Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Migrations
The sqlalchemy migrations are one of the features, and it migrates to provide a way of dealing with the database schema and its changes in the sqlalchemy projects; it migrates the data with the help of some tools like alembic is one of the data migration tools that offer the Alter statement to the specific database to change the table structure and construction provided by the migration scripts.
What are SQLAlchemy Migrations?
Migration is the need to upgrade the system, and here we need to migrate the database so that the SQLAlchemy migration technique is used. It has n number of tools to migrate the database; we used Flask-Migrate and Alembic, the most frequently used tools to handle the user data. Alembic is the database migration tool that is written with the sqlalchemy it has its migration scripts and templates for themselves; the target database is mainly focused on the new version, and optionally it steps into the upgrade as well as downgrade process; sometimes, it is in vice-versa and reverses technique. We can allow the migration script to execute the same sequential data order with the user end’s steps.
SQLAlchemy Migrations Database
The sqlalchemy will handle the database migrations with specific tools like Alembic and other PostgreSQL to handle the data in the migration environment. It has directory scripts that can be specified to the particular source code of the application environment while using the Alembic migration tool with the init command. They can be initialized with the command line utility at the specified local path, invoked in the same python module environment. Suppose we used the SQLAlchemy database migration tool for the flask type of application by using the Alembic sqlalchemy migration. Then the database operations are made up of the flask command-line interface that will be migrated on the Alembic configuration and extensions. It is the proper way to work with the flask and flask-sqlalchemy application of the actual database migrations that can be handled using the Alembic tool for the same functionality. The migration script needs to be reviewed and modified with the help of the alembic tool currently needed for detecting the changes and its models.
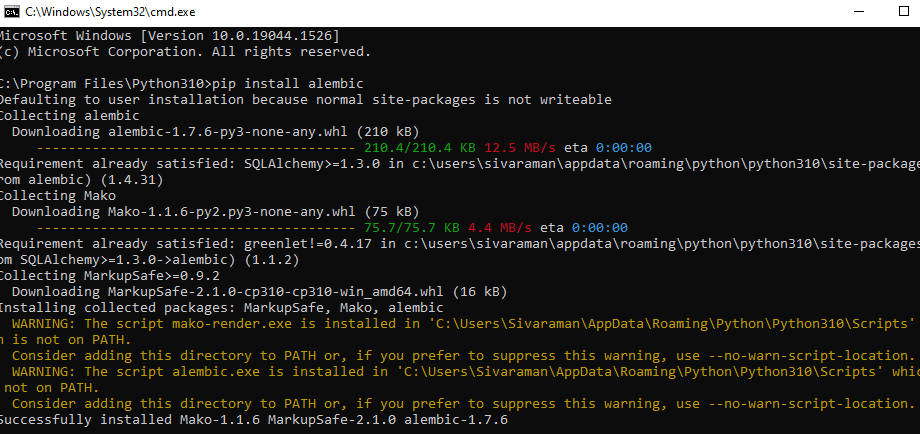
Generally, alembic is currently made up of detecting table name changes like row and column modified using anonymous constraints. One of the main sections can be read by using the Alembic tool to determine the configuration that implements the core that does not directly read the files. With the help of the migration script, the same module will be updated, and the python path will also be used as the target project with the virtual environment when the alembic command is to be run. We can customize the .py(python) file in the consumed end-user directives that cannot be including the additional directives in the command-line environments. The env.py will change the configuration code and set the environment variables in the .ini file. The Alter statement can be emitted to the database, table structure, and other constructions provided on the migration scripts. Each type of script indicates the specific series of steps that can be upgraded and the target database version. We can install the alembic by using the python-pip command like pip install alembic,
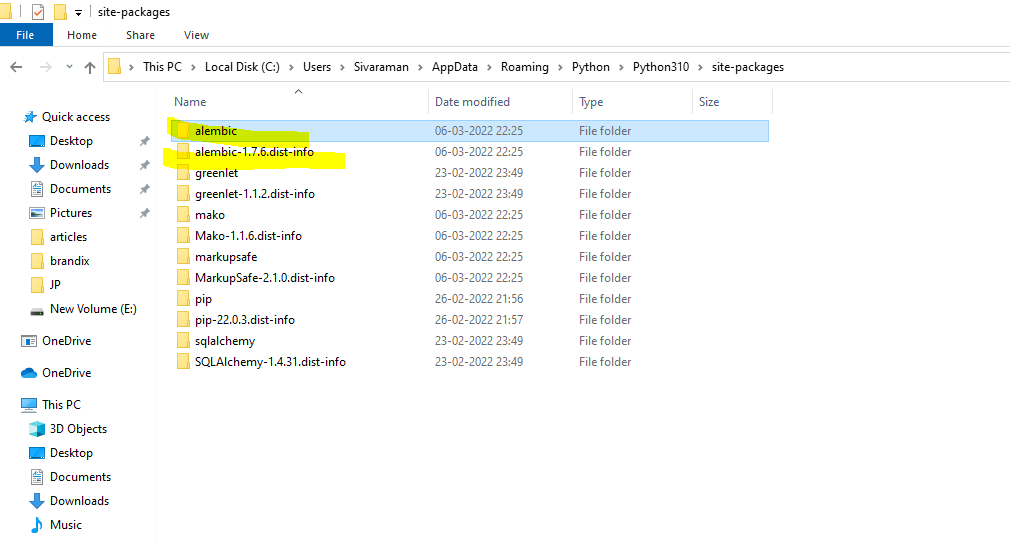
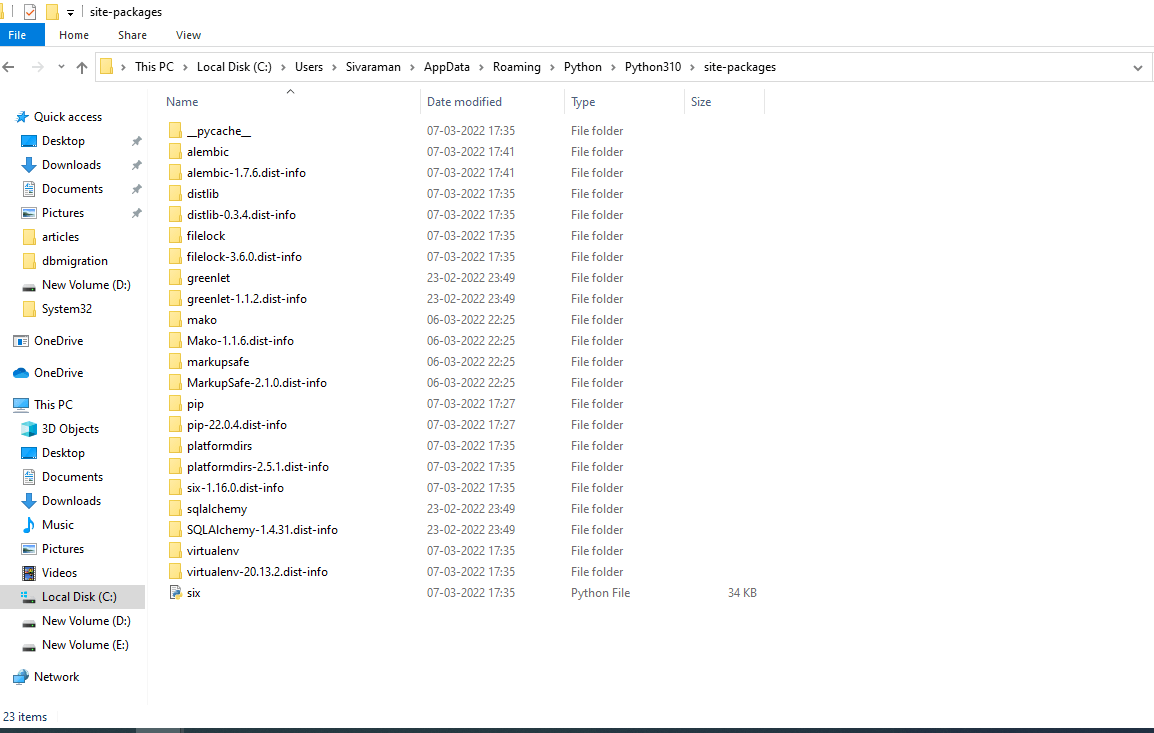
After that, we can see the alembic folder in the Appdata/Roaming/Python/Python310/site-packages,
The install will automatically add the alembic command to the virtual type of environment. Using the alembic init command to initial setup the setup.py file in the local virtual environment.
How to Use SQLAlchemy Migrations?
