Difference Between Tax Credit and Tax Deduction
Income tax is a crucial part of human civilization. Paying taxes on time to the Government makes a good citizen, and paying taxes by taking benefits makes a smart citizen. Tax evasion has been seen everywhere in the world and in every era of human civilization. To avoid being criminalized, one should be smart enough to understand taxes paid to the Government. Tax credit vs tax deduction is an important topic for learning tax planning.
Every year, millions of taxpayers search for tax deductions vs tax credits, which can help them save on taxes. Pay attention to the fact that Tax Credit vs Tax Deduction is separate. One should use Tax Credit vs Tax Deduction facilities the Government provides to save money.
What is Tax Deduction?
A tax deduction results from a tax-deductible expense or exemption that reduces the taxpayer’s taxable income. A common tax deduction on federal income tax returns is a personal exemption. How it is calculated – if your income was $ 1,00,000 and a personal exemption of $ 8,000. Your exemption would reduce your taxable income by $ 8,000. So, your taxable income will be $ 92,000.
Assesses can claim deductions on various expenses:
- Life insurance premiums.
- Donations to institutes permitted by the Government etc.
- Medical expenses for self and family.
- Contribution to funds permitted by the Government.
- Charitable donations.
- Mortgage loan interest.
- Medical and dental expenses
- Tuition and fees.
- Contributions to a traditional IRA.
- Contributions to health savings accounts (HSAs).
- Mileage for business travel.
- Unreimbursed business expenses.
- Moving expenses to start a new job.
- Job search expenses.
- Teacher’s educational expenses.
- Property and real estate taxes.
Each country has a predefined basket of deductions. The government decides these deductions for the benefit of its citizens. For example, In India, section 80C permits the deduction for tax savings.
What is Tax Credit?
A tax credit is subtracted from tax liabilities. A common tax credit example is a child tax credit. If you have a qualifying child, you can avail of a tax credit of up to $ 1,000.
How it is calculated is if your income is $ 1,00,000, and you have a personal exemption of $ 8,000. Your exemption would reduce your taxable income by $ 8,000. So, your taxable income will be $92,000. Let’s assume a 30% tax rate (ignoring tax slabs for understanding), so your tax liabilities will be $ 92,000 * 30 % = $ 27,600. Now you can claim $1,000 as a tax credit, so your effective tax will be $ 27,600 – $ 1000 = $ 26,600
1. Some Tax Credits Made Available in India
- If income has been earned outside India and a tax paid on it in that country, then a tax credit can be claimed in India for the tax paid outside.
- Anyone with an income of less than Rs. 5 lakhs per annum but liable to pay taxes can claim a tax credit of Rs. 2,000.
- Citizens who are above the age of 65 years can avail of a tax credit of up to Rs. 20,000,
2. Some Other Tax Credits Available Outside India
- Even those with disabilities falling under a particular income bracket can receive tax credits.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit (to reduce the cost of childcare or taking care of an old parent)
- Adoption Credit (for adoption expenses).
- Child Tax Credit (for parents).
- Premium Tax Credit (for people who purchased health insurance through the federal marketplace).
- Saver’s Credit (for people who contributed to a tax-advantaged retirement account).
- Lifetime Learning Credit (for higher education expenses incurred).
Each country has predefined guidelines for tax credits and a basket of predefined tax credit items.
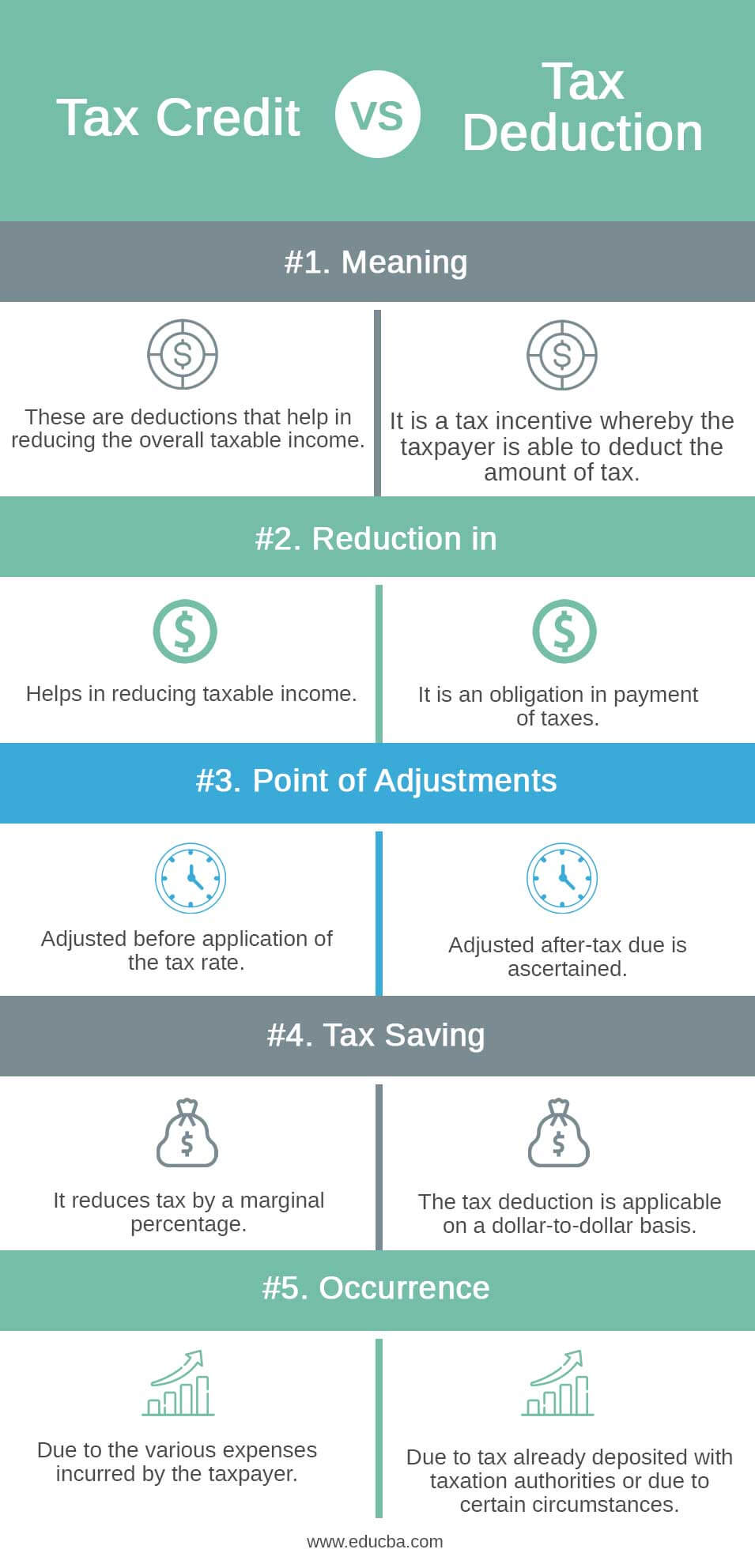
Tax Credit VS. Tax Deduction Infographics
Below are the top 5 differences between Tax Credit vs. Tax Deduction.
Key Differences Between Tax Credit VS. Tax Deductions
Even though you can save tax by using Tax Credit vs Tax Deduction facilities provided by the government, there can be a break in tax savings as almost every item has a maximum limit on tax savings. However, by studying exceptions, you can claim tax credits & tax deductions. This is the point where tax planning becomes somewhat complicated.
As an example, imagine this scenario:
- Your filing status is jointly married, with two dependent children under 18.
- You earned $55,000, all from your jobs.
- Your tax liability, before figuring allowable credits, is $1,500.
- Your two children allow for a Child Tax Credit of $2,000 ($1,000 each).
- But the child credit is limited to your tax liability because it’s non-refundable, in this case, $1,500.
- Normally, you’d have to forfeit the remaining $500 and not receive a $500 refund.
However, the exception to the rule allows you to slide the forfeited $500 over to the Additional Child Tax Credit, which means you have to do some math to get a nice refund. The Additional Child Tax Credit lets you claim the lesser of two amounts: the amount you might have to forfeit (in this case, $500) or 15% of your earned income greater than $3,000.
That’s where the tax code gets complicated again, so look at the calculation: 15% of your earned income more than $3,000 is $7,800 ($55,000 – $3,000 = $52,000; $52,000 * 15% = $7,800). Since $500 is less than $7,800, that’s the amount you’re allowed to take. Thus, you now have an extra $500 refund instead of forfeiting the credit.
Tax Deduction vs. Tax Credit: Comparative Table
Let us examine some of the differences between Tax Credit vs Tax Deduction:
| Basis of Comparison | Tax Deduction | Tax Credit |
| Meaning | These are deductions that help in reducing the overall taxable income. | It is a tax incentive whereby the taxpayer can deduct the amount of tax. |
| Reduction in | It helps in reducing taxable income | It is an obligation to pay taxes |
| Point of adjustments | Adjusted before application of the tax rate. | Adjusted after-tax due is ascertained |
| Tax saving | It reduces tax by a marginal percentage | The tax deduction is applicable on a dollar-to-dollar basis. |
| Occurrence | Due to the various expenses incurred by the taxpayer | Due to tax already deposited with taxation authorities or due to certain circumstances |
Conclusion
Both the tax credits vs. tax deductions help reduce the overall tax burden on taxpayers and help them save the tax. However, the tax credit is more favorable than tax deductions, as the former directly lowers tax liabilities. Hence, it saves more tax, whereas the latter only reduces the tax liabilities by a nominal rate.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tax Credit vs Tax Deduction. We discuss the tax Credit and Tax Deduction differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –