Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL Date Format
T-SQL date format is defined as, it is the function that has been used for arranging the fields, which are straightly conducted to show into the exhibiting format, and the format of it can able to reserve the date or time values in the database in all probabilities we can say that the date format has been used to see the dates which are formatted as MM-DD-YYYY or month will be at first as DD-MM-YYYY, when date field has been reserve as a string then it does not sort in chronicle order because we need to use the ‘ORDER BY’ statement which does not create a chronicle list.
Overview of T-SQL Date Format
Let us see the overview of date format, in which DATE_FORMAT() is the function format in which date can be specified; the date format function has been utilized for showing the date/time data in various forms in which it has specific formats and optional culture, to make use of the FORMAT function for locale-aware formatting of date or time and number values as a string.
Syntax:
FORMAT (value, format [, culture])Where,
- value is the expression of assisting data type in formatting.
- The format is the argument that contains a valid format string that can be the standard or as a pattern of custom characters for dates. It can also carry fractional utilities like “MMMM DD, yyyy (dddd).”
- Culture is the optional ‘nvarchar’ argument that can describe the culture; if the culture is not given, it can use the language of the current session. It can accept any culture that can be assisted as an argument.
It can give back a value having return type’ nvarchar or null,’ and the length of the return value is set by format.
How to T-SQL Date Format?
Let us see how to show the date value in another format:
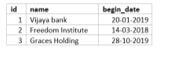
Let us suppose we have a table named ‘office’ which can have information in column id, name, and begin date.
| id | name |
begin_date |
| 1 | Vijaya Bank | 20-01-2019 |
| 2 | Freedom Institute | 14-03-2018 |
| 3 | Graces Holding | 28-10-2019 |
For every ‘office’ let, we can convert their start date to the new format, YYYY/MM/DD, where YYYY can be the four-digit year, MM is the two-digit month, and DD is the two-digit day.
Let us use the CONVERT () function; we can use the below query for conversion.
Code:
"SELECT CONVERT (NVARCHAR, begin_date, 111) AS new_date FROM office;"Output:
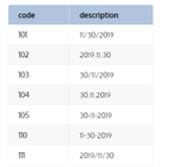
In this example, we try to change the format of Vijaya Bank’s date ‘2019-01-20’ to ‘2019/01/20’; we have used the CONVERT () function for transforming the date from provided columns which can accept three arguments as NVARCHAR as a datatype, column ‘name’ has the expression and ‘begin_date’ column, we have used the style code which can be the integer.
The famous style code is given in the below table.
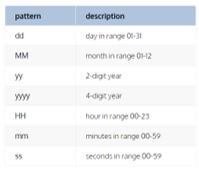
Let us use the FORMAT () function to change the date/time format; we can use the characters in the table below.
Now let us see the query which can be used with the FORMAT () function.
Code:
"SELECT FORMAT (begin_date, 'yyyy-MM-dd') AS new_date FROM office;"Output:
In the above query, the first argument is the DateTime/date/time value to format, and the second is the string in which this function can give back the NVARCHAR datatype.
T-SQL Date Format Function
The date format function in the input date format will be similar to the column format, as it is essential to match both formats.
- NOW(): This is a date format function that can give back the current date and time.
- CURTIME(): This is also the date format function that can give back the current time.
- EXTRACT(): This function can give back a single part or time.
- DATE_SUB(): This function can subtract a particular time interval from a date.
- DATE_FORMAT(): It can present the date or time in various formats.
- DATEDIFF (): This function can help to give back the number of days between two different days.
- DATE_ADD(): This function has been used to add a particular time interval to the date.
- DATE(): This function can take out the date part of a date and date or time expression.
- CURDATE(): This function can give back the current date.
Tips and Tricks of T-SQL Date Format
Given below are the tips and tricks mentioned:
- Comma-delimited output: It can give back a comma-separated value in which cursors are not used.
- Determine missing identity values: It can simply recognize misplaced values in our table.
- Generate random numbers: This is another option for SQL server mathematical functions.
- Generate random records: It can create a definite number of random records from our tables.
- Sort IP addresses: It can be categorized as VARCHAR by using numeric values.
- Split name/ split string: This is another way of splitting the full name for receiving the first and last names.
- Query/Read and import an excel file: This can be utilized DTS, and there is no need to load the data into a SQL table.
- Execute a batch of SQL scripts: This can be available in a particular directory, and there is no need to open it manually, which it can open every. SQL script and implementing it in query analyzer.
- SQL server date formats: It lists how to transform DateTime values into various date formats.
- SET vs. SELECT when assigning variables: It can show a difference between the SET command and the SELECT statement while defining a value to the local variables.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the date format is the function that can be used to arrange the fields and show the dates, so we can also discuss how to use this function and the function format and the tips and tricks related to the date format function.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL Date Format. Here we discuss the introduction, Format function, tips and tricks, and how to T-SQL date format. . You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –