Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL Loop
T-SQL loop is defined as the loops that have been utilized to recurrent the implementation of more than one statement within a particular period, which can also be called control statements, in which in the T-SQL, the looping statement has been adjusted for replicate implementation of the SQL statements or block of statements, in which that statements can be implemented repeatedly up to the particular condition will get accurate. The implementation of the statements by using the ‘WHILE’ loop can be managed from inside the loop with the help of three arguments: Boolean expression, ‘BREAK’ and ‘CONTINUE’ keywords.
What is T-SQL Loop?
The T-SQL can execute the ‘WHILE’ loop by authorizing us to duplicate the specific code while the loop condition detains; if we want another loop, then we can re-produce them with the help of the WHILE loop, so loops can be frequently used in which queries can perform most of the task. Still, sometimes loops can be instrumental and can make our life easier.
Usually, there are three types of loops:
- WHILE: If the WHILE loop condition is true, then the inside loop code has been implemented; the WHILE loop can provide the advantage of implementing the SQL statements repeatedly until the particular conditions have provided the result.
- DO…..WHILE: This loop also works as the WHILE loop, but in this statement, the loop condition has been carried out at the end of the loop, WHILE loop and DO…WHILE loop both are same and the loop can be iterated till the conditions.
- FOR: This loop can be used when we want to run the code inside the loop for the number of iterations; we can also alter how many times the loop can be executed.
T-SQL Server Loop
The server loop is the group or set of conditions that can be utilized repeatedly while implementing the SQL statement or block of the statement; the statements can be executed until the given condition is true, and the implementation of the statement in the WHILE loop can be managed inside the loop by using BREAK and CONTINUE keywords, the SQL server can allow repeating the specific code in the WHILE loop, and looping conditions can handle it.
Let us see the T-SQL server loops, in which let’s consider we have a WHILE loop at allocation.
Code:
WHILE (condition)
BEGIN
{----Body of the statement-----}
END;From the above statement, we conclude that when the WHILE loop conditions are true, then BEGIN—END block has been implemented, and if we are discussing the SQL server loop, then we can say that we have an attachment and we can able to make use of them in the WHILE loop.
Let us see the above by using the example:
Code:
DECLARE @i INTEGER;
SET @i = 1;
WHILE @i <= 10
BEGIN
PRINT CONCAT ('Pass...', @i);
SET @i = @i + 1;
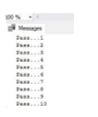
END;Output:
In the above example, we have stated the variable as @i and placed the value that is 1; if the surviving value of the variable is <=10, then we can enter it into the looping body, and statements have been executed whenever we try to enter into the body, it will increment @i by 1, in this way we can say that the value of variable @i will be ten at some places and that can stop the loop for running over and over again.
Examples of T-SQL Loop Statement
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
By utilizing BREAK and CONTINUE statements using nested IF…ELSE and WHILE.
In this example, we have tried to use the BREAK and CONTINUE keyword, and also we have used the nested IF…ELSE and WHILE statement, BREAK statement has been utilized in the T-SQL WHILE loop to instantly terminate the surviving iteration loop if there are various conditions, generally IF…ELSE statement has been used to verify whether the conditions have occurred or not. The CONTINUE keyword can be utilized in a T-SQL statement with a WHILE loop in which it can stop the surviving iteration of the loop when there is a specific code available. Then the new iteration will begin, and if we want to write even numbers only then WHILE loop has been used, we can use the CONTINUE statement to control such conditions.
Code:
USE AdventureWork2013;
GO
WHILE (SELECT AVG(RecordPrize) FROM Production.Product) < $400
BEGIN
UPDATE Production.Product
SET RecordPrize = RecordPrize * 2
SELECT MAX(RecordPrize) FROM Production.Product
IF (SELECT MAX(RecordPrize) FROM Production.Product) > $600
BREAK
ELSE
CONTINUE
END
PRINT 'Extreme for the vendor to tolerate';Output:
In this example, the WHILE loop can double the prize if the average RecordPrize is less than $400. After that, it can select the maximum prize, and also, if the maximum prize is less or similar to the $600, then the WHILE loop can restart. The prize will get doubled so that such loop can do the prize doubles until the prize receives a maximum award greater than $600, and after that, the WHILE loop can terminate, giving the message.
Example #2
By utilizing WHILE in the cursor.
Code:
DECLARE @StudentID as NVARCHAR (255)
DECLARE @Subject as NVARCHAR (55)
DECLARE Student_Cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT LogID, JobRole
FROM AdventureWorks2013.HumanResource.Student
WHERE JobRole = 'Marketing Professional';
OPEN Student_Cursor;
FETCH NEXT FROM Student_Cursor INTO @StudentID, @Subject;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
Print ' ' + @StudentID + ' '+ @Subject
FETCH NEXT FROM Student_Cursor INTO @StudentID, @Subject;
END;
CLOSE Student_Cursor;
DEALLOCATE Student_Cursor;
GOOutput:
In the above example, we have tried to utilize the @@FETCH_STATUS to manage the activities in the WHILE loop.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the WHILE loops can be used for placing conditional statements so they can have a body of the statement; if we have to execute a statement, then the loop can be used, we have also seen the definition of T-SQL, T-SQL server loop, and examples related T-SQL loop.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL Loop. Here we discuss the introduction, T-SQL server loop, and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –