Updated June 15, 2023
Differences Between Sqoop and Flume
Sqoop is a product from Apache software. Sqoop extracts useful information from Hadoop and then passes it to the outside data stores. With the help of Sqoop, we can import data from an RDBMS or mainframe into HDFS. Flume is also from Apache software. The best way of collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of data between the Hadoop Distributed File System and RDBMS is via using tools such as Sqoop or Flume.
Let’s discuss these two commonly used tools for the purpose mentioned above.
What is Sqoop?
To use Sqoop, a user has to specify the tool user wants to use and the arguments that control the particular tool. You can also then export the data back into an RDBMS using Sqoop. It works with different databases like Teradata, MySQL, Oracle, and HSQLDB.
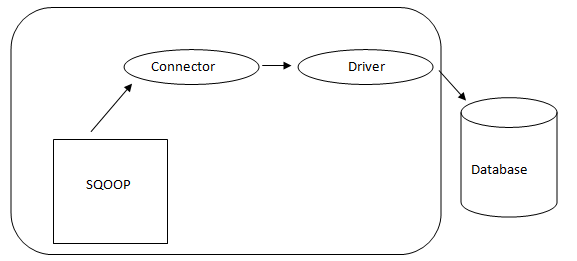
Sqoop Architecture:
The connector in a Sqoop is a plugin for a particular Database source, so, fundamentally, it is a piece of Sqoop establishment. Despite the fact that drivers are database-specific pieces and distributed by various database vendors, Sqoop itself comes bundled with different types of connectors utilized for prevalent database and information warehousing system. Thus Sqoop ships with a mixed variety of connectors out of the box as well. Sqoop gives a pluggable component for an ideal network and external system. The Sqoop API provides a convenient framework for building new connectors, allowing for easy integration of various database connectors into the Sqoop installation. This enables connectivity to different data systems by simply adding the desired connectors to Sqoop.
What is Flume?
Flume offers the flexibility to work with customizable data sources. This means that Flume can transport large volumes of data from various sources, including email messages, social media-generated data, network traffic data, and virtually any other imaginable data source.
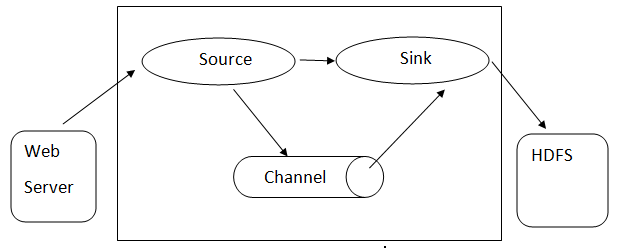
Flume architecture: –Flume architecture is based on many-core concepts:
- Flume Event is represented as the unit of data flowing, which has a byte payload and set of strings with optional string headers. Flume considers an event just a generic blob of bytes.
- Flume Agent- A JVM process hosts components such as channels, sinks, and sources. It has the potential to receive, store, and forward the events from an external source to the next level.
- Flume Flow- it is the point of time the event is being generated.
- Flume Client refers to the interface where the client operates at the origin point of the event and delivers it to the Flume agent.
- Source- A source consumes events having a specific format and delivers them via a specific mechanism.
- Channel is a passive store where events are held until the sink removes them for further transport.
- Sink – It removes the event from a channel and puts it on an external repository like HDFS. It currently supports creating text and sequence files and supports compression in both file types.
Head to Head Comparison between Sqoop vs Flume (Infographics)
Below is the top 7 comparison between Sqoop and Flume:
Key Differences between Sqoop and Flume
1. On the other hand, Flume collects data from various sources that generate data related to a specific use case. It then transfers this large amount of data from distributed resources to a centralized repository.
2. Sqoop also includes a set of commands which allows you to inspect the database you are working with. Thus we can consider Sqoop as a collection of related tools. While collecting the data, Flume scales the data horizontally by putting multiple Flume agents into action to collect and aggregate the data.
3. The key factor for using Flume is the requirement for continuous and streaming data generation.
Sqoop vs Flume Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Sqoop vs Flume.
| Basis of Comparison | SQOOP | FLUME |
|
Basic Nature
|
Sqoop works well with any RDBMS with JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) like Oracle, MySQL, Teradata, etc. | Flume works well for Streaming data source, which is continuously generating, such as logs, JMS, directory, crash reports, etc. |
| Data Flow | Sqoop is specifically used for parallel data transfer. For this reason, the output could be in multiple files. | Flume is commonly used for collecting and aggregating data because it is distributed and scalable. |
| Driven Events
|
Events do not drive Sqoop. | Flume is completely event-driven. |
| Architecture
|
Sqoop follows connector-based architecture, which means connectors know how to connect to a different data source. | In Flume, the architecture is based on an agent-based model, where the code written in Flume is referred to as an agent. |
| Where to Use | Primarily used for copying data faster and then using it for generating analytical outcomes. | Generally used to pull data when companies want to analyze patterns, root causes, or sentiment analysis using logs and social media. |
| Performance | It reduces excessive storage and processing loads by transferring them to other systems and performs quickly. | Flume is fault-tolerant, robust, and has a tenable reliability mechanism for failover and recovery.
|
| Release History | The first version of Apache Sqoop was launched in March 2012. The current stable release is 1.4.7 | The first stable version, 1.2.0 of Apache Flume, was launched in June 2012. The current stable release is Apache Flume Version 1.8.0. |
Conclusion
Sqoop vs Flume, are primarily two Data Ingestion tools used in the Big Data world. If you need to ingest textual log data into Hadoop/HDFS, then Flume is the right choice for doing that.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Sqoop vs Flume” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.