Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL INSERT
T-SQL is a Transact SQL. It is an extension of the SQL language. Similar to SQL, we have data types, functions, indexes, and procedure concepts in the T-SQL. It is a Microsoft product. SQL stands for structured query language. SQL (structured query language) is common for all RDBMS.
Structured query language (SQL) stands as an intermediate interaction to the databases. We use commands by which we get data from the database. It has INSERT, SELECT, DELETE, DROP, TRUNCATE, and many other commands related to the actions to be done with the data.
SELECT command selects the data from the table or tables based on the condition. Insert command is used to insert data into the table. Delete command is used to delete a specified row from the table based on the condition. Drop is to delete the table along with the schema totally; we can delete all the rows using the Truncate command as well. In the Truncate command case, the table schema won’t be deleted from the database.
Syntax:
Let us consider the Insert command syntax in T-SQL; – As T-SQL insert is an extension of SQL language, the syntax is similar to SQL.
There are two ways we can determine they are stated below:
1.
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME [(column_name1, column_name2, column_name3,...column_nameN)]
VALUES (col1_value, col2_value, col3_value,...colN_value);Above, we determine the column list as well. If we don’t specify the column and insert it takes the value to ‘NULL’
2.
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME VALUES (col1_value, col2_value, col3_value,...colN_value);Above syntax, all the column data should match, not an error will be thrown.
How Insert done in T-SQL?
Now let us consider the above two syntaxes and try to insert them into the table.
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME [(column_name1, column_name2, column_name3,...column_nameN)]
VALUES (col1_value, col2_value, col3_value,...colN_value);Let us create a table and use the above syntax format and insert data into the table: –
create table Test_insert_command
(
shop_id int,
product_id int,
brand_id int,
Shop_name varchar(20),
quantity int,
price int
);Now let us insert data into the table:
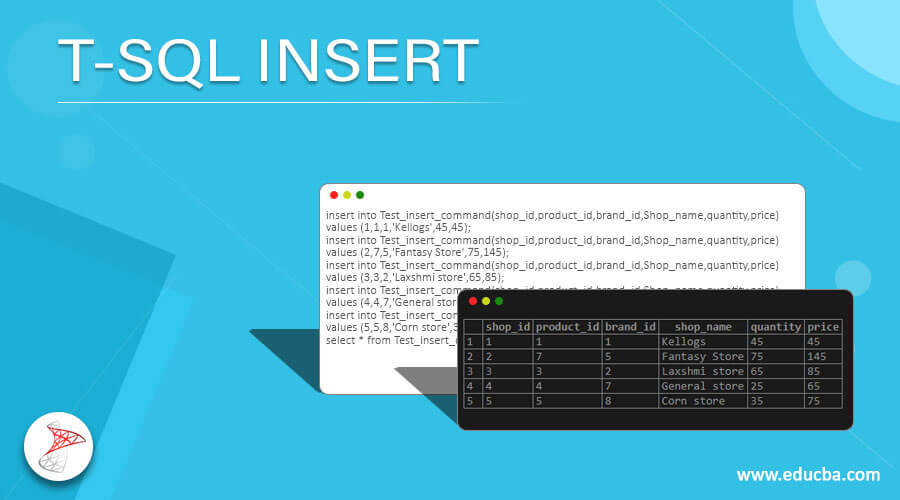
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name,quantity,price)
values (1,1,1,'Kellogs',45,45);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name,quantity,price)
values (2,7,5,'Fantasy Store',75,145);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name,quantity,price)
values (3,3,2,'Laxshmi store',65,85);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name,quantity,price)
values (4,4,7,'General store',25,65);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name,quantity,price)
values (5,5,8,'Corn store',35,75);
select * from Test_insert_command;In the above insert statement’s we have given all the values and inserted them into the table. The result will be as below:

Now let us pass only a few columns of data and see the output:
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name)
values (6,1,1,'Kels Store');
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name)
values (4,7,5,'Paradise Store');
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name)
values (6,3,2,'Luxury store');
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id,Shop_name)
values (1,4,7,'General store');
select * from test_insert_command;Output:
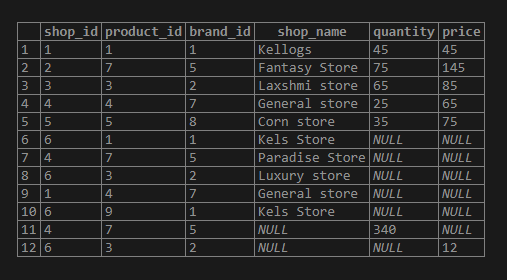
As no data is inserted in the column quantity, price the values are inserted as NULL.

Now let us change the order and insert the data.
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,brand_id,Shop_name,product_id)
values (6,1,'Kels Store',9);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id, quantity)
values (4,7,5,340);
insert into Test_insert_command(shop_id,product_id,brand_id, price)
values (6,3,2,12);
select * from test_insert_command;Output:
Now let us insert in the below format:
Syntax:
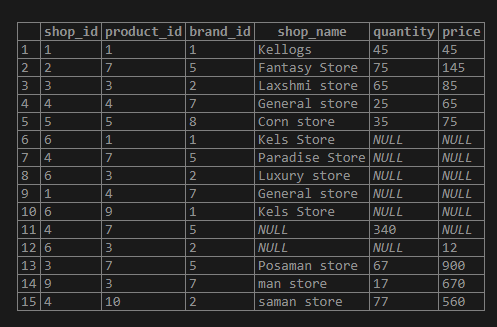
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME VALUES (col1_value, col2_value, col3_value,...colN_value);Query:
insert into test_insert_command values(3, 7, 5,'Posaman store', 67, 900);
insert into test_insert_command values(9, 3, 7,'man store', 17, 670);
insert into test_insert_command values(4, 10, 2,'saman store', 77, 560);
select * from test_insert_command;Output:
Example
Now let us see another example for the insert command:
create table test_insert
(
stud_id int,
stud_mark int,
stud_subject varchar(10)
);1. Insert data into the table:
insert into test_insert(stud_id,stud_mark,stud_subject)values (1, 89,'English');
insert into test_insert(stud_id,stud_subject,stud_mark)values (6,'English', 78);
insert into test_insert(stud_subject,stud_id,stud_mark)values ('English', 4, 89);
insert into test_insert values (8, 69,'English');
insert into test_insert values (9, 49,'English');
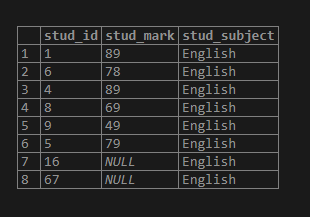
insert into test_insert values (5, 79,'English');Let us insert few more rows and perform Select statement for the above table:
insert into test_insert(stud_id,stud_subject)values (16,'English');
insert into test_insert(stud_subject,stud_id)values ('English', 67);
select * from test_insert;Output:
Conclusion
Similar to SQL, we have data types, functions, index, and procedure concepts in the T-SQL. It is a Microsoft product. SQL stands for structured query language. SQL (structured query language) is common for all RDBMS.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “T-SQL INSERT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

