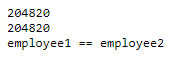Updated April 5, 2023
Introduction to Swift hashable
The swift hashable is the protocol used to compare two objects or instances of the swift class. The swift hashable protocol converts the data type values into hash code or hash value and returns on the output screen. It is a protocol using to conform the Boolean values, string values, and integer values into secure or encrypted values. The hashable protocol is converted data type values into an encrypted integer value and returns on the output window. The hashable protocol is comparing the two objects of the class or struct and returns the object value into integer format or hash code format. The hashable is an easy way to decide the one object is equal, greater, less, or not equal to another object.
Syntax
There are three parts of the syntax to become a hashable protocol.
- Part1: the Hashable keyword use with struct or class.
class ClassName: Hashable {
//defined variable here…
}OR
struct StructName: Hashable {
//defined variable here…
}- Part2: the variable value converts into hash value.
public var hashValue: Int {
return variable_name.hashValue
}- Part3: the object value returns into hash value or hash code.
print(object_name.hashValue)Description:
- The hashable part2 syntax is placed inside of the class or struct.
- The hashable provides equitable and comparable protocols with hashcode.
- The hashValue keyword displays the hash code, hash value, or integer value.
- If two objects have similar values, then their hash value must be the same.
- If two hash codes or values have the same value, then two objects do not seem necessary to have similar values.
How does hashable works in Swift?
The swift installation for the swift enum programming.
- The Ios and OS x users have installed Xcode IDE, but the user must have an account on the apple developer website.
- Users enter the playground name and select the platform name in the Xcode IDE.
- Users can get the playground window and start the coding.
- The other operating system users can use online options for swift programming.
- The user can use the https://iswift.org/playground website for swift coding.
The swift hashable create a class or struct with the “Hashable” keyword.
The variable and its datatype are defines inside of swift class or struct.
class Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var employee_age: Int
}
The swift hashable convert variable value into hash value.
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_id.hashValue ^ employee_age.hashValue
}The swift hashable create an initialize variable method as a constructor.
init(employee_id: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.employee_age = employee_age
}The swift hashable protocol supports the equatable protocol and uses the method for comparison.
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_id == rhs.employee_id && lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
}Defined objects value and Return the hashable value.
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, employee_age: 8)
print(employee1.hashValue)Combine the working procedure of the hashable protocol is below.
class Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var employee_age: Int
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_id.hashValue ^ employee_age.hashValue
}
init(employee_id: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.employee_age = employee_age
}
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_id == rhs.employee_id && lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
}
}
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, employee_age: 3)
print(employee1.hashValue)Examples
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
The swift hashable with similar object value using struct example and output.
Code:
class Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var salary: Int
var employee_age: Int
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_id.hashValue ^ employee_age.hashValue ^ salary.hashValue
}
init(employee_id: Int, salary: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.salary = salary
self.employee_age = employee_age
}
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_id == rhs.employee_id
&& lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
&& lhs.salary == rhs.salary
}
}
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, salary: 8, employee_age: 3)
let employee2 = Employee(employee_id: 1, salary: 8, employee_age: 3)
print(employee1.hashValue)
print(employee2.hashValue)Output:
Example #2
The hashable with different object values using struct example and output.
Code:
struct Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var salary: Int
var employee_age: Int
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_id.hashValue ^ employee_age.hashValue ^ salary.hashValue
}
init(employee_id: Int, salary: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.salary = salary
self.employee_age = employee_age
}
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_id == rhs.employee_id
&& lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
&& lhs.salary == rhs.salary
}
}
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, salary: 18000, employee_age: 31)
let employee2 = Employee(employee_id: 3, salary: 205400, employee_age: 38)
print("The employee1 value into hashable formate : ")
print(employee1.hashValue)
print("The employee2 value into hashable formate : ")
print(employee2.hashValue)Output:
Example #3
Swift hashable with comparison objects using struct example and output.
Code:
struct Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var salary: Int
var employee_age: Int
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_id.hashValue ^ employee_age.hashValue ^ salary.hashValue
}
init(employee_id: Int, salary: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.salary = salary
self.employee_age = employee_age
}
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_id == rhs.employee_id
&& lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
&& lhs.salary == rhs.salary
}
}
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, salary: 18000, employee_age: 31)
let employee2 = Employee(employee_id: 3, salary: 205800, employee_age: 38)
if(employee1 == employee2){
print("employee1 == employee2")
}else{
print("employee1 != employee2")
}Output:
Example #4
The hashable with similar object value except employee id considered example and output.
Code:
class Employee: Hashable {
var employee_id: Int
var salary: Int
var employee_age: Int
public var hashValue: Int {
return employee_age.hashValue ^ salary.hashValue
}
init(employee_id: Int, salary: Int, employee_age: Int) {
self.employee_id = employee_id
self.salary = salary
self.employee_age = employee_age
}
static func == (lhs: Employee, rhs: Employee) -> Bool {
return lhs.employee_age == rhs.employee_age
&& lhs.salary == rhs.salary
}
}
let employee1 = Employee(employee_id: 1, salary: 204823, employee_age: 3)
let employee2 = Employee(employee_id: 2, salary: 204823, employee_age: 3)
print(employee1.hashValue)
print(employee2.hashValue)
if(employee1 == employee2){
print("employee1 == employee2")
}else{
print("employee1 != employee2")
}Output:
Conclusion
It is a secure integer value help to the comparison between two objects. The hashable is an easy and user-friendly way to compare instances in the Boolean format.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Swift hashable” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.