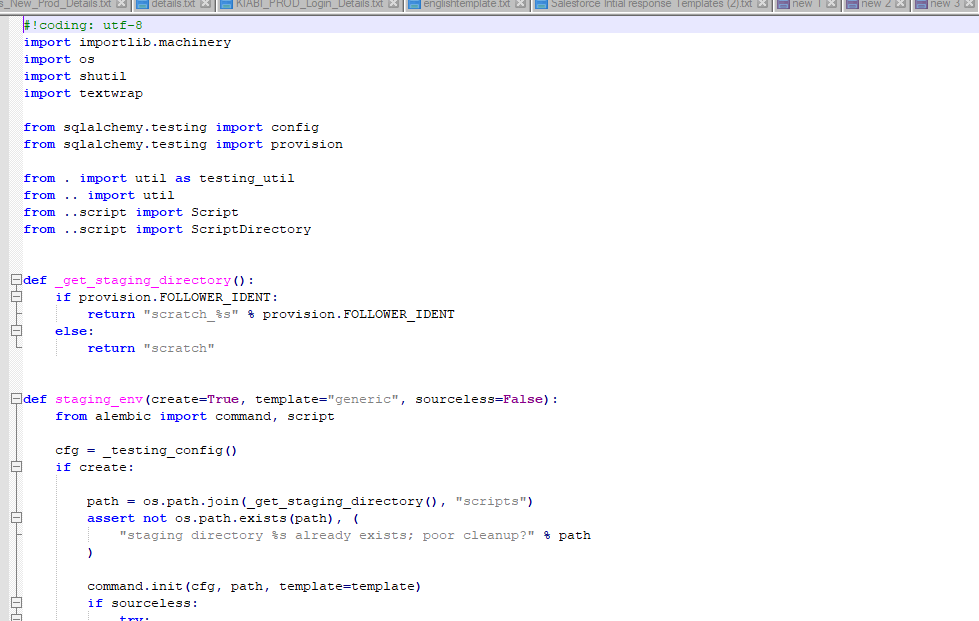
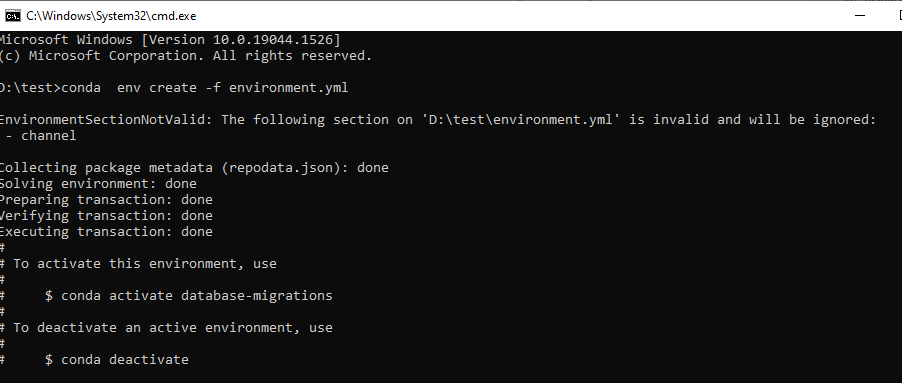
First, we will edit the env.py to create the env like conda env create -f environment.yml to set up the environment. Then we must ensure the directory structure by using the database migration database like database-migration -database name,
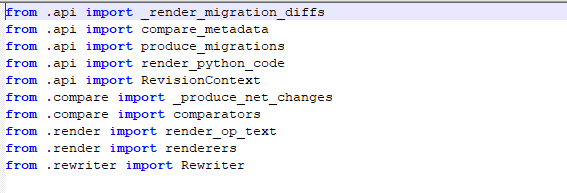
Using the __init__.py file, we can get the .api that imported the migration differences.
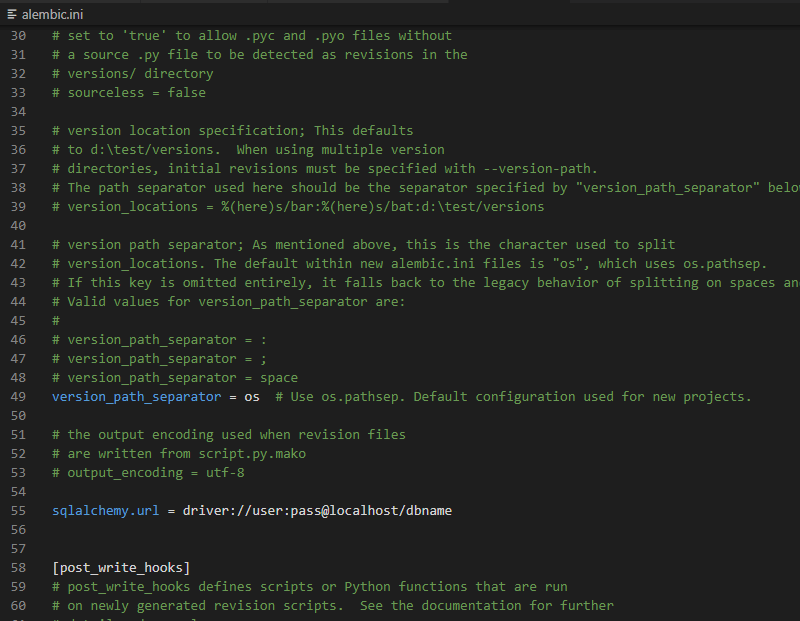
Generally, the env.py is the python-based script file used to run whenever we invoke the migration tool at the alembic migration tool. It contains instructions for configuring and generating the sqlalchemy engine in the database with some procured connections and the user and database transactions. The migration engine will invoke the same for using the database source connectivity. The script_location is the alembic environment, normally specified as the filesystem location between relative or absolute location paths. It is related to the current directory and its interpreted as the only key required by the alembic in all the cases.
