Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy unique
SQLAlchemy unique will define the number of types abstracted from standard SQL types supported by the backend database. This minor detail is hidden from SQLAlchemy, and we can be confident that any queries or statements we create will work properly. The columns that are constrained are referred to as foreign key columns. The foreign key is the “joint” that connects pairs of rows.
What is SQLAlchemy unique?
- When we indicate true in our statements on the specified column, this column will contain the unique constraints. True indicates that the Index should be created with a unique flag. Use the Unique Constraint or Index constructs explicitly specify the column.
- To use sqlalchemy in our code, we first need to install the sqlalchemy module using the pip command. Without installing sqlalchemy, we cannot use this module in our code.
- Sqlalchemy is available in the install package of pip. A foreign key in SQL is a table-level construct that restricts one or more columns in that table to only allowing values from a different set of columns.
- A sqlalchemy unique constraint is an additional attribute defined in the table, sqlalchemy, and DDL, or they can be optionally specified within the definition of a single column in the case of single-column foreign keys. The single-column foreign key is more common and specified at the column level.
- The Foreign Key argument is typically a string of the form name_of_table. name_of_column.
- User preference is resolved only when needed, allowing table objects to be easily distributed across multiple modules and defined in any order.
- The Foreign Key Constraint object can also be used to define foreign keys at the table level.
- This object can be used to describe a single-column foreign key. A composite foreign key is always a table with a composite primary key.
- The CONSTRAINT of the FOREIGN KEY directive is used in creating table queries to create the constraint in an “inline” fashion. The MetaData.create all() and MetaData.drop all() methods do this by default, employing a topological sort of all Table objects involved so that tables are created and deleted in the order of their foreign key dependency.
- Sqlalchemy unique is applied to the database table to define unique values from the table column.
How to Model SQLAlchemy unique?
Using the unique constraint on a column, we can anonymously define special restrictions on a single column. The sqlalchemy unique generates unique, explicitly specified constraints and/or has numerous columns. The Check Constraint construct can be used to establish named or nameless check constraints column level. There is limited “database independent” behavior because the check constraint text is given straight to the database. Table-level check constraints can relate to any columns in the table; however, column-level check constraints refer to the column level.
To define the SQL alchemy model, we need to install the SQLmodel.
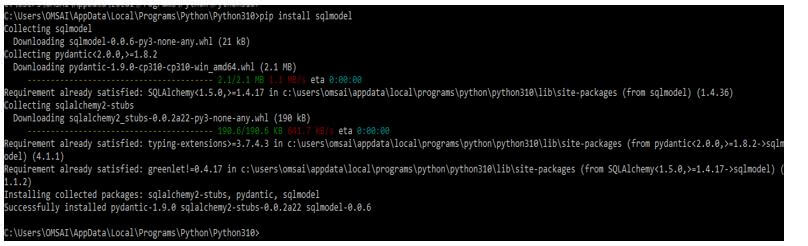
The below steps show how to install the sqlmodel module as follows.
Code:
pip install sqlmodelOutput:
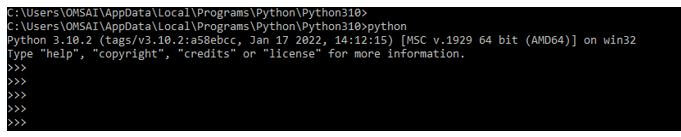
After installing all the modules, we open the python shell by using the python3 command.
Code:
pythonOutput:
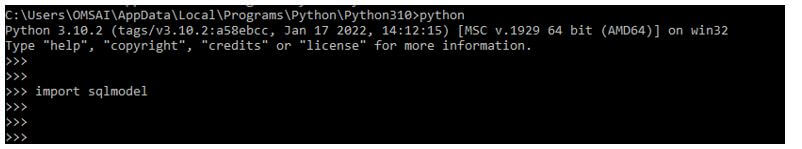
After login into the python shell in this step, we are checking sql model package is installed in our system.
Code:
import sqlmodelOutput:
Column metadata is a class attribute in SQLModel that takes table parameters. This attribute accepts both positional and keyword parameters, which are typically passed to the Table function Object() { [native code] }. Dictionary and tuple are the two formats in the attribute.
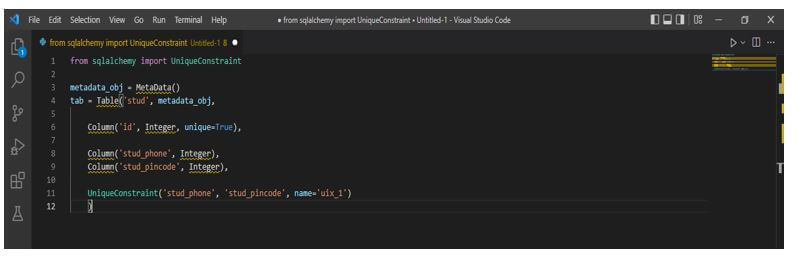
The below example shows how to model sqlalchemy unique are as follows. In the below example, first, we have imported the unique constraint package from the sqlalchemy module. Then we create metadata objects. After creating the metadata object, we define the table name as a stud. After defining the table name, we create the table column name as id, stud_phone, and stud_pincode. Finally, we are applying the sqlalchemy unique as follows for the id column.
Code:
from sqlalchemy import UniqueConstraint
metadata_obj = MetaData ()
tab = Table('stud', metadata_obj,
Column ('id', Integer, unique=True),
Column ('stud_phone', Integer),
Column ('stud_pincode', Integer),
UniqueConstraint ('stud_phone', 'stud_pincode', name='uix_1')
)Output:
SQLAlchemy Unique Database and Tables
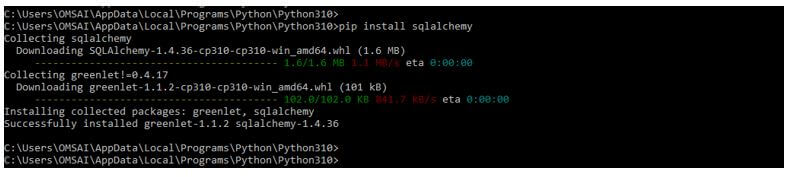
Sqlalchemy module is not coming under when installing the python package in our system. So to use sqlalchemy, we need to install the sqlalchemy module by using the pip command. Below steps that show how to install the sqlalchemy module are as follows.
In the first step, we install the sqlalchemy module using the pip command. We can install the sqlalchemy module in any operating system on which python is installed. In the below example, we are installing the sqlalchemy module.
Code:
pip install sqlalchemyOutput:
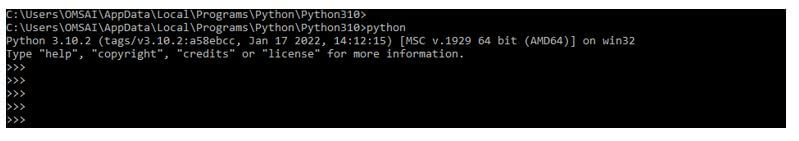
After installing all the modules, we open the python shell using the python3 command.
Code:
python3Output:
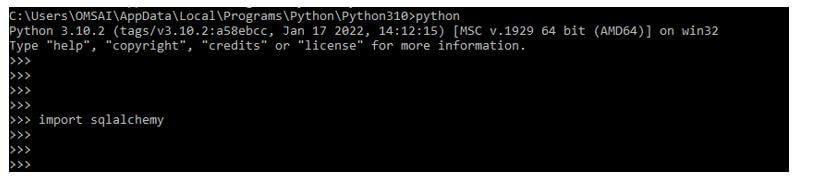
After login into the python shell in this step, we are checking sqlalchemy package is installed in our system.
Code:
import sqlalchemyOutput:
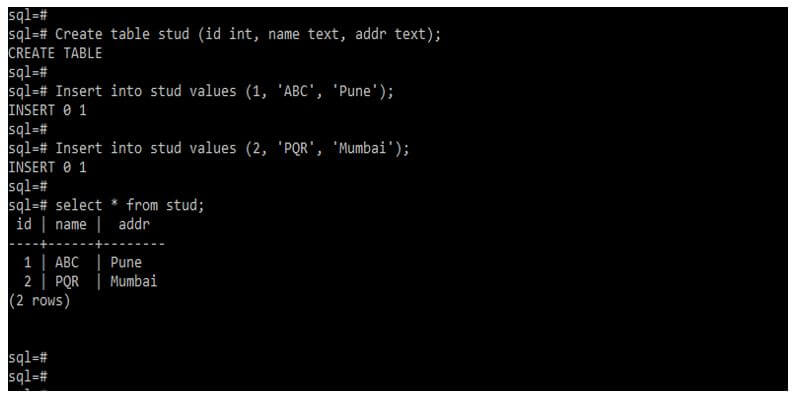
In the below example, we create the database and tables as follows.
Code:
Create database sql;
Create table stud (id int, name text, addr text);
Insert into stud values (1, ‘ABC’, ‘Pune’);
Insert into stud values (2, ‘PQR’, ‘Mumbai’);
Select * from stud;Output:
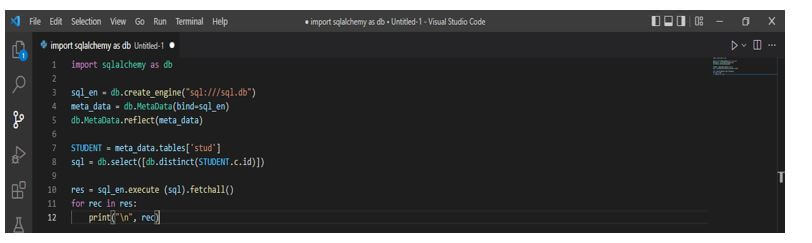
In the below example, we are fetching records from the SQL table as follows. In the below example, first, we have imported the sqlalchemy module. Then we define the database engine. Then we create a metadata object. After creating the metadata object, we use a select query to display all the records from the stud table.
Code:
import sqlalchemy as db
sql_en = db.create_engine ("sql:///sql.db")
meta_data = db.MetaData (bind=sql_en)
db.MetaData.reflect (meta_data)
STUDENT = meta_data.tables ['stud']
sql = db.select ([db.distinct (STUDENT.c.id)])
res = sql_en.execute (sql).fetchall()
for rec in res:
print("\n", rec)Output:
Conclusion
A foreign key in SQL is a table-level constraint that restricts one or more columns in that table to only allowing values from a different set of columns. Sqlalchemy unique will define the number of types abstracted from normal SQL types supported by the backend database.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQLAlchemy unique. Here we discuss the introduction, unique database, and how to model SQLAlchemy unique with tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –