Introduction to T-SQL Formatter
The T-SQL formatter is defined as it has been utilized to make the statements more attractive, which can configure the code impulsively. The working of that relies on simple algorithms and also using simple rules, which can assist in writing attractive code; when we try to format the code manually then, it can take more time, so there are various tools available to speed up the process of formatting and to make it better organized for developers, it provides the dominant option that is indenting which is most important in the formatting.
Overview T-SQL Formatter
The Formatter has been used to format the provided code to make it easy to read, write, and understandable for the users; it has the indenting option, which makes the formatting attractive; it has various options for making the document attractive, as there are multiple tools available so by using them we can able to save the time which can be the very time-consuming process when we try to make it by manually. Also, it increases the speed of formatting, which is more accessible and efficient. So it is efficient for the coder.
How does the T-SQL formatter work?
Let us see how the T-SQL formatter works by using the ‘Indentation’ of SQL code,
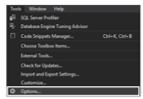
- As it has three options to choose the indentation option, first we have to go to the SSMS tools menu, and from it, we have to select ‘Options’ as shown in the below screenshot,
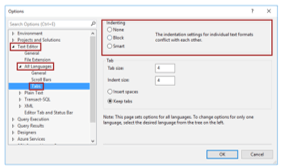
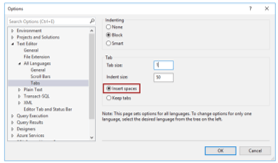
- Then the Options window will open; after that, click on the ‘Text Editor’ then, select ‘All Languages’, and then click on the ‘Tabs.’
- In the above window, when we select the ‘None’ option in the editor when we try to enter the key, then the cursor can go to the start of the following line,
- And when we try to select the ‘Block’ option and try to enter the key, then the cursor can go to the preceding line,
- There is also an option that is ‘Smart,’ which can be used by default when we try to control the particular indenting option.
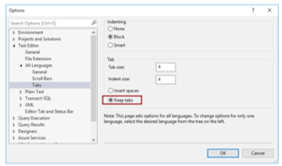
- If we want to utilize the Tab characters for indenting, then we have to select the ‘Keep tabs’ button,
- And if we want to utilize the space character, we can use the ‘Insert spaces’ button.
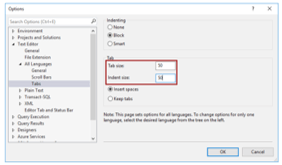
- These two options, such as ‘Tab Size’ and ‘Indent size,’ can be utilized when we want to enter the space characters,
- We can indent the code in the query editor by selecting the code which we want to indent, and then we have to click on the ‘Tab’ key, which can be available on the keyboard, and then click on the ‘Indent’ button on the editor,
- If we want to ‘Unindent’ the code, we can use ‘SHIFT+Tab’ or ‘Unindent,’ available in the editor.
T-SQL Formatted Tools
There are various tools, as given below,
- ApexSQL Refactor: It is used to format and refactor the code and objects in which it can have 200+ formatting options and near about 15 code refactor.
- Atom Beautify: Atom does not have the in-built command for formatting in which we have to install the atom-beautify package. The Palette command is also used to beautify the editor for a particular language.
- dbForge SQL Complete: This tool can be added to the SQL management and visual studio. It can accelerate the writing of code and upgrade code readability to improve productivity.
- FSQLF: It is a free formatting tool that can be built to make it easy when people are trying to construct long queries.
- Poor Man’s T-SQL formatted: It can manage the different groups of scripts that can define objects and provide a format for the various formatting standards.
- Rapid Database Extractor: This tool is free to control the SQL Server and Oracle data sources with a single user, and it can handle objects of the database.
- RazorSQL: This editor can connect with near about 40 databases, and it can run on Windows, macOS, Mac OS X, Linux, and Solaris.
- SQL Assistant: It can increase the speed of the development process, upgrading the quality of code and its correctness.
- SqlBeautifier: This tool can work with T-SQL as well as PL/SQL, PostgreSQL, and MySQL, making queries readable and understandable.
- SQL Enlight: It can impulsively review the code and examine and recognize the possible design and effect on our SQL server databases.
- SQLinForm: It is a dynamic tool that can format up to 300K lines of the statement within three seconds, and the databases manage it.
- SQL PraRup: It is a dynamic tool that can format up to 300K lines of the statement within three seconds, and the databases manage it.
- SQL Pretty Printer: This tool can configure the statements as per the standards in which it can standardize the code from other organizations.
- SQL Prompt: It allows one to write and format the SQL using a modern style, and it can customize the formatting of the code.
- SSMSBoost: This tool can take a backup of surviving documents, and the disk can allow us to get back the older working version.
- Tidycode T-Sql Formatter: This tool can allow us to neatly beautify the T-SQL code in the form of a group; hence, it is called a Tidy Code formatter.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the T-SQL formatter has made it easy to understand the code, which is formatted and time-consuming as manually it takes more time for formatting, so this article will help to know how it works and how its tools can also work.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to T-SQL Formatter. Here we discuss the introduction, overview, How does T-SQL formatter work, and tools, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –