycles, and network utilizations on query execution in the MySQL server, as these elements are the sources from which the system performance may be hampered or slow down.
Examples of MySQL Performance Tuning
Following are a few factors to be implemented for MySQL Performance Tuning and maintaining the database operations and query execution:
Example #1
Procedures for query optimization in MySQL.
We must follow the best practices to make the MySQL Performance Tuning process effective for database speed and maintenance.
a. Indexing all columns applied in WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY & JOIN clauses
An index uniquely evaluates the records from databases and allows the server to retrieve the results quicker from the MySQL queries executed.
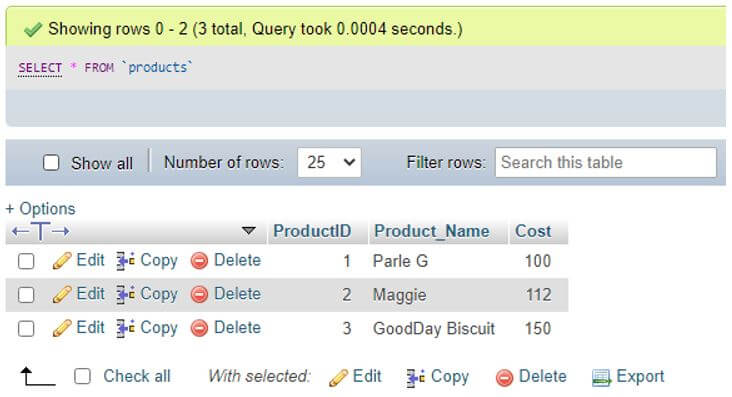
Suppose we have table Products, and we can create an index in MySQL using the query below:
Code:
select * from products;Output:
Syntax:
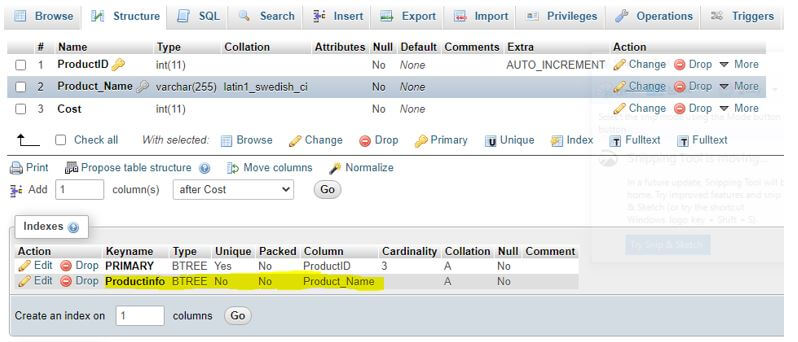
CREATE INDEX IndexName ON TableName(ColumnName1, ColumnName2,….);CREATE INDEX Productinfo ON Products (Product_Name);Output:
Improper indexing of queries may lead to table scans that will give locking-type problems and slow performance issues.
b. Escape using functions with columns
If a column has some predefined functions, then the MySQL database will not use the associated index.
For illustration, let us consider a query:
Code:
SELECT * FROM TableA WHERE UCASE(ColumnA) = 'XYZ' ;Due to the function UCASE(), the database will not apply the index on ColumnA. It would be best to build a new function-based index; otherwise, produce custom columns to optimize performance.
c. Not to use LIKE expression with a wildcard(%) at the start
The predicate such as LIKE ‘%ghj’ will cause a full table scan, leading to performance drawbacks.
For Example:
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE ColumnA LIKE '%GHJ';d. Escape pointless fields in the SELECT clause
We should specify the column names we need to fetch from the query instead of all the columns where some might not be necessary to be fetched using the SELECT * option. This may bring slow speed and execution load on the database.
e. Application of INNER JOIN rather than OUTER JOIN
We must apply outer join in MySQL only if required; otherwise, when used, not needed may reduce execution speed and hamper the performance of the database.
f. Adding, if necessary, the DISTINCT and UNION options
Without any main target, try to avoid using UNION and DISTINCT MySQL operators, which will bring undesirable sorting and slow server execution. But we can use UNION ALL instead of UNION to increase efficiency.
g. Use of ORDER BY MySQL clause for a sorted list
For an impactful result, we can use the ORDER BY clause to order the rows in the type of the used column that gives advantages for tuning performance.
h. Escape used of NULL values
We may have some column values containing NULL inputs that may harm the MySQL results during the query execution of all records. For this, we can use the IFNULL statement too to provide alternative results.
Example #2
Avoid the use of MySQL as Queue.
Using queues may affect the database performance by increasing workload and not completing the task as it creates additional load time without any reason to manage the database resources.
Example #3
I am accepting the four MySQL significant resources.
We need to work on the four primary resources that make the database function properly to have performance tuning. They are Memory, CPU, Network, and disk. We have to be careful in selecting hardware and solving any problems with it to avoid affecting the server’s performance.
Example #4
Pagination MySQL Queries.
Pagination used in applications tends to show server slow speed. This can be optimized with a user interface to display a link to the next page instead of showing the precise number of pages and irrelevant links to separate pages.
Example #5
To improve MySQL Subqueries.
Subqueries give intense work to the server, and we must prefer to use JOIN clauses as an alternative to help in database optimization.
Example #6
Query Cache in MySQL.
Caching the contents in a database like SELECT query text while fetching the result is essential in maximizing performance.
We can do this by:
Code:
SET GLOBALquery_cache_size = 30000;Example #7
Using Memcached for Caching in MySQL.
Memcached helps to speed up websites containing massive dynamic databases using distributed memory caching system. Here, the database objects are sorted in Dynamic Memory to decrease the pressure on the server.
Conclusion
MySQL Performance regulation is responsible for crafting effective query statements and provides a well-structured design of your database that will be simple to be maintained. Not only this, but it also constrains the website or software applications. The MySQL Performance Tuning process delivers tools that can support database professionals to swiftly recognize bottlenecks and inadequate target operations by analyzing query code plans and eradicating any predicting games.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Performance Tuning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.