Sqlalchemy.url= mysql+mysqldb://@localhost/database is a single database, and this is one of the generic types of configuration setting up SQLAlchemy URL that’s to be needed. So we can create a migration script with the same environment for creating new revisions like alembic revision for creating the table account that needs to be used for migration script creation.
Alembic revision and table creation in the sqlalchemy for a while importing the package, and the file contains some header information and other identifiers for both current upgrade and downgrade revisions of basic alembic directives. We can use the default method in the file like a def upgrade() and def downgrade(); for these two methods, it initially imports the empty functions, and while we execute the job to run the migration scripts manually. We run the first type of migration, assuming the database is cleaned. After that, it will upgrade using an alembic upgrade command to run the upgraded instructions.
Example of SQLAlchemy Migrations
Below are the steps:
1. We must install the PostgreSQL, alembic, and sqlalchemy in the machine.
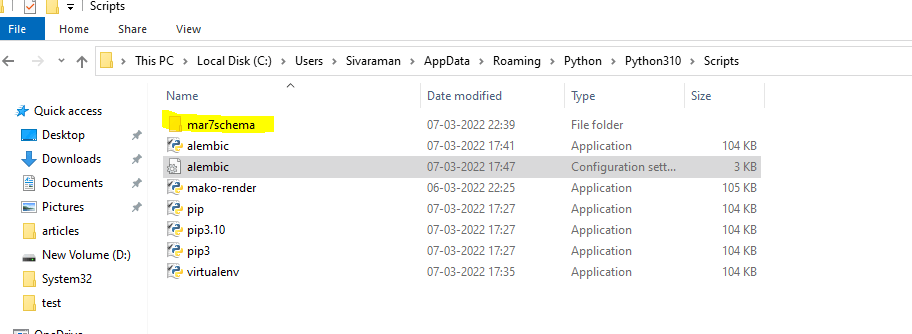
2. Then, using the command, we need to run the alembic in the mentioned path and generate the folder hierarchy as below alembic.exe init drive path(d:\test),
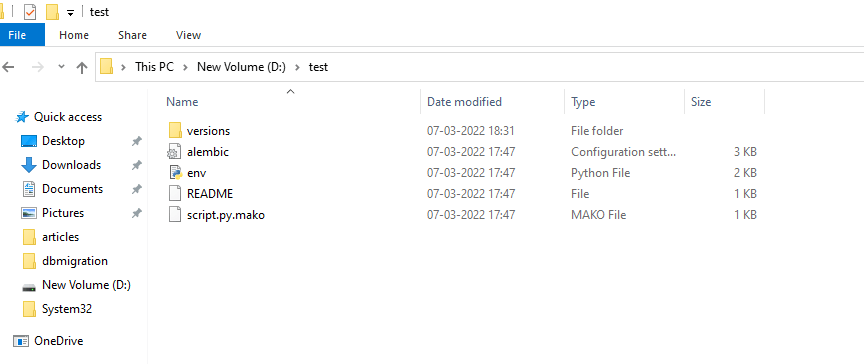
3. After that, we can create the environment.yml and readme.md file and it contains the following code,
Environment.yml:
name: database-migrations
channel:
- default
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- sqlalchemy=1.4.31
- psycopg2=2.8.6
- alembic=1.7.6readme.md:
#database-migration-scripts
## create env
conda env create -f environment.yml
## directory structure
database-migration -----> postgresdb1 ---->mar7schema
-----> mar7table
## alembic init
alembic init <schemaname>
## create revision
alembic revision -m "-message"
## for local revision
export postgresdb=postgresql://postgres:my4. By using the command conda env create -f environment.yml, we can set up the environment in the anaconda framework.
5. We can run the following command like alembic init schema name. to create the database schema name.
6. We can see the alembic.ini file in the folder.
7. Then we need to revise the database by using the command like alembic revision -m “message” it will create the revision like below,
8. We need to create the employee_data in the revision python file like below,
"""create employee data
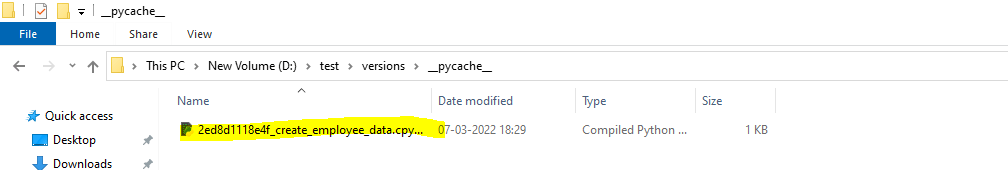
Revision ID: 2ed8d1118e4f
Revises:
Create Date: 2022-03-07 18:29:34.423987
"""
from alembic import op
import sqlalchemy as sa
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer,String
from sqlalchemy.schema import Sequence, CreateSequence
# revision identifiers, used by Alembic.
revision = '2ed8d1118e4f'
down_revision = None
branch_labels = None
depends_on = None
def upgrade():
op.execute(CreateSequence(Sequence('table_sid_seq')))
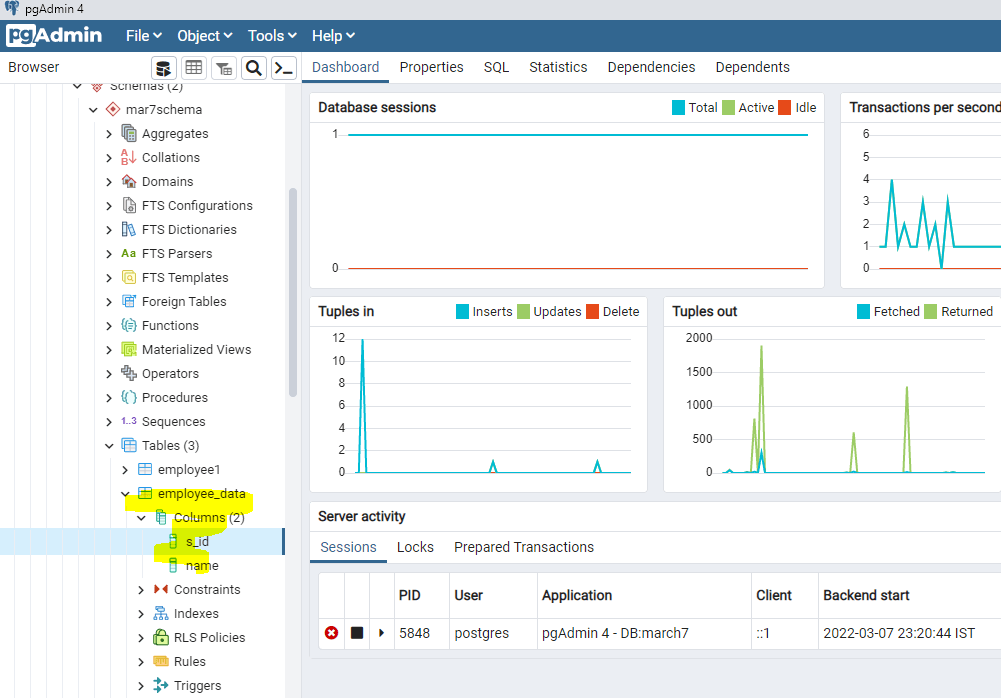
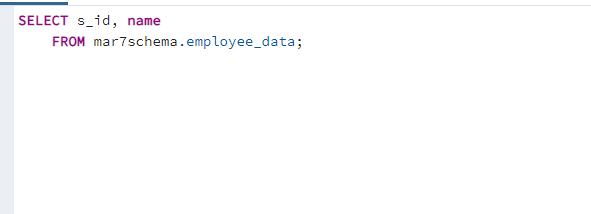
op.create_table("employee_data",
Column("s_id",Integer, nullable=False, server_default=sa.text("nextval('table_sid_seq'::regclass)")),
Column("name", String, nullable=False),
schema="mar7schema")
def downgrade():
op.drop_table("employee_data",schema="mar7schema")9. Then we need to run the alembic upgrade head –-sql the database is created successfully.
Conclusion
The SQLAlchemy migration is the upgraded technique and feature to handle the user data in both the front and back end. It is one of the important aspects of large-scale systems, and it must be handled properly to prevent data losses and other system availabilities.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLAlchemy Migrations” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.