Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL ROUND
T-SQL ROUND is a function with syntax that accepts three parameters such as number, decimal point, and operations. The number is a required parameter to provide a rough value figure. Decimals are the number of decimal points to figure out the number, and operation is the optional parameter that can be zero rather than zero. Hence if it is zero, it figures out the output as the number of decimals, and if it is any value, then the ROUND function() can truncate the output to the number of decimal points.
What is T-SQL ROUND?
The ROUND() is the function in T-SQL that can be used to figure out a number to a particular number of decimal points, it can always give back a value, and if the value of the operation is negative and more significant than the number of digits before the decimal point, the ROUND can give back a zero value in the output. If the value which is other than zero has been specified, then it may truncate a numeric expression; it also gives back a numeric value that can figure out the particular length, so we can say that the ROUND() function can give back values that are figure out to the nearest value depend on the length, this function can also be able to utilize different values for getting various values or as per the needs.
T-SQL ROUND Function?
The ROUND() is the function in T-SQL that can give back a value nearest to the number of decimal places. The ROUND() function can be utilized to figure out a particular number to a decimal point; it can accept all kinds of numbers, which may be negative, positive, or zero. It can also accept fraction numbers, which always give back a number after being rounded to a decimal point.
Syntax of ROUND() Function in T-SQL
"ROUND (numbers, decimal_points, operation)"Where,
- numbers: It is the number that can be figured out to be a number.
- decimal_points: It is the number of decimal points that are figured out; this value can be positive or negative; if we try not to use this parameter, then this ROUND() function will figure out a number to the decimal points so that this parameter will be the required parameter.
- Operations: The optional parameter can be zero or a numeric value other than zero.
Some things are needed to keep in mind:
- First, if the value of the operation parameter is zero or not given, then the ROUND() function can figure out the output to the number of decimal points.
- If the value in the operation parameter is rather than zero or numeric, then the ROUND() function can truncate the output to the number of decimal points.
Examples of T-SQL ROUND
Let us see the examples of T-SQL ROUND using the ROUND() function:
Example #1
To get back a round number up to the following two decimal points.
Code:
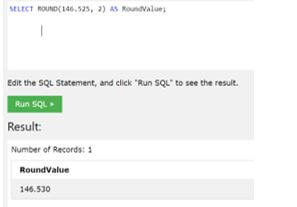
SELECT ROUND (146.525, 2) AS RoundValue;Output:
In the above example, we have used a value ‘146.525,’ and we try to figure out a value from the provided value in which we have found a rounded value up to two decimal points, as shown in the screenshot.
Example #2
To get back a number up to the following three decimal points with operational argument 1, truncate the particular number to the provided decimal points, i.e.,3.
Code:
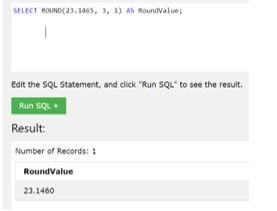
SELECT ROUND(23.1465, 3, 1) AS RoundValue;Output:
In the above example, we have taken a value ’23.1465,’ and we want to figure out a number up to the three decimal points in which we can refer to the output shown in the screenshot.
Example #3
Using a ROUND() function with a variable to figure out a number to -2 decimal place.
Code:
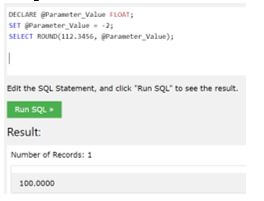
DECLARE @Parameter_Value FLOAT;
SET @Parameter_Value = -2;
SELECT ROUND(112.3456, @Parameter_Value);Output:
In this example, we have to figure out a number by setting the parameter value, as the provided value is 112.3456, so rounding the value up to two decimal points, we get a value as shown in the output.
Example #4
To return a rounded number to the zero decimal point.
Code:
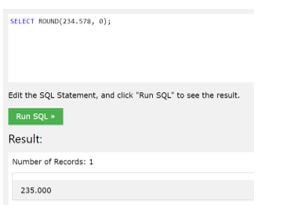
SELECT ROUND (234.578, 0);Output:
In this example, we have used a value as 234.578, and we have to round that value up to the 0 decimal points so you can refer to the output given above.
Example #5
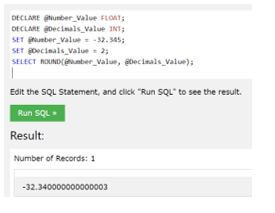
An example of the ROUND() function uses variables to figure out a number to the three decimal points.
Code:
DECLARE @Number_Value FLOAT;
DECLARE @Decimals_Value INT;
SET @Number_Value = -32.345;
SET @Decimals_Value = 2;
SELECT ROUND (@Number_Value, @Decimals_Value);Output:
In this example, we have used a negative value as ‘-32.345’, that value to be rounded up to the two decimal points, and we get the result as shown in the screenshot.
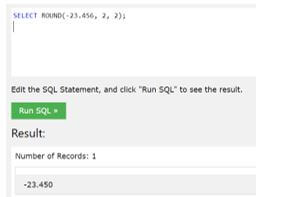
Example #6
To return a number to the following two decimal points using operational parameter 2, which can truncate the particular number to the provided decimal points, i.e., 2.
Code:
SELECT ROUND (-23.456, 2, 2);Output:
In the above example, we used a negative number ‘-23.456’, which can be rounded up to two decimal points using two as an operational parameter.
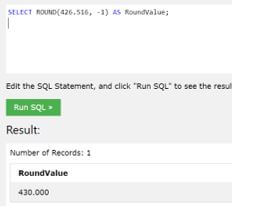
Example #7
To get back a number to -1 decimal points.
Code:
SELECT ROUND (426.516, -1) AS RoundValue;Output:
In this example, we have used a negative value in which we want a rounded value, as shown in the screenshot.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the ROUND() is the function that can be used when we want the output in decimal places in which it can figure out the output nearest to the decimal points; we have also seen the T_SQL ROUND() function and T-SQL ROUND examples in detail.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL ROUND. Here we discuss the introduction, T-SQL ROUND function? and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –