Updated May 20, 2023
Introduction to SQL EXCLUDE
In SQL, in order to EXCLUDE certain rows from being returned by a SELECT query, we use some restricting or excluding conditions based on some criteria. EXCLUDE conditions in SQL usually appear in the WHERE clause of the statement or in the HAVING clause of an aggregate query. Some commonly used EXCLUDE operators in SQL are NOT, NOT IN, NOT LIKE, ‘!=’, EXCEPT, NOT NULL, etc.
You must wonder what happens when you mention a restricting condition in a SELECT statement. It is pretty simple. When the SELECT query runs, the database server applies the restricting condition on each row fetched while searching. If the row meets the mentioned condition, it is included.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing exclude queries in SQL are as follows:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name1 conditional_operator comparision_expression;If you want to write exclude queries using the EXCEPT operator, the syntax is as follows :
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, ...
FROM table_name1
EXCEPT
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, ...
FROM table_name2;Parameters:
The parameters used in the syntax mentioned above are as follows :
- column_name1, column_name2, …: columns or field names that must be fetched for the final result set.
- table_name1, table_name2: database tables from which the columns mentioned above have to be fetched.
- conditonal_operator: operators such as (NOT IN, NOT LIKE, NOT NULL, NOT EQUAL TO (!=), etc.)
- comparison_expression: subquery or expression based on which exclusion has to be done.
Examples of SQL EXCLUDE
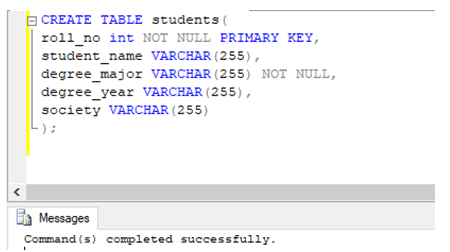
To illustrate the excluding or restricting specific rows in SQL, let us create a dummy table called “students.” We can use the following CREATE statement to create the student’s table.
CREATE TABLE students(
roll_no int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_name VARCHAR(255),
degree_major VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
degree_year VARCHAR(255),
society VARCHAR(255)
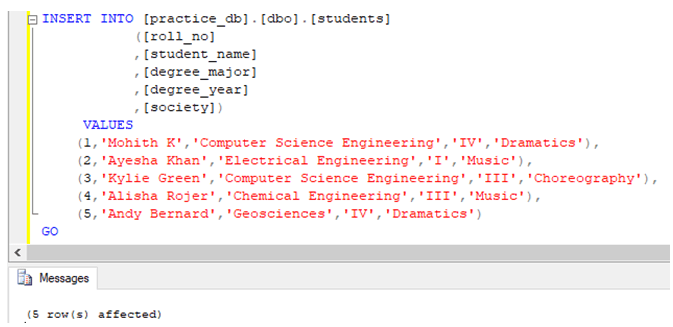
);Having created the student’s table. Let us insert a few records in it to work with.
INSERT INTO [practice_db].[dbo].[students]
([roll_no]
,[student_name]
,[degree_major]
,[degree_year]
,[society])
VALUES
(1,'Mohith K','Computer Science Engineering','IV','Dramatics'),
(2,'Ayesha Khan','Electrical Engineering','I','Music'),
(3,'Kylie Green','Computer Science Engineering','III','Choreography'),
(4,'Alisha Rojer','Chemical Engineering','III','Music'),
(5,'Andy Bernard','Geosciences','IV','Dramatics')
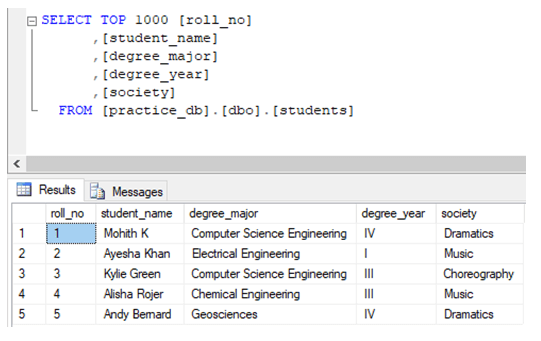
GOThe data in the students table looks something as follows:
Now we are all set to try some examples of excluding rows in SQL.
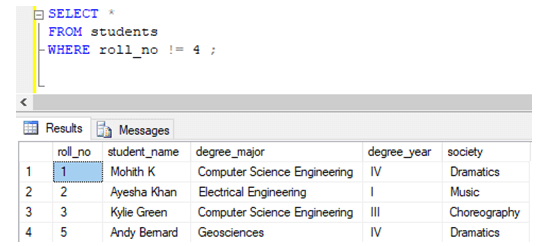
Example #1
Exclude rows using NOT EQUAL to operator
Find details of all the students excluding students with roll_no 4.
SELECT *
FROM students
WHERE roll_no != 4 ;
Example #2
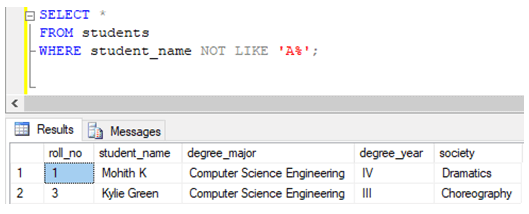
Exclude rows using the NOT LIKE operator.
Find details of all the students excluding student whose name starts with A.
SELECT *
FROM students
WHERE student_name NOT LIKE 'A%';Example #3
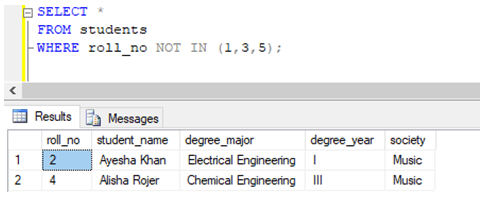
Exclude rows using the NOT IN operator
Find details of all the students, excluding students whose roll_no is not 1, 3, or 5.
SELECT *
FROM students
WHERE roll_no NOT IN (1,3,5);Example #4
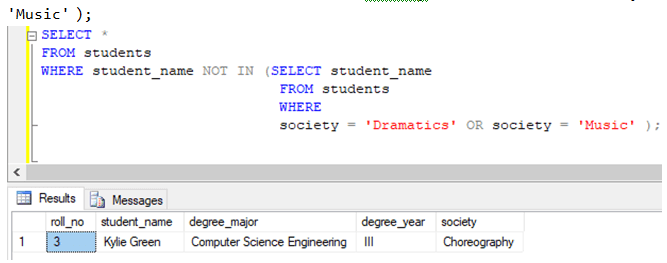
Exclude rows using the NOT IN operator with subqueries on the same table.
Find details of all the students, excluding students from the ‘Dramatics’ or ‘Music’ society.
SELECT *
FROM students
WHERE student_name NOT IN (SELECT student_name
FROM students
WHERE
society = 'Dramatics' OR society = 'Music' );Exclude rows using the NOT IN operator with subqueries on a different table.
To illustrate this, let us create a table called “home_town” that contains details about students’ home cities in the student’s table.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[home_town](
[roll_no] [int] NOT NULL,
[home_city] [varchar](50) NULL
)
INSERT INTO [practice_db].[dbo].[home_town]
([roll_no]
,[home_city])
VALUES
(2, 'New York'),
(3, 'New Jersey'),
(5, 'Denver')
GOExample #5
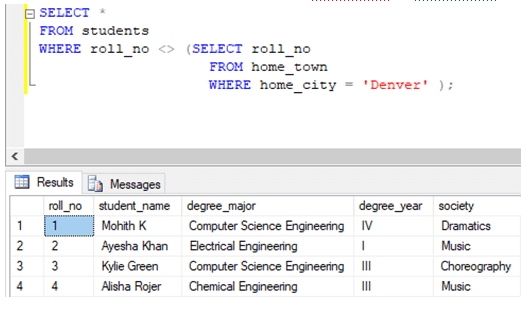
Find details of all the students, excluding students whose roll_no is not in the list of roll_nos where the home_city is ‘Denver.’
SELECT *
FROM students
WHERE roll_no <> (SELECT roll_no
FROM home_town
WHERE home_city = 'Denver' );Example #6
Exclude rows with NULL values from a LEFT / RIGHT JOIN
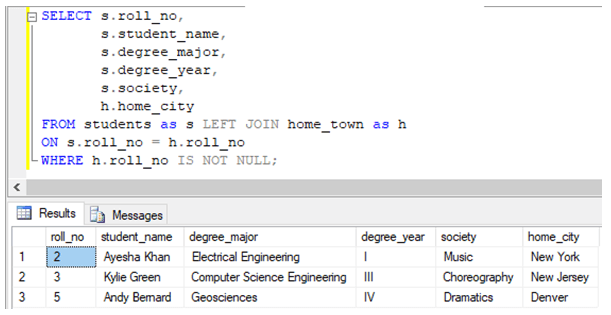
Find the roll_no, student_name, degree_major, society, and home_city for students, excluding rows where home_city is NULL or does not exist.
SELECT s.roll_no,
s.student_name,
s.degree_major,
s.degree_year,
s.society,
h.home_city
FROM students as s LEFT JOIN home_town as h
ON s.roll_no = h.roll_no
WHERE h.roll_no IS NOT NULL;Example #7
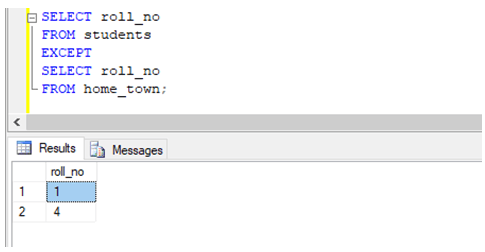
Exclude rows using EXCEPT operator.
We can use EXCEPT operator to exclude rows present only in the results of the first select statement but not in the second.
Find the roll_no of all the students except those mentioned in the home_town table.
SELECT roll_no
FROM students
EXCEPT
SELECT roll_no
FROM home_town;Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- It helps limit the number and kind of rows that can make it to the final result set.
- It helps to extract and insert only relevant results when using SQL queries, such as SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
Conclusion
To restrict the kind and number of rows a SELECT query should return, we use some exclude conditions that work as filter criteria. These filter criteria are mentioned in the WHERE clause of SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL EXCLUDE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.