Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL Stuff
T-SQL stuff is defined as it is a function that can remove a section of a string and then it can add another section into the string which can begin at a particular state, it can remove the particular span in the first string and at the beginning state after that, it can add a second string within the first string, it can accept four arguments, ‘string’ can be modified, ‘start’ is the state in the string to begin for removing the characters, length is the number of character removed from the string, and new_string is a string which can be added at the beginning state.
What is T-SQL STUFF?
The STUFF() is the function that can be used to remove a section of a string and to add a new substring from its provided beginning position in T-SQL, this function can perform tasks as it can change the date or time format, also it can add or remove the number of characters from the given string as it can accept the four arguments through which we can able to provide the input string, the starting position from which we can able to delete the string also we can able to give the length which can say how much characters we need to delete from the string, and it can return the character string if we have provided the character string which is supported by the character data type and it will give back the binary data if the provided string is supported by the binary data type.
Using T-SQL STUFF()
We can utilize the STUFF() function for performing the following tasks,
- To remove the characters from the string for that we have to substitute the aggregate characters by using the length argument, but if we have used the zero substitute then it will not allow deleting characters from a string.
- We have to identify the beginning stages within the string from where we can have the number of characters and that can be described with the help of length arguments which we need to remove.
- We also have to define the substitution for the string that we need in the new argument so that the new string can be renewed at the beginning state.
- As we know the syntax for the STUFF () function is also given below,
"STUFF (origin_string, begin, length, add_string)"So, let us see how this function can delete the zero characters when having beginning position ‘1’,
DECLARE @origin_string VARCHAR(50);
SET @origin_string = 'SQL Server';
SELECT STUFF(@origin_string, 1, 0, 'Windows') AS 'STUFF function';- So, in the above example, we have used the variable with VARCHAR datatype and within the string, we have to STUFF ‘Windows’ word at the ‘1’ position without deleting any record.
- By using the STUFF () we can able to add one string into another string and also, and we can able to convert the date and time format.
- We can also able to delete or cut down the specific string and insertion of the other string also can be done by using the STUFF () function.
T-SQL STUFF() Function
In T-SQL STUFF() is the function is used to remove the segment of characters from the beginning string and after that, it can add the series of characters within the source string which can begin at the particular position, in which we can say that the STUFF() function has been utilized to remove a series of provided length of characters from the beginning string and adding the provided series of characters from the particular beginning index.
Syntax:
STUFF(origin_string, begin, length, add_string)where,
- origin_string: It is the source string that is to be modified.
- begin: It is a state in a string to begin to start the removing some characters.
- length: It is the integer value that can describe the number of characters for removing, if the value of length is negative then it can give back a null string.
- add_string: It is an expression related to the character data in which the value of it can be constant, variable, or column, in which it can add a new string within the string at the beginning position.
T-SQL Stuff Examples
There are some examples given below by using the STUFF() function,
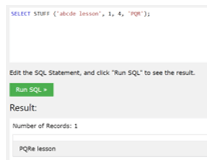
- Let us see the example to delete 4 characters from the given string which can begin from the first position and after that, we have given a text ‘PQR’ which can be added at position 1,
SELECT STUFF ('abcde lesson', 1, 4, 'PQR');Output:
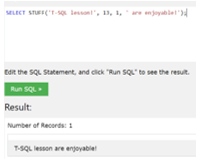
- Now we will see an example to remove 1 character from the given string which can begin at position 12 and then we have to add the string ‘are enjoyable’,
SELECT STUFF ('T-SQL lesson!', 13, 1, ' are enjoyable!');Output:
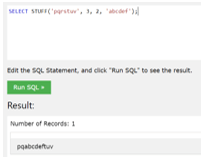
- Example to give back a string of characters which can be generated by removing 2 characters from the first string ‘pqrstuv’, and beginning from the position ‘3’ at ‘r’ and adding the second string at the removing point.
SELECT STUFF ('pqrstuv', 3, 2, 'abcdef');Output:
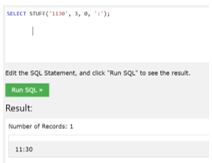
- Example to transform time from HHMM to HH: MM with the help of the STUFF() function,
In this example we have utilized the STUFF() function to add the ‘:’ (colon) at the center of the time having format HH MM and it will give back the time value in format HH: MM.
SELECT STUFF ('1130', 3, 0, ':');Output:
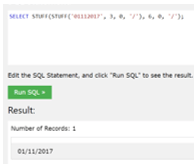
- Example to convert the date format from MMDDYYYY to MM/DD/YYYY with the help of the STUFF() function,
In this example, we have the STUFF() function two times to convert the format as shown in the given statement.
SELECT STUFF (STUFF ('01112017', 3, 0, '/'), 6, 0, '/');Output:
Conclusion
In this article we conclude that the T-SQL STUFF() function can able to remove a section of a string and after that, it can be added to another section of string in a specific position, we have also seen the examples, using STUFF() function so this article.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “T-SQL Stuff” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.