Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy Delete
The SQLAlchemy delete is one of the features. It’s to be performed the remove operation on a single table that has to be simple and do the commit transaction for deleting the object from the mapped classes from the session using the delete operations; we also linked many database tables on the other end with little more difficult for to handling the datas user session will be saved on the database side.
Overview of SQLAlchemy Delete
The SQLAlchemy has many features; that delete is one of the methods, and it’s an operation for deleting the datas from the UI to the back end. Mainly the delete operation is performed on the query API; it is produced in the session object; the ORM level will be constructed on the sql object. It is the source of all the select statements generated by the ORM with formulated user query operations as high-level operations data collections. The generative interface is where using the successive calls returns the new query object for additional criteria and other options associated with the query. These objects are normally initiated using the generated session query with common cases directly using the query.with_session() method.
Using the object instance, we can perform the delete operations in the SQL tool; the deleting record is similar to the add() and uses delete() operations. For each operation, the user session is calculated and triggered to the query attribute on the model class; then, it will be fetched with the query object for all over the records. We can use the method for retrieving the records like the all() or first() method before running the query; the table already has some records for performing this operation. First, the session is created, then its to be added on the same by using the commit transaction is successfully saved on the database. So, the session must also be deleted whenever the user performs the delete operation.
SQLAlchemy Delete Multiple Rows
Generally, there are multiple ways to delete the rows in the table; if we want to delete the number of rows within the selected ranges, we must use the AND and BETWEEN operators to perform this operation. The delete() SQL Expression will construct the multiple tables, and the function will generate the new instance of delete which already represents the delete statement in the SQL. It will affect the single and multiple rows from a table; the API perspectives are very similar to that of the update() method. The construction will traditionally return the rows and variants on some database backends. The update and delete operations will mainly support the use of other and related queries referred to as the subqueries WHERE clause is mostly referred to as the backend for multiple tables.
The delete method of the query will support bulk delete operations, which might be related to the user session. The query probably will be more stylish and elegant ways to interact with the database. For example, sometimes, the synchronize session is evaluated and called for to fetch the records by using the id and evaluate the current criteria for the operators; the user session is rollback() and flush() the records if we want to use the try-except blocks the exceptions are caught through the above methods. Like UPDATE and ORM enabled versions of the DELETE operations, the user session and construction will be non-expired feature objects matched through the given deletion criteria.
Example of SQLAlchemy Delete
Given below are the example of SQLAlchemy Delete:
Example #1
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, ForeignKey, Column, Integer, String
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_engine('mysql+mysqldb://@localhost/feb26', echo = True)
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
class Mar3(Base):
__tablename__ = 'mnths'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key = True)
name = Column(String)
class Second(Base):
__tablename__ = 'second'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key = True)
mntid = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('mnths.id'))
Mar3.second = relationship("Second", order_by = Second.id, back_populates = "mnths")
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session = Session()
x = session.query(Mar3).get(2)
session.delete(x)
session.query(Mar3).filter_by(name = 'January').count()
x = Mar3.delete().where(Mar3.c.name == "January")
engine.execute(x)
sql = text("SELECT * from month")
res = engine.execute(sql).fetchall()
for r in res:
print("\n", r)Output:
The above example is one of the basic steps for creating the table and declaring the classes for creating id and name attributes columns. Initially, the declarative base class is mainly declared and used for creating the classes and imported relationships for both tables. That is, first, we created the primary key table here. I used the id attribute as the primary key; it’s a unique one it will not accept duplicate and null values. Then, when we use the relationship concept, both the tables are merged and joined together, then they will automatically be referred to as the foreign key references.
The unique session-id is created for each session and will automatically execute the first table key id that must be compared and checked with the second table reference. The sessionmaker() method helped create the session and passed the query in the session reference. And also used the delete() method on the same reference to perform the delete operations in the table. Here I used the month table to select the months from January to December, and it has a unique id like 1 to 12. I used the condition like table reference(Mar3.c.name == “January”) for performing the delete operations on the same table, then finally by using the execute() method to perform the delete operation on the database table. To retrieve the records, we need to confirm the other list of datas in the table query like select * from the month(tablename).
Example #2
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy import select, update, delete, values
user = ''
password = ''
host = 'localhost'
port = 3306
database = 'march4'
def get_connection():
return create_engine(
url="mysql+mysqldb://@localhost/feb26".format(
user, password, host, port, database
)
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
engine = get_connection()
print(
f"Welcome To My domain your connection is {host} for user {user} created successfully.")
except Exception as ex:
print("Sorry your connection is not created some interruption is occured please check and try it again \n", ex)
sql1 = delete(month).where(month.id.in_([2, 3, 4]))
sql2 = delete(month).where(month.id == 2)
db.session.execute(sql1)
db.session.commit()Output:
Example #3
Code:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData, Table, Column, Integer, String,VARCHAR
eng = create_engine('mysql+mysqldb://@localhost/feb26', echo = True)
mt = MetaData()
days = Table(
'days', mt,
Column('id', Integer, primary_key = True),
Column('name', VARCHAR(255) ),
)
mt.create_all(eng)
conn = eng.connect()
stmt = days.delete().where(days.d.name == 'sunday')
conn.execute(stmt)
s = days.select()
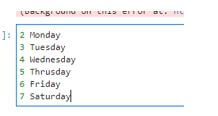
conn.execute(s).fetchall()Output:
Conclusion
The SQLAlchemy delete is one of the CRUD operations to remove the datas in the table. If we use the engine to create the database, the same will be referred to the other similar objects and instances. For each query, the session id is generated for future reference.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLAlchemy Delete” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.