Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL DATEPART
T-SQL DATEPART is a function that can give back a particular section of date in which it provides the result as an integer value, and the section of date which it gives is a section of a date that we want in return. So we can say that if we have a condition to get back a particular date section, then the DATEPART() function has been used. It accepts two arguments, date_part and input_date, in which date_part is the section of a date to be extracted, and the input_date is the date from which we can get the date part.
What is T-SQL DATEPART?
The DATEPART() is the function in T-SQL that can be used to extract a section of date that can be specified through a parameter; it accepts two arguments, such as interval as a date_part and date as an input-date, so if we provide a date in date-part. We must extract the year from it and specify the YY in the interval or input part. It will give out the related year from the provided value, in which we can get only the integer format values, as the date part of the section has been accepting the abbreviations for extraction means, for example, year have abbreviation as yy, yyyy, moth having abbreviation as mm, m, in this way we can use the abbreviation for all other date_part.
T-SQL DATEPART Function
The DATEPART() is the function that can give back a particular section of date and a result in an integer format; it can accept two arguments, the interval, and the date.
Syntax:
"DATEPART (interval, date)"Where,
- interval: It is a section from which we can get a date part that can be a specific date, as it gives back an integer value for the particular interval.
- date: It is a section of date which is to be extracted in which we can describe the date in it for getting a particular value of interval; it allows us to define direct values for bringing back the values from its given data types, such as Date, DateTime, Datetimeoffset, Datetime2, Smalldatetime, and Time.
The interval parameter in the DATEPART() is a required part as we can say that it is an input_part, so it can accept various input parameters such as date, month, year, minute, etc., which are given in the below parameter section. The date_part is also a required value in which it can be the date which has been utilized, and that may have a datatype such as a date, DateTime, datetimeoffset, datetime2, and the smalldatetime or time.
Let us see an example of the DATEPART () function, which can give back a particular section of date; it can use the SELECT statement for writing the query such as given below:
Code:
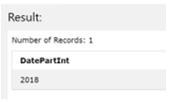
"SELECT DATEPART (yy, ‘2018/07/21’) AS DatePartInt"Output:
In this example, we try to get a year from the provided value; as we can see, date_part is the input section from which we can get back a value specified in the input_part, as we can give date as input. We have to extract the year that means ‘yy’ from that given date so we can see the output, which is the year provided in the input section that 2018.
Let us see another example to obtain a month part of the given date:
Code:
"SELECT DATEPART(month, '2018/07/22') AS DatePartInt;"Output:
T-SQL DATEPART Parameters
Mainly it has two parameters as interval/input_part and the date as date_part; let us see the parameters of DATEPART with their abbreviations:
Interval: It has various parameters with abbreviations so let us discuss which abbreviation has been used for the specific parameter:
- year, yyyy, yy = Year: To rectify the year from a defined date.
- quarter, qq, q = Quarter: To fix the quarter from a specified date.
- month, mm, m = Month: To fix the month from a defined date.
- dayofyear, dy, y = Day of the year: We can obtain a day of the year on a specified date.
- day, dd, d = Day of the month: It gets the Day of the month as a defined date.
- week, ww, wk = Week: It provides the week number of the current date in a defined date in which how many weeks are there in a year.
- hour, hh = hour: It provides an hour section of the defined date.
- minute, mm, n = Minute: We can get a minute section of the particular date.
- second, ss, s = Second: We can obtain a minute section of the defined date.
- millisecond, ms = Millisecond: It gets a millisecond value from the specified date.
- microsecond, mcs = Microsecond: It obtains a microsecond value from the defined set.
- nanosecond, ns = Nanosecond: It receives nanosecond value from the specified date.
- tzoffset, tz = Timezone offset: It obtains time zone offset within the local time zone and GMT.
- iso_week, isowk, isoww = ISO week
Date: This is also a required field we have to provide for extracting the result using the interval parameter.
T-SQL DATEPART Date/Time: The DateTime is the data type of T-SQL whose format is YYYY-MM-DD (hh:mm: ss[.nnn]); it has an 8-byte storage capacity within the range,
Example:
Code:
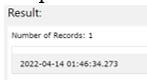
DECLARE @date DATETIME= GETDATE();
SELECT @date;
SELECT DATEPART(YY, @date) AS Year,
DATEPART(QQ, @date) AS Quarter,
DATEPART(WK, @date) AS Week;Output:
In the above example, we have used the DateTime datatype with datepart in which we can get results as date and time.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the DATEPART() is the function that can accept interval and date_part arguments. Moreover, it can give back a section of date as an integer value; we also saw various parameters and functions that will help us understand the concept.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL DATEPART. Here we discuss the introduction, T-SQL DATEPART function, and parameters. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –