Updated June 28, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Types
The SQLAlchemy type is one of the built-in types that can be used for the database, which is the independent data type and one of the basic specific types used to map the application data into the database schema. In addition, it provided the TypeEngines for breaking into the generic types across the multiple database engines, and the dialect-specific types are also handled globally. Specifying the sql datatypes used by each data column of every table when defining the MetaData used with the application is essential.
When we can use the unless tables are defined with the autoload=True in which the SQLAlchemy provided the datatypes with the TypeEngines created as the instances provided by the SQLAlchemy classes. When using Python classes, developers convert them to the native database values and vice versa for the TypeEngine objects. Let us use the String type as assigned for the special characters like varchar etc. The TypeEngines also provide the SQL text for creating or building tables with the specified metadata, which can be accessed through the table.create() or create_all() methods. We used the application for the SQLAlchemy in the different set of methods that helps to construct the generic type engines with various database engines. A specific set of databases further modified with the object conversation from and to the databases, the SQLAlchemy mainly allowed constructing the application with specified custom type engines.
Different Types of SQLAlchemy
It has n number of types, among which some of the SQLAlchemy types are as follows:
1. Built-in Types
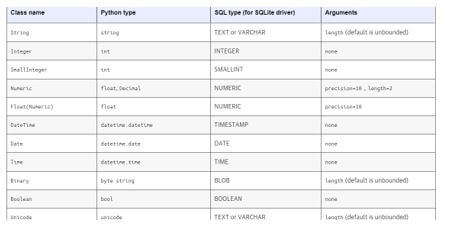
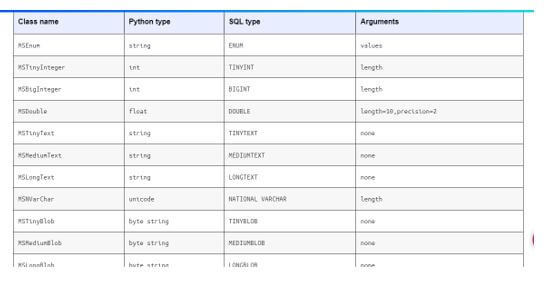
SQLAlchemy includes it as one of its types, and it mainly provides it with fairly basic ideas, but it is yet to be completed with the TypeEngines for SQL support for additional database column types. We used TypeEngines supported with their corresponding type engines defined in the CLOB. Developers derive these from other TypeEngines and may or may not further specialize them with the finer-grained specification of the underlying database types. Here are some of the SQL types, along with the drivers and Arguments mapped with the class name and Python type.
The table above shows some of the class names, like data types mapped to the Python and sql types with the database drivers. We can specify the arguments with the multi-type and single types based on the parameter called by our end.
The rest of the types, along with the Sql and Python types, are for this. Developers will use it with the TypeEngines to specify the table rows and columns. Developers also import generic engines to the code, such as the SQLAlchemy.types package.
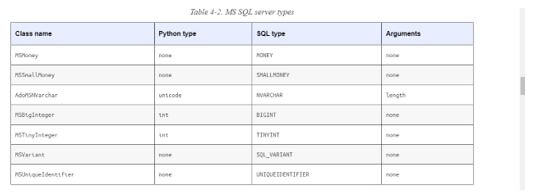
2. Dialect-Specific Types
If we want to generate the dialect-specific content for sql alchemy, it combines with generic and dialect-specific type engines. Developers also create it using the Create Table queries from the generic types. In some instances, it may be the dialect-specific types in addition to the generic types. The system uses SQLAlchemy to communicate with various DBAPI implementations and databases. The dialect acts like a factory for the other database-specific object implementation, including the ExecutionContext, complied, default generator, and the TypeEngine. Here, it’s one of some key features with distinct components known as the Core and ORM; the core and the orm sqltoolkit will mainly be abstracted using the smooth layers with an over wide range of DBAPI implementations and behaviors.
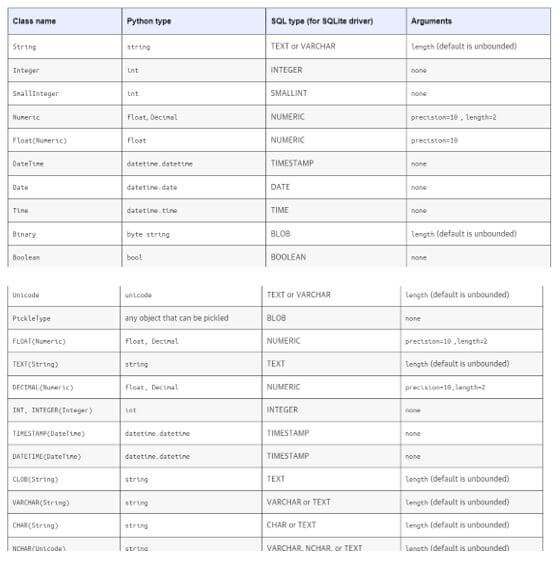
The above diagram shows the list of class names, the Python and sql types, and arguments to connect the database drivers with the parameters.
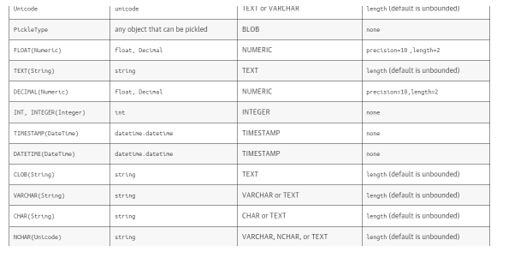
3. Generic Types
The generic types packages contain the generic TypeEngines offered by SQLAlchemy, a wide support range of portable column types. Therefore, we can list the TypeEngines more supported by the portable column types, their Python types, and the sql representations. Furthermore, the Type Engines are more defined with all the CLOBs that may or may not specialize in finer-grained database specification types.
The TypeEngines are more specified with the table rows and columns with the instance type for the TypeEngine class if the default parameters construct the SQL type more.
4. Application-Specific Custom Types
Generally, the SQLAlchemy provides a wide range and set of rich generic database-specific types. However, it is more helpful and widely able to create specific application custom types. Then, for instance, it may wish to emulate the database engine not supported with enumerations type by restricting column values. It contains two types of SQLAlchemy, TypeEngine, and TypeDecorator, for more direct implementation through the TypeEngine subclass.
Whether it may contain already Implementing the TypeDecorator and Creating a New TypeEngine to implement and decorate the TypeEngine subclass.
Examples of SQLAlchemy Types
Given below are the examples of SQLAlchemy Types:
Example #1
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import types
class Firstclasses(types.TypeDecorator):
news=types.Integer
def __init__(a, vars, *al, **cde):
types.TypeDecorator.__init__(a, *al, **cde)
a.vars = vars
def paramsbind(a, value, engine):
outs = a.news.paramsbind(value, engine)
if outs not in a.vars:
raise TypeError(
"The values outss is %s must be one of the output %s" % (outs, a.vars))
return outs
def resout(a, value, engine):
'Have a Nice day thanks for your support'
return a.news.resout(value, engine)
print("Thanks for the first example regarding SQLAlchemy types")Output:
The first example is creating the class and passing the type TypeDecorator to convert the inputs to the Integer format, which may be the integer input ranges called numbers. And we defined the set of methods with passing parameters and validated the conditions by using the if statement and return and raising the error in TypeError() method. For the same in resout() method and returning the parameters.
Example #2
Code:
from SQLAlchemy import types
class secondclasses(types.TypeDecorator):
second=types.String
def __init__(ab, vars2, *vas, **ref):
types.TypeDecorator.__init__(ab, *vas, **ref)
ab.vars2 = vars2
def newsmeth(ab, vals, eng):
ress = ab.second.newsmeth(value, eng)
if ress not in ab.vars2:
raise TypeError(
"Please find the output results from the newmeth methd" % (ress, ab.vars2))
return ress
def resout(ab, vals, eng):
'Have a Nice day thanks for your support'
return ab.second.resout(vals, eng)
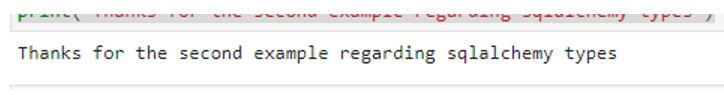
print("Thanks for the second example regarding SQLAlchemy types")Output:
In the above example, we used the types like String to convert the values. I have mentioned the second class to declare the def type in the rich generic and database-specific types. Creating the application with the custom-specific types for every instance in the emulate enumerations of the values stored in the database table columns is more helpful. It generally has two ways to create the application with the specific customer types and implement it for similar existing TypeEngine for the TypeDecorator more involved in the TypeEngine Subclasses.
Conclusion
SQLAlchemy includes many functions, operators, and keywords for connecting database data to the application UI. For example, type is one of the database formats. It operates the table columns from the specified databases and tables previously constructed using the SQLAlchmey with the database drivers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLAlchemy Types” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.